District Profile of Punjab | Punjab State (PPSC) PSC: Preparation - PPSC PCS (Punjab) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Divisions of Punjab |

|
| Firozpur Division |

|
| Faridkot Division |

|
| Patiala Division |

|
| Ropar Division |

|
Divisions of Punjab
The state of Punjab is divided into five administrative divisions. Each division consists of various districts. Here’s a detailed look at each division:
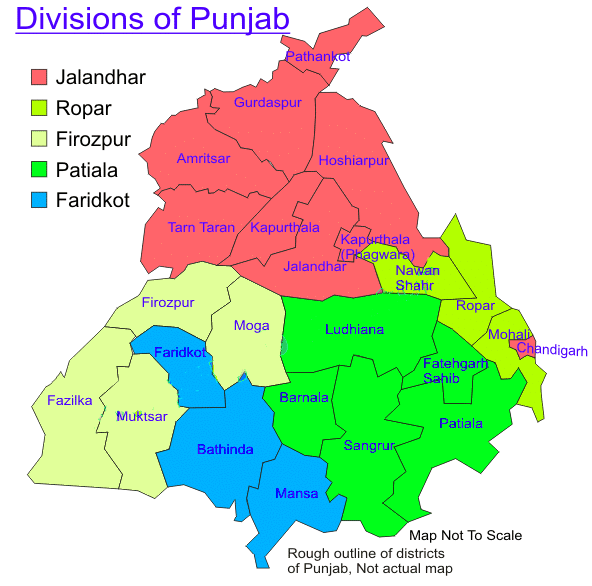
Jalandhar Division
Amritsar District
- Origin: The district gets its name from the Amrit Sarovar, the sacred tank surrounding the Golden Temple, which was founded by Guru Ram Das Ji. During the British era, it was part of the Lahore division. Amritsar is the heart of Sikhism and home to its most important worship site.
- Location: Amritsar district, part of the Jalandhar division, is situated in the Majha region of Punjab. Located in the northern part of the state, it is bordered by Gurdaspur district to the northeast and Kapurthala and Tarn Taran districts to the south.
- Administration: Administratively, Amritsar is divided into five tehsils: Amritsar I, Amritsar II, Ajnala, Baba Bakala, and Majitha. The Deputy Commissioner oversees the district's general administration, while a Municipal Corporation manages public works and health services in the city.
Important Statistical Data:
- Total Area: 2,683 sq km
- Total Population: 2,490,656
- Headquarters: Amritsar
- Sex Ratio: 889 females per thousand males
- Density: 928 inhabitants per sq km
- Literacy Rate: 75.84%
Famous Personalities: Baba Bakala, Guru Arjan Dev, Mahakavi Santokh Singh, Bhai Veer Singh.
Introduction to Gurdaspur District
Gurdaspur District, located in Punjab, India, has a rich history and a diverse cultural landscape. This district is known for its historical significance, administrative divisions, and notable personalities.
- Origin: Gurdaspur was established by Guriya ji in the early 17th century, and the city was named after him. A significant historical event in the district includes the enthronement of Mughal emperor Akbar in Kalanaur, a town within Gurdaspur.
- Location: Gurdaspur District is situated in the northwestern part of Punjab, sharing an international border with Pakistan. It is bordered by the districts of Amritsar, Hoshiarpur, Pathankot, and Kapurthala. The district is traversed by two major rivers, the Beas and the Ravi. Gurdaspur is the third most populous district in Punjab, following Ludhiana and Amritsar.
- Administration: The district is administratively divided into three tehsils: Gurdaspur, Batla, and Dera Baba Nanak. Within these tehsils, there are eight sub-tehsils and eleven blocks.
- Headquarters: The administrative headquarters of Gurdaspur District is located in the town of Gurdaspur.
- Demographics: The total area of Gurdaspur District is 2,610 square kilometers, with a population of approximately 2,298,323 people. The population density is 649 inhabitants per square kilometer. The literacy rate in the district is 81.1%, and the sex ratio stands at 895 females for every thousand males.
Famous Personalities Gurdaspur District has been home to several renowned individuals, including:
- Dev Anand: Actor
- Chetan Anand: Director
- Vijay Anand: Director
- Vinod Khanna: Actor
- Shiv Kumar Batalvi: Writer
- Guru Randhawa: Singer
- Preet Harpal: Singer
- Alla Rakha and Zakir Hussain: Tabla Players
- Teja Singh: Singh Sabha Movement Leader
- Mumtaz Mufti: Writer
Hoshiarpur District
- Origin: Hoshiarpur District was originally part of the ancient kingdom of Katoch, located in Jalandhar. The district was historically divided between the Rajas of Datarpur and Jaswan.
- Location: Hoshiarpur District is situated in the northeastern part of Punjab, India. It shares its eastern boundary with the state of Himachal Pradesh and is bordered by the scenic Shivalik hills to the northeast. The Beas River forms its northwestern boundary, separating Hoshiarpur from Himachal Pradesh in the east and Gurdaspur district in the west. The district shares borders with Kangra and Una districts of Himachal Pradesh to the northeast, Jalandhar and Kapurthala districts to the southwest, SBS Nagar and Rupnagar districts to the south, and Gurdaspur district to the northwest.
- Administration: Administratively, Hoshiarpur District is divided into four tehsils: Hoshiarpur, Mukerian, Dasua, and Garshankar.
- The district has a total of seven Vidhan Sabha (legislative assembly) seats: Chabbewal, Dasua, Garshankar, Hoshiarpur, Mukerian, Shamchaurasi, and Urmar.
- Famous For: Hoshiarpur is renowned for its production of wooden toys, inlay and lacquer-finished furniture, and musical instruments such as tablas, harmoniums, and sitars. The district is also home to the Vedic Research Institute.
- Headquarters: Hoshiarpur
- Total Area: 3,365 square kilometers
- Total Population: 1,586,625
- Density: 683 inhabitants per square kilometer
- Literacy Rate: 85.40%
- Sex Ratio: 961 females per thousand males (the highest in the state)
Jalandhar District
- Origin: This district derives its name from Jalandhar, a demon king mentioned in ancient texts like the Puranas and the Mahabharata. The name Jalandhar means “area inside the waters,” reflecting its historical geography. The region was once drained by three rivers: the Sutlej, Beas, and Ravi.
- Location: Jalandhar District is situated on the fertile plain between the Beas and Sutlej rivers. It is bordered by Nawanshahr to the east, Kapurthala to the west, Hoshiarpur to the north, and Firozpur, Moga, and Ludhiana to the south. The district is well-connected by road and rail, with the nearest airport being Raja Sansi International Airport in Amritsar.
- Administration: The district is divided into five tehsils: Jalandhar I, Jalandhar II, Shahkot, Nakodar, and Phillaur.
- Famous For: Jalandhar is renowned for its sports goods industry, particularly as the Mecca of Indian Hockey.
- Headquarters: Jalandhar
- Total Area: 2,632 sq km
- Total Population: 21,93,590
- Density: 836 inhabitants per sq km
- Sex Ratio: 915 females per thousand males
- Famous Personalities: Kartar Singh Duggal, Jagjit Singh, Sunil Dutt
- Literacy Rate: 82.4%
About Kapurthala District
- Origin: Kapurthala District was established in the 11th century by Rana Kapur, a member of the Rajput Royal House of Bhattis from Jaisalmer. Originally a princely state ruled by the Ahluwalia Sikh family, it became part of PEPSU (Patiala and East Punjab States Union) on August 20, 1948, leading to the district's formation.
- Location: Kapurthala is one of the smallest districts in Punjab, both in area and population. It consists of two non-contiguous parts: the main Kapurthala-Sultanpur Lodhi area and the Phagwara tehsil. The district is bordered by Hoshiarpur, Gurdaspur, and Amritsar to the north; the Beas River and Tarn Taran Sahib to the west; Jalandhar to the east; and the Sutlej River and Firozpur to the south. The major part of the district lies between the Beas and Kali-Bein rivers, known as the Bet area.
- Administration: Administratively, Kapurthala District is divided into four tehsils: Kapurthala, Bhulath, Sultanpur Lodhi, and Phagwara.
- Famous For: The district is renowned for the Rail Coach Factory, a significant rail manufacturing unit. Major crops include wheat, rapeseed and mustard, sunflower, and berseem. The Kanjli wetland, a notable ecological site, is also located in Kapurthala.
- Headquarters: Kapurthala
- Total Area: 1,633 sq km
- Total Population: 815,168
- Literacy Rate: 80.20%
- Density: 500 inhabitants per sq km
- Sex Ratio: 912 females per 1,000 males
Pathankot District
- Origin: Pathankot District was formed by splitting off from Gurdaspur District and officially became a district on July 27, 2011.
- Location Pathankot District is situated in the northern part of Punjab, at the foothills of the Shiwalik Hills. It shares an international border with the Narowal district of Pakistani Punjab. Additionally, it borders the Kathua district of Jammu and Kashmir, as well as the Chamba and Kangra districts of Himachal Pradesh. The district is traversed by two major rivers, the Beas and the Ravi. Historically, it was part of the Nurpur princely state, ruled by the Pathania Rajputs before 1849 AD.
- Administration: Administratively, Pathankot District is divided into two tehsils: Pathankot and Dharkalan. It also has two sub-tehsils: Narot Jaimal Singh and Bamial.
- Famous For: Pathankot is known as the meeting point of Punjab, Himachal Pradesh, and Jammu and Kashmir. It is the last city in Punjab on the national highway that connects Jammu and Kashmir to the rest of India. Due to its strategic location, the district is also referred to as "Cock Neck City." Furthermore, Pathankot serves as a gateway to popular Himachal hill stations such as Dalhousie, Dharmshala, Kangra Valley, Jwalaji, and Chintpurni.
- Headquarters: Pathankot
- Established: July 27, 2011
- Total Area: 929 sq km
- Literacy Rate: 84.6%
- Total Population: 626,154
- Sex Ratio: 907 females for every 1,000 males
District of Tarn Taran Sahib
- Origin: The Tarn Taran Sahib district was established in 2006 when it was carved out from the Amritsar district. The city of Tarn Taran Sahib was founded by the fifth Guru of the Sikhs, Guru Arjan Dev, who also gave it its name.
- Location: The district is situated with Amritsar district to the north, Kapurthala district to the east, Pakistan to the west, and Firozpur district to the south.
- Administration: Tarn Taran Sahib district is administratively divided into four tehsils: Tarn Taran, Patti, Khadur Sahib, and Bhikhiwind.
- Famous For: The district is renowned for the Gurdwara of Tarn Taran Sahib, which features one of the largest Sarovars (sacred water tanks) among all Sikh Sarovars.
- Headquarters: Tarn Taran Sahib serves as the district headquarters.
- Total Area: The district covers an area of 2,414 square kilometers.
- Total Population: The population of the district is 1,119,627.
- Literacy Rate: The literacy rate in the district is 67.84%.
- Density: The population density is 464 inhabitants per square kilometer.
- Sex Ratio: The sex ratio is 900 females for every thousand males.
Firozpur Division
- Origin: Firozpur District was established in the 14th century by Firozshah Tughlaq, a ruler known for his passion for founding cities.
- Location: Firozpur District is located on the India-Pakistan border. It is bordered by Moga District to the east, Faridkot District to the south, and Tarn Taran Sahib to the north. The Sutlej River separates Firozpur from Jalandhar and Kapurthala districts to the northeast, while Fazilka District borders it to the southwest.
- Administration: The district is divided into three tehsils: Firozpur, Zira, and Guru Har Sahni (the latter was created in 2011).
- Famous For: Firozpur is known as Shaheedon ki Dharti (Land of Martyrs) because it is the final resting place of Shaheed Bhagat Singh, Shaheed Rajguru, and Shaheed Sukhdev, who were buried on the banks of the Sutlej River in Firozpur.
- Headquarters: The district headquarters is located in Firozpur.
- Total Population: 20,29,074
- Density: 382 inhabitants per square kilometer
- Literacy Rate: 68.92%
- Sex Ratio: 893 females per thousand males
Fazilka District Overview
- Origin: Fazilka District was established on July 27, 2011. Prior to its formation, it was part of Firozpur District.
- Location: Fazilka District is located near the India-Pakistan border, which is approximately 11 kilometers away. It is bordered by Firozpur District to the north, Muktsar Sahib and Faridkot Districts to the east, Rajasthan to the south, and Pakistan to the west.
- Agriculture and Economy: The district is known for its fertile land, particularly in the rice and cotton-growing regions. Fazilka is one of the major rice-exporting centers in India. Before the partition, the town was a significant wool market in undivided Punjab. The primary crops cultivated in the district include wheat, rice, guava, and cotton.
- Administration: Fazilka District is divided into three administrative tehsils: Fazilka, Jalalabad, and Abhor.
- Headquarters: The district headquarters is located in Fazilka.
- Area and Population: The total area of Fazilka District is 3,113 square kilometers, with a population of 76,492.
- Literacy Rate: The literacy rate in Fazilka District is 68%.
District Muktsar Sahib
- Origin: The Muktsar Sahib District holds significant historical and religious importance, particularly in the Sikh tradition. It is reputedly the site where Guru Gobind Singh Ji, the tenth Sikh Guru, fought his last battle against the Mughals in 1705, an event known as the Battle of Muktsar. During this fierce conflict, 40 of Guru Gobind Singh's disciples, known as the 40 Muktas, made the ultimate sacrifice for their faith.
- Location: The district is geographically situated with Rajasthan to the south, Faridkot to the north, and the districts of Firozpur, Fazilka, and Bathinda to the west and east, respectively.
- Administration: Muktsar Sahib District is administratively divided into three tehsils: Sri Muktsar Sahib, Giddarbaha, and Malout.
- Famous For: One of the notable events in the district is the annual Maghi Mela,. large fair celebrated on the day following Lohri in January. This festival attracts many visitors and is a significant cultural event in the region.
- Headquarters: The administrative headquarters of the district is located in Muktsar Sahib.
Moga District: Overview
- Origin: Moga district was established in 1995 and is named after Moga Singh Gill, an ancestor of the Gill Community. It was the 17th district formed in Punjab. Before becoming a district, Moga was part of Faridkot district and was located along the Firozpur-Ludhiana road.
- Location: Moga district is bordered by several other districts: Jalandhar to the north, Ludhiana to the east, Bathinda to the south, and Faridkot and Firozpur to the west. Barnala district lies to the southeast of Moga.
- Administration: The district is divided into four tehsils (administrative divisions): Moga, Bagha Purana, Nihal Singhwala, and Dharamkot, with the latter being created in 2011.
- Agriculture: Moga district is known for its large-scale production of wheat and rice, making it one of the prominent agricultural regions in Punjab. Towns such as Bagha Purana, Dharamkot, and Nihal Singh are located within this district.
- Headquarters: Moga city serves as the headquarters of the district.
- Population: The total population of Moga district is 9,95,746.
- Literacy Rate: The literacy rate in the district is 70.68%.
- Area: Moga district covers a total area of 2,235 square kilometers.
- Density: The population density is 446 inhabitants per square kilometer.
- Sex Ratio: The sex ratio is 893 females for every thousand males.
Faridkot Division
Bathinda District
- Origin: The Bathinda district was established with the formation of PEPSU in 1948 and became part of the newly created Faridkot Revenue Commissioners Division.
- Location: Bathinda district is located in the southern part of Punjab, in the heart of the Malwa region. It is bordered by Sirsa and Fatehabad districts of Haryana to the south, Barnala and Mansa districts to the east, Moga district to the northeast, Faridkot district to the northwest, and Muktsar district to the west.
- Historical Names: According to Raverty, an officer in the British Indian Army, Bathinda was known as Tabarhindh. Ibn Batuta referred to it as Batrind.
- Administration: The district is divided into four tehsils: Bathinda, Rampura Phul, Talwandi Sabo, and the newly created Maur.
- Headquarters: Bathinda
- Total Area: 3,344 km²
- Total Population (2011): 1,388,525
- Density: 414 inhabitants per square kilometer
- Literacy Rate: 69.6%
- Sex Ratio: 865 females per 1,000 males
Faridkot District
- Origin: Faridkot district was established in 1972 when Faridkot tehsil was taken from Bathinda district, and Moga and Muktsar tehsils were taken from Firozpur district. However, in 1995, Faridkot district was divided into three parts, with Moga and Muktsar becoming independent districts. Initially part of Firozpur division, Faridkot district became separate in 1996.
- Location: Faridkot district is located in the southwestern part of Punjab, India. It is bordered by Firozpur district to the northwest, Fazilka district to the north, Muktsar district to the southwest, Moga district to the northeast, and Bathinda district to the south.
- Administration: The district is divided into three tehsils: Faridkot, Kotakpura, and Jaitu.
- Headquarters: The administrative headquarters of the district is located in Faridkot.
- Total Population: The district has a total population of 6,17,508.
- Density: The population density is 424 inhabitants per square kilometer.
- Sex Ratio: The sex ratio is 890 females for every thousand males.
- Literacy Rate: The literacy rate in the district is 69.55%.
Mansa District
- Origin: Mansa District was established on April 13, 1992, carved out from the larger Bathinda District. It is relatively small in both population and area.
- Location: Mansa is located in Punjab's cotton-producing region, often referred to as the "Area of White Gold." The district shares its borders with Bathinda to the northwest, Sangrur to the northeast, Haryana to the south, and Barnala to the north. The Ghaggar River runs through the southwestern corner of the district, specifically in the Sardulgarh tehsil.
- Administration: The district is divided into three tehsils: Mansa, Budhlada, and Sardulgarh.
- Headquarters: The administrative headquarters of the district is located in Mansa.
- Population: The total population of the district is 769,751.
- Literacy Rate: The literacy rate in Mansa District is 62.8%.
- Area: The total area of the district is 2,174 square kilometers.
- Population Density: The district has a population density of 350 inhabitants per square kilometer.
- Sex Ratio: The sex ratio in Mansa District is 880 females for every thousand males.
Patiala Division
Barnala District: An Overview
Origin Barnala District has its roots in a place called Anahadgarh, founded by Baba Ala Singh in 1772. Baba Ala Singh was the founder of the Patiala state. Initially, Barnala was part of the Princely State System and later became the district headquarters. It was eventually merged into the Patiala and East Punjab States Union (PEPSU) and downgraded to a sub-divisional headquarters. Barnala was officially designated as a district on November 19, 2006. Today, it holds the distinction of being the least populous district in Punjab.
Location Barnala District is situated in the state of Punjab and shares its borders with several other districts:
- North: Ludhiana District
- North-West: Moga District
- West: Bathinda District
- East: Sangrur District
- South: Mansa District
Administration The district is administratively divided into two tehsils:
- Barnala
- Tapa
Headquarters: The administrative headquarters of Barnala District is located in the town of Barnala.
Population and Demographics Total Population. 5,95,527 Literacy Rate. 68.9% Area. 1423 square kilometers Population Density. 419 inhabitants per square kilometer Sex Ratio. 876 females for every thousand males
Fatehgarh Sahib District
- Origin: This district was established on April 13, 1992, and is named after the youngest son of Guru Gobind Singh, the 10th Guru of the Sikhs.
- Location: Fatehgarh Sahib District is situated in Punjab, India. It is bordered by Ludhiana and Rupnagar to the north, Patiala to the south, SAS Nagar to the east, and Sangrur to the west. The district is the second least populous in Punjab. Four major canals run through the district: Sirhind Canal, Bhakra Canal, Narwana Branch, and Sutlej-Yamuna Link Canal.
- Administration: The district is divided into four tehsils: Fatehgarh Sahib, Bassi Pathana, Amloh, and Khamanon.
- Headquarters: The district headquarters is located in Fatehgarh Sahib.
- Total Population: 600,163
- Density: 508 inhabitants per square kilometer
- Literacy Rate: 80.3%
- Sex Ratio: 871 females for every thousand males
Ludhiana District
- Origin: Ludhiana district was established during the Lodhi dynasty, which ruled Delhi from AD 1451 to 1526. It is centrally located in the Malwa region of Punjab and is the most populous district in the state.
- Location: The district is bordered to the north by the Sutlej River, which separates it from Jalandhar and Nawanshahr districts. It shares boundaries with Rupnagar and Fatehgarh Sahib districts to the east, Moga district to the west, and Sangrur and Barnala districts to the south and southeast, respectively.
- Famous For: Ludhiana is known as the "Manchester of India" due to its extensive production of hosiery products. It is also home to the renowned Punjab Agricultural University.
- Administration: The district is divided into seven tehsils: Ludhiana (East), Ludhiana (West), Samrala, Khanna, Payal, Raikot, and Jagraon.
- Famous Sites: Notable attractions in Ludhiana include Qila Mubarak, Moti Bagh Palace, and the National Institute of Sports (NIS).
District of Patiala
Origin: Patiala District was once a renowned princely state in the historical region of Punjab, located in the southeastern part of the present-day state.
Location: The district is bordered by Fatehgarh Sahib and SAS Nagar to the north, Sangrur to the west, and the Haryana districts of Ambala, Kurukshetra, and Kaithal to the east and south, respectively. Patiala is part of the Indo-Gangetic plains and features three distinct regions:
- Upland plains
- Co-infested foothill plains
- Flood plains of the Ghaggar River
Administration: Patiala District is subdivided into five tehsils: Patiala, Patran, Nabha, Samana, and Rajpura.
District Statistics: Headquarters: Patiala Total Area: 3,430 square kilometers Total Population: 1,895,686 Literacy Rate: 76.3% Population Density: 596 inhabitants per square kilometer Sex Ratio: 888 females for every 1,000 males
Sangrur District
Origin: Sangrur District was established in 1948 with the creation of the Patiala and East Punjab States Union (PEPSU). Its boundaries changed when PEPSU merged with Punjab in 1956 and again during the reorganization of Punjab in 1966.
Location: Sangrur District is located:
- North: Ludhiana District
- West: Barnala and Mansa Districts
- East: Patiala and Fatehgarh Sahib Districts
- South: Fatehabad District (Haryana)
(Note: Barnala was formerly part of Sangrur District but is now a separate district.)
Administration: The district is divided into seven tehsils:
- Sangrur
- Sunam
- Malerkotla
- Lehra
- Moonak
- Dhuri
- Dirbha
Headquarters: Sangrur
Total Population: 1,655,169
Literacy Rate: 67.99%
Total Area: 3,685 sq km
Density: 449 inhabitants per sq km
Sex Ratio: 885 females per thousand males
Ropar Division
Nawanshahr/Shaheed Bhagat Singh Nagar District (SBS Nagar)
Origin: Nawanshahr, now known as Shaheed Bhagat Singh Nagar, was established as the 16th district of Punjab on November 7, 1995. It was carved out from the Hoshiarpur and Jalandhar districts. The town of Nawanshahr was originally built by the Afghan military chief Nausher Khan during the reign of Alauddin Khilji.
Location: The district is bordered by four other districts: Jalandhar to the west, Rupnagar to the east, Hoshiarpur to the north, and Ludhiana to the south.
Famous For: Shaheed Bhagat Singh Nagar is the third least populous district in Punjab, following Barnala and Fatehgarh Sahib. The district is renowned for being the native village of the freedom fighter Shaheed Bhagat Singh, with his ancestral village, Khatkar Kalan, located within this district.
Administration: The district is administratively divided into three tehsils: Nawanshahr, Balachaur, and Banga.
Statistical Data: Headquarters - Nawanshahr
- Total Area - 1266 sq km
- Total Population - 6,12,310
- Literacy Rate - 80.3%
- Density - 480 inhabitants per sq km
- Sex Ratio - 954 females per thousand males
Rupnagar District
- Origin: This district gets its name from its headquarters, Ropar. It was established by a Raja named Rokeshar in the 11th century, who named the area after his son, Rup Sen.
- Location: Rupnagar District is situated along the Chandigarh-Ludhiana highway. It shares borders with Nawanshahr, Mohali, and Fatehgarh Sahib districts in Punjab. To the east and north, it is bordered by Himachal Pradesh, while Hoshiarpur and Shaheed Bhagat Singh Nagar lie to the west. Ludhiana, Fatehgarh Sahib, and SBS Nagar are to the south.
- Famous For: Recent archaeological excavations in Rupnagar have revealed that the town was once a significant center of the well-developed Indus Valley Civilization. The major cities in Rupnagar district include Morinda, Kurali, and Anandpur Sahib. Morinda, also known as Baghawala or the city of gardens, is located along the Chandigarh-Ludhiana highway.
- Administration: Rupnagar District is divided into five tehsils: Rupnagar, Anandpur Sahib, Nangal, Chamkaur Sahib, and the newly created Morinda.
- Headquarters: Rupnagar
- Total Area: 1440 sq km
- Total Population: 6,84,627
- Literacy Rate: 82.19%
- Density: 505 inhabitants per sq km
- Sex Ratio: 915 females per thousand males
Sahibzada Ajit Singh Nagar (Mohali)
- Origin: This district was created on April 14, 2006, as the 18th district of Punjab, carved out from parts of Rupnagar and Patiala. It is named after Sahibzada Ajit Singh, the eldest son of Guru Gobind Singh.
- Location: Sahibzada Ajit Singh Nagar, also known as Mohali, is bordered by Chandigarh to the east, Rupnagar to the north, Fatehgarh Sahib and Patiala to the west, and Haryana to the south. The district is part of the Chandigarh Tricity and is emerging as a major IT hub in Northern India.
- Administration: The district is divided into three tehsils: Kharar, SAS Nagar (Mohali), and Dera Bassi.
- Famous For: Mohali is home to the renowned Punjab Cricket Association IS Bindra Stadium, a world-class cricket facility known internationally.
- Headquarters: Ajitgarh
- Total Population: 9,94,628
- Literacy Rate: 91.96%
- Total Area: 1,098 sq km
- Density: 837 inhabitants per sq km
- Sex Ratio: 909 females per thousand males
|
23 videos|50 docs|47 tests
|
FAQs on District Profile of Punjab - Punjab State (PPSC) PSC: Preparation - PPSC PCS (Punjab)
| 1. पंजाब के जिलों का विभाजन क्या है और इसमें कौन-कौन से विभाग शामिल हैं? |  |
| 2. PPSC PCS परीक्षा में पंजाब के जिलों की जानकारी का महत्व क्या है? |  |
| 3. पंजाब में फिरोजपुर विभाग की विशेषताएँ क्या हैं? |  |
| 4. PPSC PCS परीक्षा में कैसे तैयारी करें ताकि जिलों के विभाजन के प्रश्नों में सफलता मिले? |  |
| 5. क्या PPSC PCS परीक्षा में फरीदकोट और पटियाला विभाग के विशेष प्रश्न आते हैं? |  |















