Past Year Questions: Municipal Solid Waste Management | Topic wise GATE Past Year Papers for Civil Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Q1: An organic waste is represented as
C240 O200 H180 N5 S
(Atomic weights: S-32, H-1, C-12, O-16, N-14)
Assume complete conversion of S to SO2 while burning.
SO2 generated (in grams) per kg of this waste is _____ (rounded off to 1 decimal place). [2024, Set-2]
Ans: (9.9 to 10.2)
Sol:
Organic waste = C240 O200 H180 N5 S
Weight of organic waste =1 kg
Burning of organic waste converts
sulfur into sulfur dioxide as follows:
C240 O200 H180 N5 S → x CO2 + yH2O + zH2O + SO2
i.e. 6362 of organic waste produces 64g of sulfur dioxide.
So,
1kg of organic waste produces 64/6362 x 1000gm of SO2
So, Amount of SO2 produced =10grams/kg
Q2: The following table gives various components of Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) and a list of treatment/separation techniques. [2024, Set-1]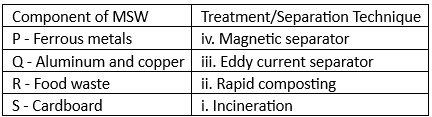
The Correct match is
(a) P-iii, Q-iv, R-i, S-ii
(b) P-iv, Q-iii, R-ii, S-i
(c) P-iii, Q-iv, R-ii, S-i
(d) P-iv. Q-iii, R-i, S-ii
Ans: (b)
Sol:
I. Various MSW separation techniques
(a) Screening process
(b) Size reduction process
Reduction in size of MSW can be done using following mechanical devices:
(a) Shredders
(b) Flail mill hammer
(c) Glass crusher
(c) Density separation process
It is the process of separation of light materials such as paper and plastic from heavy materials such as metals.
It is carried out using air density separators.
(d) Magnetic separation process
It is the process of separating ferrous metals from MSW
It is carried out using magnetic separators.
(e) Current separation process
It is the process of separating aluminum and copper from MSW.
It is carried out using Eddy current separator.
II. Various MSW treatment technique
(a) Sanitary landfills
(b) Composting
(c) Incineration
(d) Pyrolysis
Hence, correct option is (B).
Q1: In the context of Municipal Solid Waste Management, 'Haul' in 'Hauled Container System operated in conventional mode' includes the [2023, Set-2]
(a) time spent by the transport truck at the disposal site
(b)time spent by the transport truck in traveling between a pickup point and the disposal site with a loaded container
(c)time spent by the transport truck in picking up a loaded container at a pickup point
(d) time spent by the transport truck in driving from the depot to the first pickup point
Ans: (b)
Sol:
In hauled container system, 'Haul' time includes. The time required to reach the disposal site, starting after the container whose contents
are to be emptied has been loaded on the track, plus the time after leaving the disposal site until the truck arrives at the location where the empty container is to be redeposited.
Time spent at the disposal site is not included.
Q2: The composition and energy content of a representative solid waste sample are given in the table. If the moisture content of the waste is 26% the energy content of the solid waste on dry-weight basis is ____ MJ/kg (round off to one decimal place). [2023, Set-1]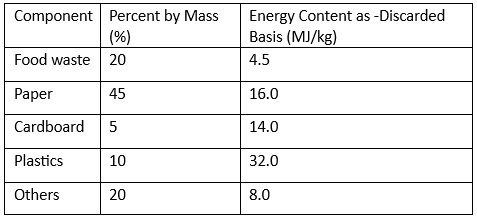 Ans: (18 to 19)
Ans: (18 to 19)
Sol:
Assuming 1Kg of solid waste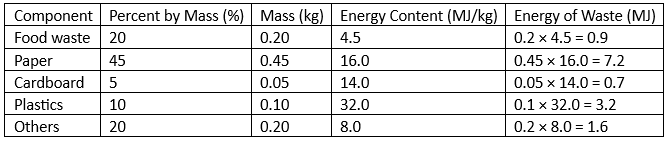 Energy produce from 1Kg work = 13.6mJ
Energy produce from 1Kg work = 13.6mJ
Moisture content = 26%
Solid content = 100 - 26 = 74%
Therefore 1Kg of waste consist of = 0.7 Kg dry mass
∴ Energy content based on dry weight
= 13.6/0.74 = 18.378 mJ/kg
≃ 18.40 MJ/Kg
Q3: Which of the following statements is/are TRUE for the Refuse-Derived Fuel (RDF) in the context of Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) management? [2023, Set-1]
(a) Higher Heating Value (HHV) of the unprocessed MSW is higher than the HHV of RDF processed from the same MSW.
(b) RDF can be made in the powdered form
(c) Inorganic fraction of MSW is mostly converted to RDF.
(d) RDF cannot be used in conjunction with oil.
Ans: (b)
Sol:
(A) is false. The Higher Heating Value (HHV) of Refuse-Derived Fuel (RDF) processed from Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) is typically higher than the HHV of unprocessed MSW. This is because RDF processing removes non-combustible materials from MSW and concentrates the combustible fraction.
(B) is true. RDF can be produced in various forms including pellets, fluff, and powdered form. The form of RDF depends on the specific process and intended end use.
(C) is partially true. RDF processing typically removes a significant portion of the inorganic fraction of MSW, but not all of it. The remaining inorganic fraction is typically mixed with the RDF product.
(D) is false. RDF can be used as a fuel in a variety of combustion systems, including those that burn oil. In fact, RDF is often used as a supplemental fuel in cement kilns and other industrial processes that also use oil as a fuel.
Q1: At a municipal waste handling facility, 30 metric ton mixture of food waste, yard waste, and paper waste was available. The moisture content of this mixture was found to be 10%. The ideal moisture content for composting this mixture is 50%. The amount of water to be added to this mixture to bring its moisture content to the ideal condition is _______metric ton. (in integer) [2022, Set-2]
Ans: (24 to 24)
Sol:
Wt. of water initially present = frac 10100 x 30 = 3mT
Wt. of solid = 30 - 3 = 27mT
In ideal condition,
Wt. of solid = 27mT
M/C = 50
Wt. of water = 27mT
Amount of water needed to get ideal condition = 27 - 3 = 24mT
Q2: In a city, the chemical formula of biodegradable fraction of municipal solid waste (MSW) is C100 H250 O80 N has to be estimated.
Assume oxygen in air (by weight) =23% and density of air = 1.3 kg/m3. Atomic mass: C = 12, H = 1, O = 16, N = 14.
C and H are oxidized completely whereas N is converted only into NH3 during oxidation.
For oxidative degradation of 1 tone of the waste, the required theoretical volume of air (in m3/tone) will be (round off to the nearest integer) [2022, Set-2]
(a) 4749
(b)8025
(c) 1418
(d) 1092
Ans: (a)
Sol:
C100 H250 O80 N + x O2 → 100 CO2 + 247/2 H2O + NH3
80 + x X 2 = 200 + 247/2
x = 121.75
1 mole of MSW required 121.75 mole of oxygen No. of moles of MSW
No. of moles of O2 required = 121.75 x 1tone/2744g
wt. of O2 = 121.75/2744 x 32 tone
Mass of air = 1.42/0.23 x 103 Kg
Density of air = 1.3Kg/m3
Volume of air = 6.174/1.3 x 103 m3
= 4749.2m3 per tone of MAW
Q3: To design an optimum municipal solid waste collection route, which of the following is/are NOT desired: [2022, Set-2]
(a) Collection vehicle should not travel twice down the same street in a day.
(b) Waste collection on congested roads should not occur during rush hours in morning or evening.
(c) Collection should occur in the uphill direction.
(d) The last collection point on a route should be as close as possible to the waste disposal facility.
Ans: (c)
Sol:
Some heuristic guidelines that should be taken into consideration when laying out routes are as follows :
1. Existing policies and regulations related to such items as the point of collection and frequency of collection must be identified.
2. Existing system characteristics such as crew size and vehicle types must be coordinated.
3. Wherever possible, routes should be laid out so that they begin and end near arterial streets, using topographical and physical barriers as route boundaries.
4. In hilly area, routes should start at the top of the grade and proceed downhill as the vehicle becomes loaded.
5. Routes should be laid out so that the last container to be collected on the route is located nearest to the disposal site.
6. Waste generated at traffic-congested locations should be collected as early in the day as possible.
7. Sources at which extremely large quantities of waste are generated should be serviced during the first part of the days.
8. Scattered pickup points (where small quantities of solid waste are generated) that receive the same collection frequency should, if possible, be serviced during one trip or on the same day.
Q4: In a solid waste handling facility, the moisture contents (MC) of food waste, paper waste, and glass waste were found to be MC f, MC P and MC g respectively. Similarly, the energy contents (EC) of plastic waste, food waste, and glass waste were found to be EC PP, EC f and EC g
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct? [2022, Set-2]
(a) MC f > MC p> MC g
(b) EC pp > EC f >EC g
(c) MC f < MC p< MC g
(d) EC pp< EC f < EC g
Ans: (a, b)
Sol:
Typical specific weight and moisture content data for residential, commercial, industrial. and agricultural wastes.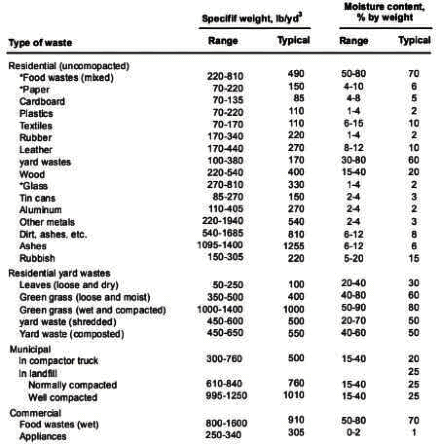 Moisture content
Moisture content
Mc f > Mc p > Mc g
Typical values for short residue and energy content of residues MSW.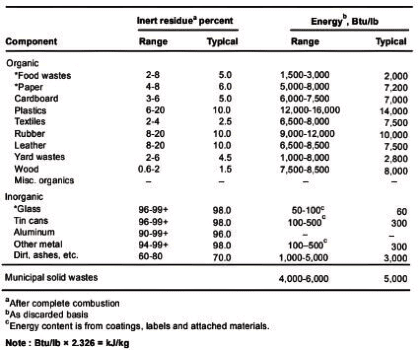
Energy content
EC pp > EC f > EC g
Q1: Determine the correctness or otherwise of the following Assertion [a] and the Reason [r]. [2021, Set-2]
Assertion [a]: One of the best ways to reduce the amount of solid wastes is to reduce the consumption of raw materials Reason [r]: Solid wastes are seldom generated when raw materials are converted to goods for consumption.
(a) Both [a] and [r] are true and [r] the correct reason for [a]
(b) Both [a] and [r] are true but [r] is not the correct reason for [a]
(c) Both [a] and [r] are false
(d) [a] is true but [r] is false
Ans: (d)
Sol:
Solid waste generated by the use of raw material, processing and finished goods
FAQs on Past Year Questions: Municipal Solid Waste Management - Topic wise GATE Past Year Papers for Civil Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What are the key components of Municipal Solid Waste Management? |  |
| 2. What are the common methods of treating municipal solid waste? |  |
| 3. What are the environmental impacts of inadequate solid waste management? |  |
| 4. How can communities improve their municipal solid waste management practices? |  |
| 5. What role does legislation play in municipal solid waste management? |  |
















