Forests of Punjab | Punjab State (PPSC) PSC: Preparation - PPSC PCS (Punjab) PDF Download
Introduction
Forests hold significant importance in Punjab as they provide various resources such as timber, pulp, herbs, fuelwood, and fodder. Additionally, forests play a crucial role in preventing soil erosion, enhancing soil fertility, and reducing pollution. According to the India State of Forest Report 2017, the total Recorded Forest Area in Punjab is 3,084 square kilometers, which constitutes 6.12% of the state's total geographical area.
Divisions of Forests in Punjab
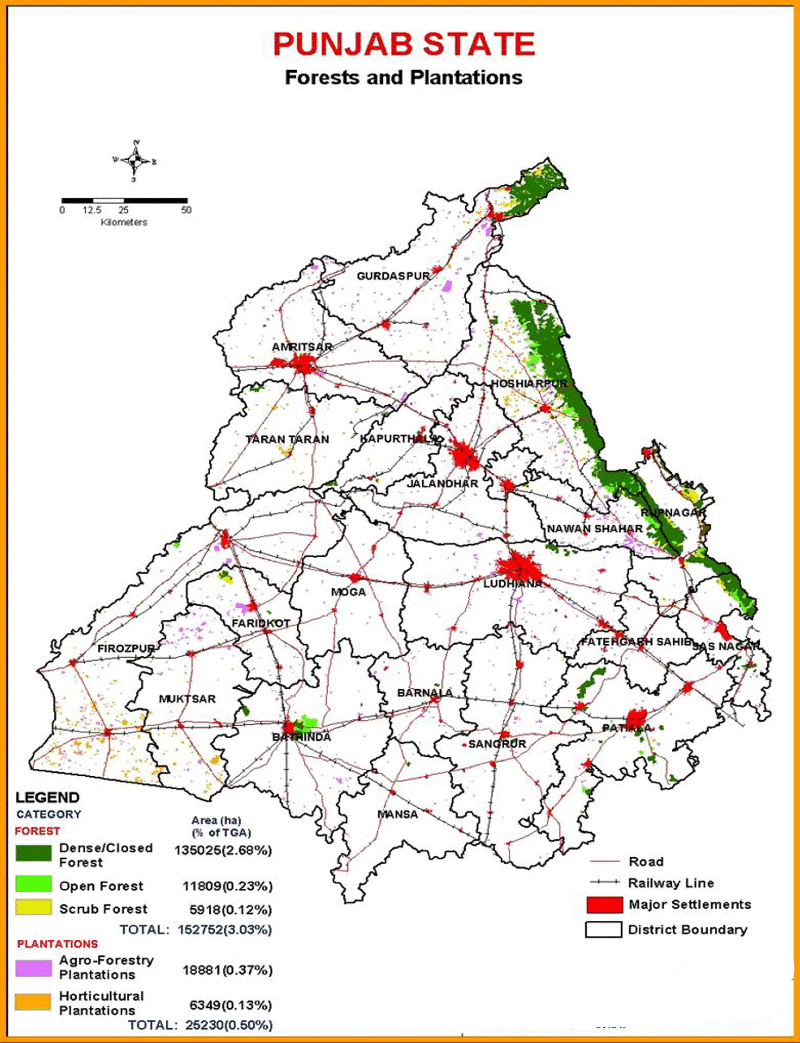
In Punjab, forests are classified into three types:
Reserved Forests
- Reserved forests are permanently designated for the production of timber and other forest products.
- In these forests, grazing and cultivation rights are allowed.
- As per the Forest Report 2017, the reserved forest area in Punjab is 44 sq km, accounting for 1.43% of the total forest area.
Protected Forests
- Protected forests are areas where grazing and cultivation rights are subject to minor restrictions.
- These forests offer a balance between protection and resource use.
- The protected forest area in Punjab is 1,137 sq km, representing 36.87% of the total forest area, according to the Forest Report 2017.
Unclassed Forests
- Unclassed forests consist mainly of inaccessible forests and unoccupied wastelands.
- These areas are not classified under the other categories due to their remote or unoccupied nature.
- The area of unclassed forests in Punjab is 1,903 sq km, making up 61.70% of the total forest area.
Forest Cover in Punjab
According to the India State Forest Report 2017, Punjab has a forest cover of 1,837 square kilometers, which constitutes 3.65% of the state's total geographical area. The forest cover is categorized into different canopy density classes as follows:
- Very Dense Forest:. sq km (0.02% of total area)
- Moderately Dense Forest: 806 sq km (1.60% of total area)
- Open Forest: 1,023 sq km (2.03% of total area)
The remaining 96.28% of the state is non-forest area.
District-Wise Forest Cover in Punjab
The forest cover in Punjab varies significantly across districts. The districts with the highest forest cover are:
- Hoshiarpur: 725 sq km
- Rupnagar: 260 sq km
- Gurdaspur: 213 sq km
Conversely, the districts with the lowest forest cover are:
- Fatehgarh Sahib:. sq km
- Barnala:. sq km
- Moga:. sq km
The following table provides a detailed district-wise distribution of forest cover in Punjab: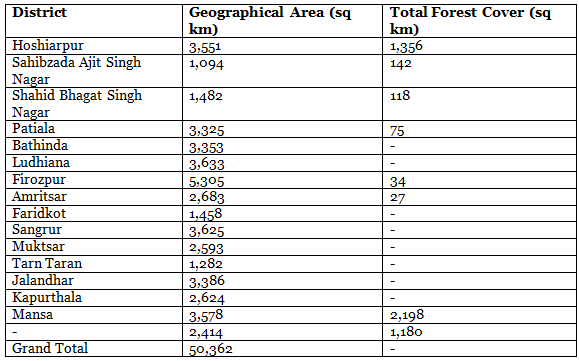
Classification of Forests in Punjab
The forests in Punjab exhibit a range of vegetation types, from pine forests to thorn forests, influenced by variations in altitude and climate. Based on the Champion and Seth classification, the forests of Punjab are categorized as follows:
- Northern Dry Deciduous Mixed Forests: These forests are characterized by a predominance of broad-leaved trees. Common species include mahogany and babool, along with scrub vegetation like wild karanda. Other important trees in this forest type include eucalyptus, teak, shisham, poplar, and mango.
- Dry Deciduous Scrub Forests: Found mainly in the Kandi tract, these forests are dominated by species such as khair. Other notable trees include Indian rosewood, silk cotton tree, amla, Indian ash tree, Indian mahogany, and amaltas.
- Khair and Sissoo Forests in the Foothills: These predominantly man-made forests are located in areas like Amritsar, Tarn Taran, and Kapurthala. They are primarily planted with khair, sissoo, and eucalyptus hybrids, with groves of mango also found in these forests.
- Shiwalik Chir Pine Forests: Situated at elevations of 850 meters and above, these forests are dominated by chir pine. Other tree species found in conjunction with pines include terminalia chir, amla, and khair. Districts such as Ropar, Hoshiarpur, SBS Nagar, and Gurdaspur are part of this forest type.
- Dry Deciduous Bamboo Forests: These forests are primarily found in the Dasuya Forest Division, with notable presence in Hoshiarpur and Gurdaspur. Patiala and Kapurthala are home to pure bamboo forests. The main species in these forests is male bamboo, along with other species like Indian ash tree, bistendu, bastard teak, elm, and amaltas.
Main Species of Forest
Some of the main species of forest in Punjab are follows:
Bamboo Forests: These forests are primarily found in the Shiwalik hills, particularly in the Dasuya Forest Division and in specific areas of Hoshiarpur and Gurdaspur Forest Divisions, such as Dholbaha and Salidhar forests. In the Dasuya Forest Division, areas like Bindravan, Karanpur, and Nanad Bir consist of almost pure bamboo forests. The dominant species is Dendrocalamus strictus, often associated with other species like rajain and khair.
Broad Leaf Forests
Eucalyptus, shisham, poplar, mango, neem, toot, teak, ailanthus, and tun are some of the important species found in broadleaf forests.
- These forests are primarily located in the plains of Punjab.
- They are managed according to specific guidelines outlined in working plans.
Coniferous Forests:
Coniferous forests are located in the Shiwalik hills of Punjab. The main species found in these forests is chir (Pinus roxburghii), along with other species such as amla (Phyllanthus emblica), khair (Acacia catechu), and scattered trees of Terminalia species.
Scrub Forests:
- Scrub forests are found in the Shiwalik hills and various Bir forests of Punjab. The dominant species in these forests is Acacia.
- Babool and Indian rosewood are commonly found along riverine areas and in the plains.
- In recent years, economically important tree species such as eucalyptus, drek (Nerium oleander), ailanthus, tun, poplar, and others have been introduced in these scrub forests, both in the hills and plains.
Significance of Forests in Punjab
Timber Production: Forests in Punjab are a source of various types of timber, including shisham, talli, mango, and eucalyptus. Employment Opportunities: Forests provide jobs to around 8% of Punjab's working population. Revenue Contribution: Forests contribute to the overall revenue of Punjab. Raw Material Supply: Forests supply raw materials to several industries in Punjab, including:
- Sports goods industry
- Paper industry
- Varnish and dye industry
- Resin and turpentine industry
- Various small and cottage industries
Forest Policy of Punjab
Forest resources in Punjab are crucial for the environment and need to be protected, conserved, and enhanced to maximize their environmental benefits for society.
The Forest Policy of Punjab aims to:
- Increase forest and tree cover from the current 6.3% to 15% of the state’s geographical area.
- Practice sustainable forestry using modern technology and scientific knowledge.
- Promote non-timber uses of forests such as eco-tourism, Non-Timber Forest Produce, medicinal plants, and biodiversity.
- Provide technical assistance, financial incentives, and extension services for social forestry, agroforestry, and tree farming to diversify land use.
Department for Forest Development
Punjab State Forest Development Corporation
The Punjab State Forest Development Corporation Limited was established on May 23, 1983, under the Companies Act of 1956. The corporation aims to acquire standing trees from the State Forest Department by paying their price, harvest them using more efficient tools, and provide timber wood to the right consumers. This initiative aims to eliminate unscrupulous middlemen and establish forest-based industries.
Agroforestry in Punjab
Farmers in Punjab are being encouraged to adopt Agroforestry, which is a land-use management system where trees or shrubs are grown around or among crops or pastureland. This practice not only helps farmers earn good money from the trees after seven years but also improves soil quality.
With the increasing demand for timber and plywood in the construction and paper-making industries, the need for trees under Agroforestry is also rising. Agroforestry is especially important for Punjab at a time when the state's traditional agriculture has reached a point of saturation. The State Government has committed to increasing the area under Agroforestry from the existing 6.3 per cent to 15 per cent in the coming years.
The main tree species identified for Agroforestry in Punjab include Poplar, Eucalyptus, Dek, and Bamboo. The Kandi and Talwara regions have been identified as suitable areas for bamboo forests.
Punjab Bamboo and Fiber Development Board
National Bamboo Mission is a scheme sponsored by the central government, with full funding from the Central Government. It is being carried out by the Horticulture Division under the Department of Agriculture and Cooperation in the Ministry of Agriculture, New Delhi. The mission aims to promote the growth of bamboo by increasing the area under bamboo cultivation, improving yields, and ensuring scientific management. It also focuses on marketing bamboo and bamboo-based handicrafts, creating employment opportunities, and other related activities.
Government Initiatives for Forest Development in Punjab
The government has launched several initiatives aimed at enhancing forest development in Punjab. Here are some of the key initiatives:
- Rehabilitation of Waterlogged and Degraded Areas: The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) has allocated ₹1,918 crore for the rehabilitation of waterlogged and degraded areas in Punjab. This includes bio-drainage, agroforestry, and other plantation activities.
- Punjab Forestry Watershed Development Project (PFWDP): This state government initiative focuses on various activities such as plantations, farm/agroforestry, forest research and training, and infrastructure development related to forestry.
- Plantation in Malwa Region: In 2012-13, the Department of Forests implemented a project for plantation along major roads in the Malwa region. The project aimed at removing Mesquite and establishing high-quality plantations, with an outlay of ₹9.38 crores over six years.
- Green Punjab Mission (GPM): Launched on July 1, 2012, this mission aims to increase forest and tree cover in non-forest areas such as villages, schools, hospitals, and institutional lands. The goal is to raise the forest and tree cover from 6.12 percent to 15 percent over 15 years. The mission is funded by various state governments.
|
23 videos|50 docs|47 tests
|
FAQs on Forests of Punjab - Punjab State (PPSC) PSC: Preparation - PPSC PCS (Punjab)
| 1. पंजाब में वन विभाग की संरचना क्या है ? |  |
| 2. पंजाब में वन आवरण की स्थिति क्या है ? |  |
| 3. पंजाब में प्रमुख वन जातियाँ कौन सी हैं ? |  |
| 4. पंजाब में वनों का महत्व क्या है ? |  |
| 5. पंजाब में वनीकरण के लिए सरकार द्वारा क्या कदम उठाए गए हैं ? |  |





















