Energy Resources of Punjab | Punjab State (PPSC) PSC: Preparation - PPSC PCS (Punjab) PDF Download
Introduction
The energy sector is crucial for the economies of developing countries. It encompasses the production of conventional, alternative, and renewable sources of energy. While non-renewable resources are depleted through human use, renewable resources can sustain indefinite exploitation by humans.
In the state of Punjab, both the agriculture and industrial sectors rely heavily on the energy sector. According to the Economic Survey 2017-18, the per capita electricity consumption in Punjab is as follows: 13796 MkWh by the domestic sector, 4028 MkWh by the commercial sector, 16000 MkWh by industry, 12356 MkWh by agriculture, and 1591 MkWh by other sectors.
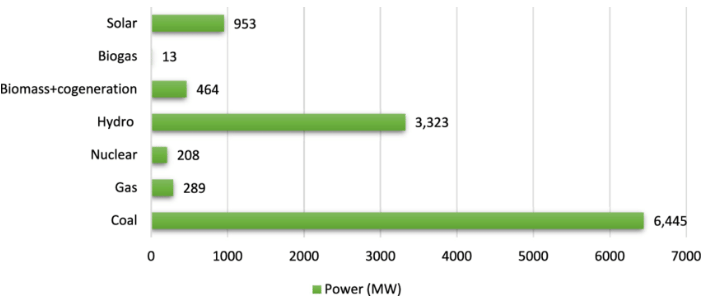
Power Plants in Punjab
Punjab has a total installed capacity of 4967 MW for electric power generation. The power plants in the state are either thermal power plants (running on coal) or hydro power plants.
Thermal Power Plants in Punjab
Here are some of the thermal power plants located in Punjab:
Guru Gobind Singh Super Thermal Power Plant:
- Location: Ghanauli village near Ropar, Punjab, on the banks of the Sutlej River.
- Type: Coal-based power plant operated by PSPCL.
- Started: 1984
- Installed Capacity: 1260 MW
- Water Source: Nangal-Hydel Channel
- Coal Supply: Bihar, West Bengal, and Madhya Pradesh
- Achievements: Received an incentive award for reducing fuel oil consumption in 1999
Guru Nanak Dev Thermal Power Plant:
- Location: Bathinda, Punjab
- Type: Medium-sized coal power station
- Started: 1982
- Installed Capacity: 440 MW
- Coal Supply: Bituminous coal from Jharkhand
- Purpose: Meets irrigation needs of lower Punjab
Guru Har Gobind Thermal Power Plant:
- Location: Lehra Mohabbat, Bathinda, Punjab
- Started: 1998
- Installed Capacity: 920 MW
- Stages: Stage I and Stage II
- Water Source: Bathinda branch of Sirhind canal
- Coal Supply: PANEM captive mines, a joint venture with EMTA Group and Coal India Ltd.
Talwandi Sabo Power Ltd. (TSPL):
- Type: Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) by Punjab State Electricity Board (PSEB)
- Purpose: Constructing a 1980 MW thermal power plant
- Location: Village Banawala, Mansa-Talwandi Sabo road, Mansa district, Punjab
- Developer: Sterlite Energy Ltd. (part of Vedanta group)
- Coal Supply: Basundhara coalfields
Rajpura Thermal Power Plant:
- Location: Near Rajpura town, Patiala district, Punjab
- Capacity: Expected to generate 1400 MW of power
- Developer: Larsen and Toubro Ltd.
- Technology: Latest technology
- Coal Supply: South-Eastern Coal Field (SECL), Bilaspur, Chhattisgarh
Proposed Thermal Power Plants:
- Goindwal Sahib Thermal Power Plant: Located in Tarn Taran district, expected to generate about 540 MW of electricity.
- Gidderbaha Thermal Power Plant: Located in Ghagga village near Gidderbaha town, Muktsar district, expected to generate about 2640 MW of electricity.
Hydro Power Plants in Punjab
Hydro power plants are a significant source of renewable energy in Punjab, harnessing the power of water to generate electricity. Here are some notable hydro power plants in the state:
Anandpur Sahib Hydel Project:
- Location: About 32 km downstream of the Bhakra Dam, towards the Ropar district.
- Overview: This project was developed to utilize the water from the Bhakra Nangal system, made possible by the interlinking of the Beas and Sutlej rivers at Dehar.
- Commissioned: 1985
- Generation Capacity: 134 MW
Ranjit Sagar Dam:
- Location: On the Ravi River near Thein village in Pathankot district, Jammu and Kashmir.
- Overview: Also known as Thein Dam, this 160 m high earth core cum gravel shell dam is a massive multipurpose river valley project. It is named after Maharaja Ranjit Singh, the famous ruler of Punjab.
- Installed Capacity: 600 MW
Mukerian Hydel Project:
- Location: Near Talwara township in Hoshiarpur district.
- Overview: This project is built on the Mukerian Hydel Channel, which originates from the Shahnehar barrage, located downstream of the Pong Dam on the Beas River.
- Total Capacity: 207 MW
Upper Bari Doab Canal (UBDC) Hydel Project (Stage I and II):
- Location: Near Pathankot in Punjab.
- Overview: This project includes three powerhouses situated on the Upper Bari Doab Canal, which draws water from the Madhopur Headworks on the Ravi River.
- Total Installed Capacity: 91.32 MW
Shanan Project:
- Location: Jogindernagar in Mandi district, Himachal Pradesh, across the Uhl River.
- Overview: Commissioned in 1932 with an initial capacity of 12 MW, the project has been upgraded to provide 110 MW. It was allocated to Punjab by Himachal Pradesh under the Punjab Reorganisation Act, 1966.
Proposed Hydro Power Plants:
- Mukerian Hydel Power Project (Stage II and III): Located in Hoshiarpur district, Stage II will generate about 18 MW, and Stage III will generate about 42 MW.
- Shahpur Kandi Project: Situated on the Ravi River, this project will generate about 206 MW.
- Upper Bari Doab Canal Project (Stage III): Located in Pathankot district, this stage will generate about 85 MW.
Small/Micro Hydro Power Projects:
In Punjab, small-scale hydro power projects offer economically viable power generation options at various locations for a wide range of applications. Some of the small or micro powerhouses were commissioned in Nidampur and Daudhar in 1987, and in Rohti and Thuhi in 1989. These projects include different schemes such as irrigation canals, run-of-river systems, tailrace of existing hydel channels, irrigation dam outlets, and more.
Renewable Sources of Energy
- Punjab has a significant potential for renewable energy due to its numerous perennial rivers, which support both major and micro-scale hydel power plants. In recognition of its capacity to develop renewable energy, Punjab was awarded the Best Performing State Award in February 2015.
- The state's agricultural economy also provides a great opportunity to develop non-conventional sources of energy, such as biogas from agricultural wastes like sugarcane trash, cotton stalks, paddy husk, and cow dung.
The renewable sources of energy in Punjab include:
Biomass Power Projects:
- The State Government has successfully implemented seven biomass power projects, generating a total of 62.5 MW of energy from this renewable source. Additionally, plans are underway to establish the world’s largest cattle dung-based Bio CNG Plant at Haibowal Dairy in Ludhiana.
Wind Power Projects:
- The state shows potential for higher wind speeds at altitudes around 100 meters. In response, the State Government has set up a micro wind turbine project with a capacity of 40 KW in Kallar Kahar, located in the Chakwal district.
Solar Power Initiatives in Punjab:
- Punjab boasts a significant potential for solar energy, benefiting from over 300 days of sunshine each year. This abundant renewable energy source is being effectively harnessed by the Punjab Energy Development Agency (PEDA). The state experiences solar insolation levels ranging from 4 to 7 KWH per square meter.
- The largest solar power plant in Punjab is situated in Mansa, with a capacity of 31.5 megawatts (MW). Additionally, the world's largest single rooftop solar power plant, with a capacity of 19.50 MW, has been commissioned at Dera Beas in Amritsar. Furthermore, a 9.5 MW solar power plant, established under the Jawaharlal Nehru Mission, has been commissioned in the Bathinda district of Punjab.
New and Renewable Sources of Energy Policy (NRSE), 2012
The New and Renewable Sources of Energy Policy, established in 2012, aims to develop and promote technologies related to new and renewable energy sources, along with energy conservation measures. It also provides financial and fiscal assistance to address the depletion of conventional energy sources and environmental pollution. Currently, NRSE projects generate 1,446.5 MW of energy, with plans to expand to 2,400 MW by 2022. Punjab has significant potential in the NRSE sector, which is being harnessed. The policy aims to achieve several objectives to maximize the utilization of these resources:
- Increase NRSE Share: Aim to raise the share of new and renewable sources of energy to 10% of the total installed power capacity in the state by 2022.
- Promote Rural Renewable Energy: Encourage renewable energy initiatives to meet energy and lighting needs in rural areas and supplement energy requirements in urban, industrial, and commercial sectors.
- Attract Private Investment: Create favorable conditions to attract private sector investment in NRSE projects, along with broader participation from public communities and civil society.
- Decentralized Renewable Energy: Provide decentralized renewable energy solutions for agriculture, industry, commerce, and households, particularly in rural areas, to improve power quality and reduce transmission and distribution losses.
- Support R&D and Emerging Technologies: Facilitate research, development, demonstration, and commercialization of new and emerging technologies in the renewable energy sector, such as fuel cells, hydrogen and chemical energy, and alternative fuels for transportation.
State Government Departments of Energy Sector
Punjab State Power Corporation Ltd.:
Punjab State Power Corporation Ltd. (PSPCL) is the electricity generating and distributing company of the Government of Punjab, India. Established in 2010, PSPCL was tasked with the operation and maintenance of the state's electricity generating projects and distribution system. The corporation has implemented various modern technologies such as:
- Electronic meters
- Remote control of transformers
- Remote meter reading
- Advanced techniques to prevent energy theft
These innovations have significantly reduced energy losses and increased revenue for the state.
Originally formed as a statutory body on February 1, 1959, under the Electricity Supply Act of 1948, the Punjab State Electricity Board (PSEB) was reconstituted into PSPCL and the Punjab State Transmission Corporation Ltd. (PSTCL) on April 16, 2010. This restructuring was part of major reforms by the state government to improve power development and distribution.
Punjab Energy Development Agency (PEDA):
The Punjab Energy Development Agency (PEDA) was established in September 1991 as a state nodal agency to promote and develop renewable energy programs and projects, as well as energy conservation initiatives in Punjab. PEDA is registered as a society under the Societies Act of 1860.
PEDA operates in several key functional areas:
- Promotion and development of small/micro hydel projects on canals.
- Promotion and development of biomass/agro residue-based power projects.
- Co-generation power projects in sugar mills and the paper industry.
- Promotion and development of solar photovoltaic and solar thermal power projects.
- Promotion and development of waste-to-energy projects.
- Promotion and development of biomass-based gasifiers.
- Implementation of the Energy Conservation Act.
- Raising awareness and publicizing the adoption of non-conventional energy sources and energy-saving/conservation practices.
The Punjab Genco Ltd.:
The Punjab Genco Ltd. is a wholly owned company of the Punjab Energy Development Agency (PEDA). It was formerly known as Punjab Renewable Energy Development and Punjab Genco Ltd. The company was established to fulfill the statutory requirements of the Electricity Supply Act of 1948 for power generation.
|
23 videos|50 docs|47 tests
|
















