Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Notes > Electrical Machines > Electrical Machines Basics
Electrical Machines Basics | Electrical Machines - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
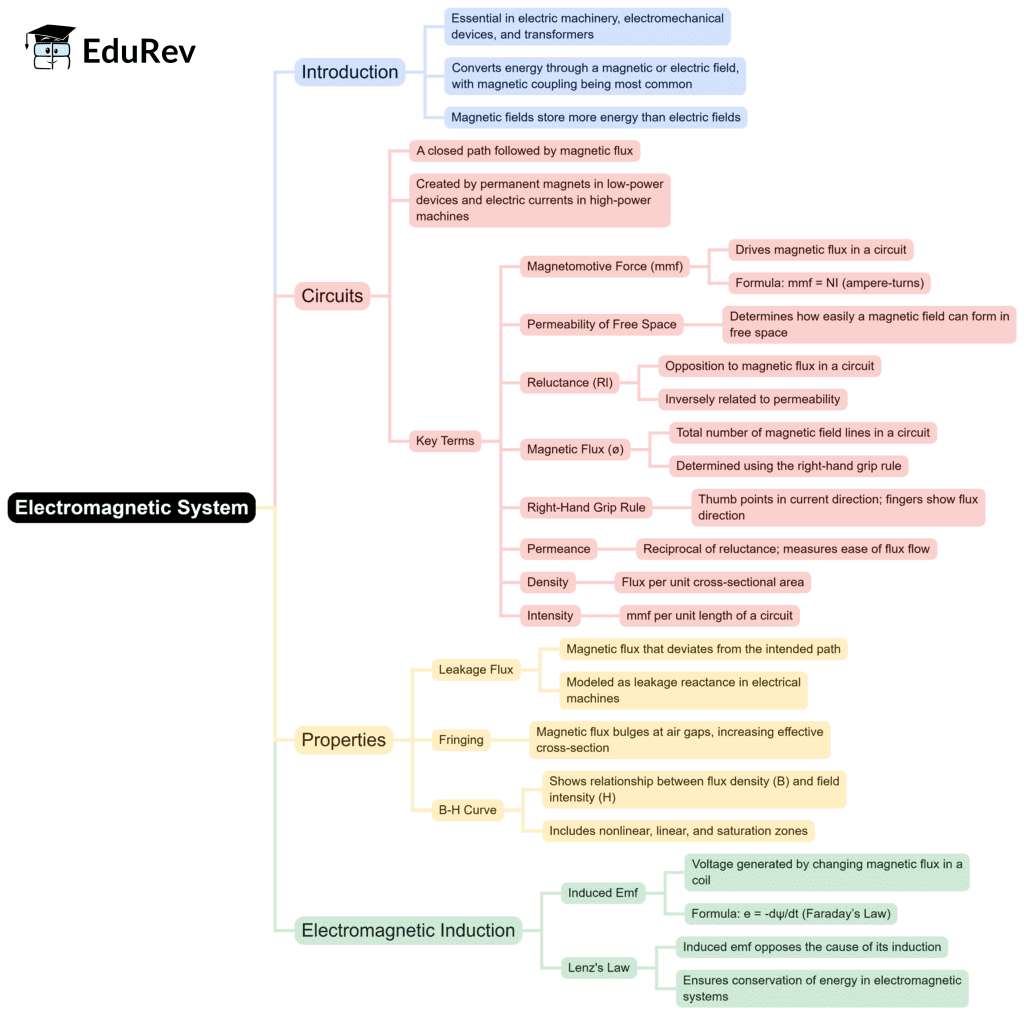
The document Electrical Machines Basics | Electrical Machines - Electrical Engineering (EE) is a part of the Electrical Engineering (EE) Course Electrical Machines.
All you need of Electrical Engineering (EE) at this link: Electrical Engineering (EE)
|
19 videos|93 docs|25 tests
|
FAQs on Electrical Machines Basics - Electrical Machines - Electrical Engineering (EE)
| 1. What are the basic types of electrical machines? |  |
| 2. How does a transformer work? |  |
Ans. A transformer works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. It consists of two coils of wire, known as the primary and secondary windings, wrapped around a magnetic core. When alternating current flows through the primary winding, it creates a changing magnetic field that induces a voltage in the secondary winding, allowing for the transfer of electrical energy from one circuit to another while changing the voltage level.
| 3. What is the difference between synchronous and asynchronous (induction) motors? |  |
Ans. The main difference between synchronous and asynchronous motors lies in their rotor operation. Synchronous motors operate at a constant speed that is synchronized with the supply frequency, while asynchronous (induction) motors have a rotor speed that is not synchronized with the supply frequency, resulting in slip. Synchronous motors are generally used in applications requiring precise speed control, whereas induction motors are widely used in various industrial applications due to their simplicity and robustness.
| 4. What is back EMF in DC motors? |  |
Ans. Back EMF (Electromotive Force) in DC motors is the voltage generated by the motor's armature winding as it rotates within the magnetic field. This voltage opposes the applied voltage and is proportional to the motor's speed. Back EMF is a crucial factor in determining the motor's efficiency and performance, as it regulates the current flowing through the motor according to the load conditions.
| 5. Why is it important to understand the power factor in electrical machines? |  |
Ans. Understanding the power factor is important because it measures the efficiency of power usage in electrical machines. A power factor of 1 (or 100%) indicates that all the power supplied is being used effectively for work, while a lower power factor indicates inefficiencies due to reactive power. Improving the power factor can lead to reduced energy costs, improved system stability, and the capability to increase the load capacity of electrical systems without additional infrastructure.
Related Searches


























