Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Social Studies (SST) Class 10 > Cheatsheet: The Rise of Nationalism in Europe
Cheatsheet: The Rise of Nationalism in Europe | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Nationalism? |

|
| Timeline and Key Events |

|
| Important Figures |

|
| Effects of Nationalism in Europe |

|
What is Nationalism?
Nationalism: A sense of shared identity and pride among people, based on culture, language, history, and territory. It encourages people to form independent nations with self-rule.
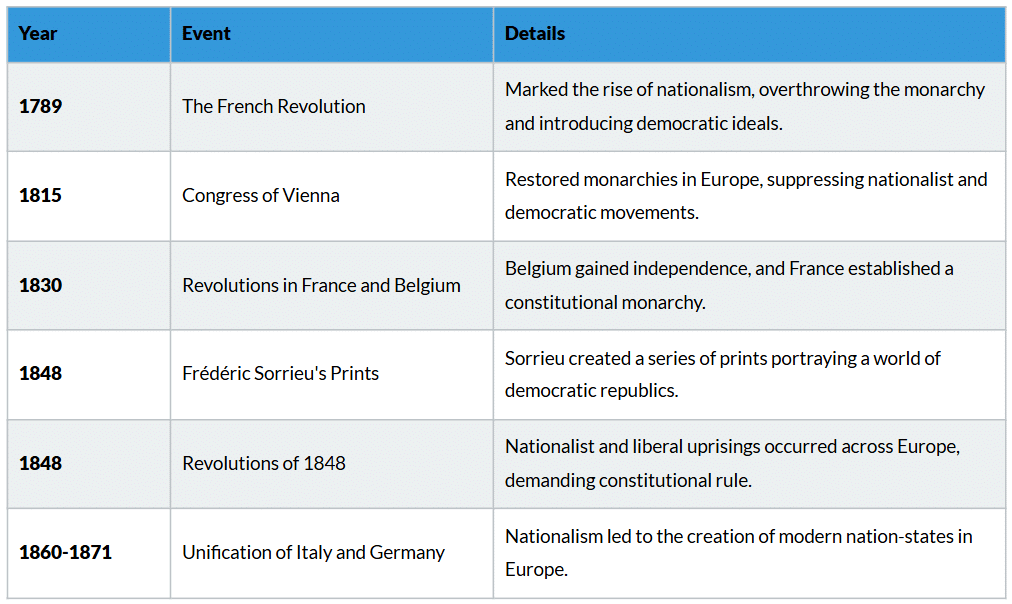
Timeline and Key Events
This timeline covers the key historical events related to Frédéric Sorrieu's vision of a world of democratic and social republics. His work in 1848 reflected the rise of nationalism and aspirations for nation-states in 19th-century Europe.
The Dream of Worldwide Democratic and Social Republics
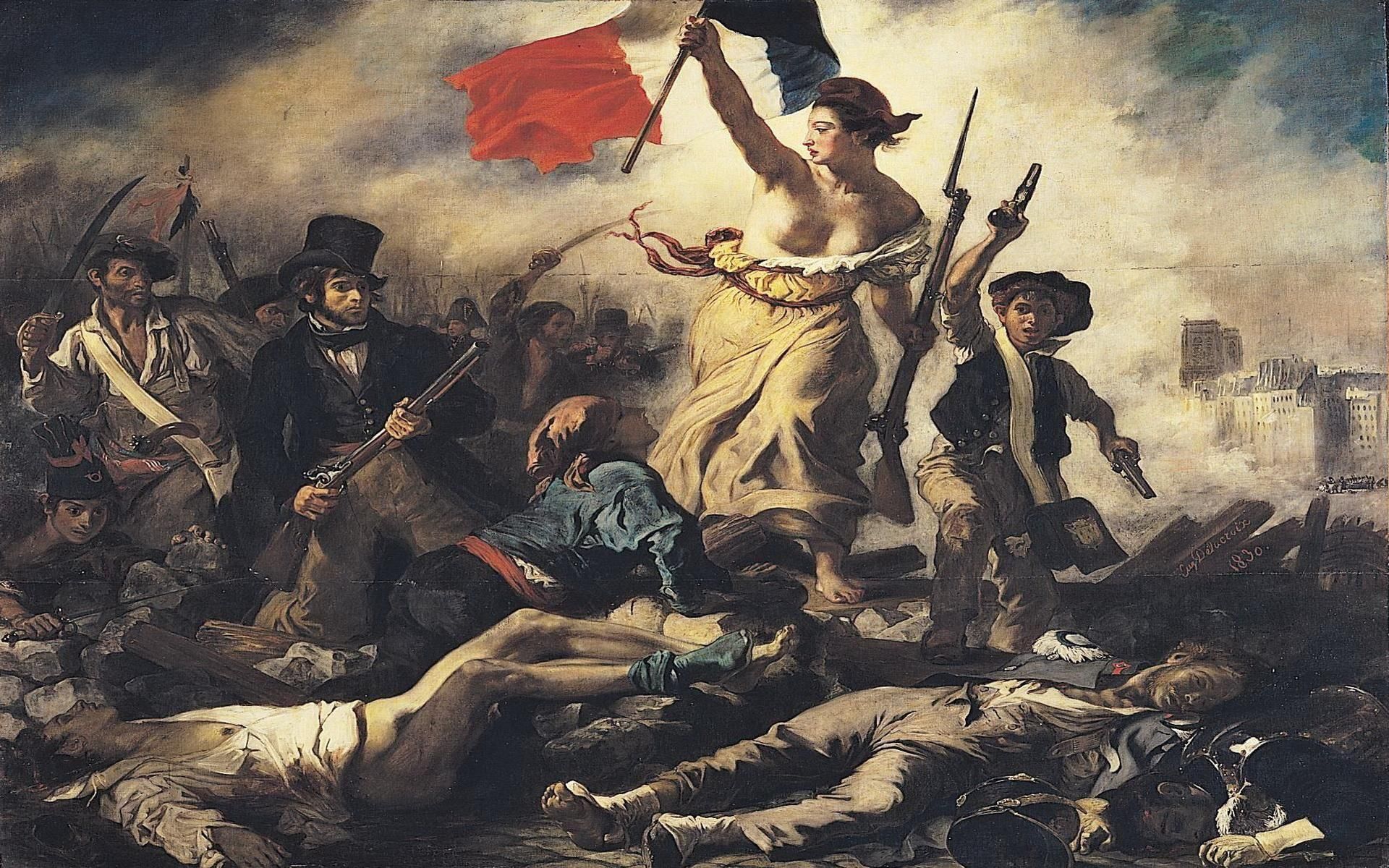
Key Takeaways
- The French Revolution laid the foundation for modern nationalism.
- The 19th century saw multiple revolutions driven by liberal and nationalist ideals.
- The unification of Germany and Italy demonstrated the power of nationalism in shaping modern Europe.

Important Figures
- Giuseppe Mazzini: Italian nationalist, founded Young Italy.
- Giuseppe Garibaldi: Led military campaigns for Italian unification.
- Count Cavour: Prime Minister of Sardinia-Piedmont, diplomat behind Italy’s unification.
- Otto von Bismarck: Prussian Chancellor, architect of German unification.
- Napoleon Bonaparte: Spread revolutionary ideas but also centralized power.
Effects of Nationalism in Europe
- Creation of nation-states (Italy, Germany)
- Decline of multi-national empires (Austro-Hungarian, Ottoman)
- Increased demand for rights and constitutions
- Set the stage for future conflicts (World Wars)
Conclusion
Frédéric Sorrieu’s vision reflected the widespread nationalist aspirations of the 19th century. His prints symbolized the transition from monarchies to democratic nation-states, a shift that shaped modern Europe.
The document Cheatsheet: The Rise of Nationalism in Europe | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Social Studies (SST) Class 10.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
94 videos|630 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Cheatsheet: The Rise of Nationalism in Europe - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. What were the main causes of the rise of nationalism in Europe during the 19th century? |  |
Ans. The rise of nationalism in Europe during the 19th century was influenced by several key factors, including the impact of the French Revolution, which inspired the ideas of liberty, equality, and fraternity. The spread of Romanticism also encouraged people to embrace their cultural identities. Additionally, the decline of empires such as the Ottoman and Austro-Hungarian Empires created a power vacuum, leading various ethnic groups to seek self-determination and nationhood.
| 2. How did the unification of Italy and Germany contribute to the rise of nationalism in Europe? |  |
Ans. The unification of Italy and Germany in the 19th century significantly contributed to the rise of nationalism by demonstrating that fragmented states could come together to form strong nation-states. Leaders like Giuseppe Garibaldi and Otto von Bismarck played crucial roles in these processes, which inspired nationalist movements across Europe, encouraging other regions to pursue their own unification and independence efforts.
| 3. What role did wars and conflicts play in the rise of nationalism in Europe? |  |
Ans. Wars and conflicts played a pivotal role in the rise of nationalism in Europe. The Napoleonic Wars spread nationalistic ideas across Europe, leading to a sense of unity among people with shared heritage. Additionally, conflicts such as the Franco-Prussian War fueled nationalist sentiments, as they rallied citizens around the idea of national pride and identity, ultimately leading to the establishment of nation-states.
| 4. How did nationalism affect the various ethnic groups within empires in Europe? |  |
Ans. Nationalism had a profound impact on various ethnic groups within empires in Europe, as many sought to assert their identities and gain independence. Ethnic groups like the Poles, Czechs, and Hungarians pushed for self-determination and autonomy from larger empires. This often led to tensions and conflicts within multi-ethnic empires, as different groups vied for recognition and rights, resulting in a fragmentation of these empires.
| 5. What were the positive and negative outcomes of nationalism in Europe? |  |
Ans. The outcomes of nationalism in Europe were both positive and negative. On the positive side, nationalism fostered a sense of unity and pride among people, leading to the creation of nation-states and promoting cultural revival. However, on the negative side, nationalism also led to exclusionary practices, xenophobia, and conflicts between nations and ethnic groups, which sometimes escalated into wars and violence, as seen in the Balkan conflicts in the early 20th century.
Related Searches
















