Basic Concepts: Classification | General Intelligence and Reasoning for Competitive Exams - SSC MTS / SSC GD PDF Download
Understanding the number system is vital for competitive exams like SSC, especially for the Classification section in General Intelligence and Reasoning. This topic is filled with thought-provoking conceptual problems that challenge your logical abilities. Instead of merely solving questions, focus on deeply understanding the concepts. Try exploring different methods to tackle problems, as this will enhance your reasoning skills and provide thorough preparation for the exam.

What is Classification?
"Classification" refers to the process of organizing items from a given group based on a common characteristic they share, and then identifying the item that does not belong. These questions involve words, letters, or numbers. In such questions, a group of items is presented, with all but one being similar in some way. The task is to select the item that does not fit with the rest of the group.
Different Types of Questions asked in Competition Exams
Type 1: Choosing the Odd Word
In these types of problems, a set of words is provided that are related to the real world and share common characteristics, except for one. The task is to identify the "odd one out."
Examples
Example 1: In each of the following questions, four words have been given out of which three are alike in some manner while the fourth one is different. Choose the odd one.
(a) Mustard
(b) Onion
(c) Olive
(d) Sesame
Ans: (b) Onion
In this set, three words—Mustard, Olive, and Sesame—are types of seeds, while Onion is a vegetable. Therefore, Onion is the odd one out because it does not belong to the category of seeds.
Example 2: In each of the following questions, four words have been given out of which three are alike in some manner while the fourth one is different. Choose the odd one.
(a) Pistol
(b) Sword
(c) Gun
(d) Rifle
Ans: (b) Sword
Pistol, Gun, and Rifle are all firearms, which are weapons that use gunpowder to fire projectiles. On the other hand, a Sword is a bladed weapon that does not rely on gunpowder or firearms, making it the odd one out.
Type 2: Choosing the Odd Pair of Words
In this type of classification, different pairs are grouped based on shared characteristics or properties such as names, places, uses, situations, origin, and so on. The task is to understand the relationship between the pairs and identify the one pair that is differently related.
Examples
Example 1: In each of the following questions, four pairs of words are given out of which words in three pairs bear a certain common relationship. Choose the pair in which the words are differently related.
(a) Petrol : Car
(b) Ink : Pen
(c) Garbage : Dustbin
(d) Lead : Pencil
Ans: (d) Lead : Pencil
In all the other pairs—Petrol : Car, Ink : Pen, and Garbage : Dustbin—the first item is needed by the second for its functioning. However, in the pair "Lead : Pencil," the lead is an essential part of the pencil, but it doesn't serve as a requirement for the pencil's functioning in the same sense as the others. Thus, "Lead : Pencil" is the odd one out.
Example 2: In each of the following questions, four pairs of words are given out of which words in three pairs bear a certain common relationship. Choose the pair in which the words are differently related.
(a) China : Beijing
(b) Russia : Moscow
(c) Japan : Singapore
(d) Spain : Madrid
Ans: (c) Japan : Singapore
In the other pairs—China : Beijing, Russia : Moscow, and Spain : Madrid—the first word refers to the country, and the second word is the capital city of that country. However, in the pair "Japan : Singapore," Singapore is not the capital of Japan; the capital of Japan is Tokyo. Therefore, this pair has a different relationship.
Type 3: Choosing the Odd Letter Group
In these types of problems, several groups of letters are provided, and the task is to identify the one that is different from the others. The candidate is required to choose this odd group as the answer.
Examples
Example 1: Choose the group of letters which is different from others.
(a) H
(b) Q
(c) T
(d) Z
Ans: (b) Q
All the other letters—H, T, and Z—occupy even-numbered positions in the English alphabet (H is 8th, T is 20th, and Z is 26th), whereas Q occupies the 17th position, which is odd-numbered. Therefore, Q is the odd one out.
Example 2: Choose the group of letters which is different from others.
(a) DG2
(b) EK5
(c) JR6
(d) PY8
Ans: (c) JR6
In all the other options, the letters follow a consistent pattern where the first letter and the second letter have a fixed alphabetical difference, and the number is related accordingly.
In (a) DG2: D and G are 3 positions apart, and the number is 2.
In (b) EK5: E and K are 6 positions apart, and the number is 5.
In (d) PY8: P and Y are 9 positions apart, and the number is 8.
However, in (c) JR6: J and R are 8 positions apart, but the number is 6, which does not follow the same pattern. Therefore, JR6 is the odd one out.
Type 4: Choosing the Odd Number / Pair of Numbers
Odd Number
In these types of questions, a set of numbers is given, where all but one share certain common characteristics. The task is to identify the "different one" as the answer.
Odd Numeral Pair/Group
In these types of questions, a set of number pairs or groups is provided, where all but one are similar in some way. The numbers in these similar pairs may share a common property or follow the same rule. The task is to identify the odd pair or group.
Examples
Odd Number
Example 1: In each of the following questions, four numbers are given. Out of these, three are alike in a certain way but the fourth one is different. Choose the one which is different from the rest four/three.
(a) 35
(b) 49
(c) 50
(d) 63
Ans: (c) 50
35, 49, and 63 are all divisible by 7
35 = 7 × 5
49 = 7 × 7
63 = 7 × 9
However, 50 is not divisible by 7, making it the odd one out.
Example 2: In each of the following questions, four numbers are given. Out of these, three are alike in a certain way but the fourth one is different. Choose the one which is different from the rest four/three.
(a) 385
(b) 572
(b) 671
(d) 427
Ans: (d) 427
In the other numbers, the middle digit is the sum of the other two digits:
385: 8 = 3 + 5
572: 7 = 5 + 2
671: 7 = 6 + 1
However, in 427, the middle digit 2 is not the sum of the other two digits (4 + 7 = 11, not 2). Therefore, 427 is the odd one out.
Odd Numeral Pair/Group
Example 1: Choose the numeral pair/group which is different from others.
(a) 71, 7, 3, 17
(b) 67, 71, 3, 5
(c) 41, 5, 3, 47
(d) 37, 14, 19, 7
Ans: (d) 37, 14, 19, 7
In all the other pairs/groups, the numbers consist solely of prime numbers.
(a) 71, 7, 3, 17: All prime numbers.
(b) 67, 71, 3, 5: All prime numbers.
(c) 41, 5, 3, 47: All prime numbers.
However, in (d) 37, 14, 19, 7, the number 14 is a composite number, making it the odd one out.
Example 2: Choose the numeral pair/group which is different from others.
(a) 95 – 82
(b) 69 – 56
(c) 55 – 42
(d) 48 - 34
Ans: (d) 48 – 34
In all the other pairs, the first number is 13 more than the second:
(a) 95 – 82 = 13
(b) 69 – 56 = 13
(c) 55 – 42 = 13
However, in (d) 48 – 34 = 14, the difference is 14, not 13. Therefore, this pair is the odd one out.
Type 5: Choosing the Odd Figure
In these problems, a set of figures is provided, where all but one share similar characteristics or features. The task is to identify the figure that is different from the rest of the set.
Examples
Example 1: In each of the following questions, four figures are given. Out of these, three are alike in a certain way but the fourth one is different. Choose the one which is different from the rest three.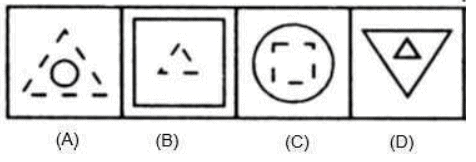
(a) (A)
(b) (B)
(c) (C)
(d) (D)
Ans: (d) (D)
In all other cases, one of the two figures is made of dotted lines.
Example 2: In each of the following questions, four figures are given. Out of these, three are alike in a certain way but the fourth one is different. Choose the one which is different from the rest three.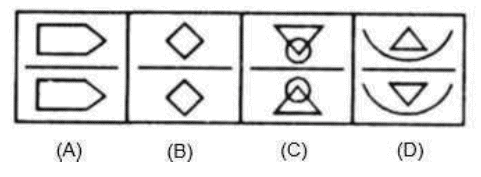 (a) (A)
(a) (A)
(b) (B)
(c) (C)
(d) (D)
Ans: (d)
In all other figures, the two figures on either side of the line are inverted image of one another.
|
110 videos|104 docs|89 tests
|
FAQs on Basic Concepts: Classification - General Intelligence and Reasoning for Competitive Exams - SSC MTS / SSC GD
| 1. What is classification in the context of data analysis? |  |
| 2. What are the main types of classification algorithms? |  |
| 3. How is classification different from regression? |  |
| 4. What are some common applications of classification? |  |
| 5. What metrics are used to evaluate the performance of classification models? |  |

















