Societal Impact Chapter Notes | Computer Science for Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Digital Footprints |

|
| Digital Society and Netizens |

|
| Data Protection |

|
| Cyber Crime |

|
| Indian Information Technology Act (IT Act) |

|
| Impact on Health |

|
Introduction
Digital technologies have brought about significant changes in our lives, making tasks more convenient, faster, and easier to manage. Previously, communication took time, but with emails and instant messaging, we can now connect with multiple people instantly, enhancing our efficiency and productivity.
Various industries, including banking, aviation, manufacturing, and e-commerce, heavily depend on computers and digital technologies for their operations. The widespread use of smartphones and high-speed Internet has further integrated digital technologies into our daily lives. The introduction of personal computers, the Internet, and smartphones has made these technologies accessible to all.
While digital technologies offer many advantages, they also carry risks of misuse. It is essential to understand their societal impact and adopt best practices to maintain a productive and safe digital environment.
Digital Footprints

Digital Footprints: Digital footprints are the trails of data left behind when we use the internet, either consciously or unconsciously. They include everything from the websites we visit to the emails we send, as well as specific device details such as IP addresses and locations. Active vs. Passive Footprints:
- Active Footprints: Data we intentionally share online, like social media posts, emails, or website comments.
- Passive Footprints: Data generated without our explicit action, such as when visiting websites or using apps that track activity.
Growth of Digital Footprints: Every internet user has a digital footprint that grows with increased usage. Browsers save browsing history, cookies, passwords, and other data, all contributing to this footprint.
Storage and Control: Most digital footprints are stored on servers hosting applications. Users often cannot erase or control this data; once generated, it can be difficult to remove completely.
Caution Advised: Since digital footprints can trace users, locations, and device details, caution is needed regarding online sharing. Even deleted activities may leave residual footprints.
Digital Society and Netizens

In the modern world, we increasingly rely on digital technologies for managing tasks. Daily activities such as communication, social networking, banking, shopping, entertainment, education, and transportation are becoming highly dependent on online transactions. This reflects the growing trend of digital technology use across all aspects of human life.
However, as participants in digital society, it is crucial to act responsibly online, adhering to the ethics, morals, and values guiding our interactions. Anyone who uses digital technology and the Internet is a digital citizen or netizen.. good netizen uses digital technology safely, ethically, and legally.
A responsible netizen follows proper net etiquettes, communication, and social media etiquettes.
Net Etiquettes
As in real-world social interactions, proper manners online are essential. This means being ethical, respectful, and responsible while using the Internet.
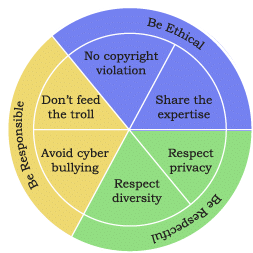
(A) Be Ethical
- No Copyright Violation: Do not use copyrighted materials without the creator’s permission, including streamed audio/video or downloaded images and files.
- Share Expertise: Share truthful, clear, and verified knowledge online. Ensure you have adequate understanding and check if the information already exists to avoid redundancy.
(B) Be Respectful
- Respect Privacy: Everyone has rights to privacy and personal expression. Respect others’ privacy and do not share private content without consent.
- Respect Diversity: Honour the diversity of knowledge, culture, and experience in groups or public forums.
(C) Be Responsible
- Avoid Cyberbullying: Cyberbullying includes insulting, humiliating, or intimidating behaviour online such as spreading rumours, threats, sharing personal information, sexual harassment, or public ridicule. It has real-world consequences and can be traced via digital footprints.
- Don’t Feed the Trolls: Internet trolls post inflammatory or off-topic messages to provoke others for amusement. Ignoring them is the best way to discourage such behaviour.
Communication Etiquettes
Digital communication spans email, texting, instant messaging, calls, video conferencing, and social networks, facilitating effective idea exchange and collaboration. Digital citizens must follow certain etiquettes for effective communication.
(A) Be Precise
- Respect Time: Avoid unnecessary replies and do not expect immediate responses due to other priorities.
- Respect Data Limits: Avoid sending large attachments; use compressed files or cloud service links.
(B) Be Polite
- Whether communication is synchronous or asynchronous, maintain politeness and avoid aggressive or abusive language.
(C) Be Credible
- Be cautious when posting comments or emails, as credibility builds over time. Users often judge reliability by previous posts on forums.
Social Media Etiquette
Social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and YouTube enable users to share content and interact. Their influence spans politics, business, culture, and education. Adhering to social media etiquette is essential.
(A) Be Secure
- Choose Password Wisely: Use strong, frequently changed passwords and never share personal credentials. Be aware of data breaches.
- Know Who You Befriend: Be cautious when connecting with unknown individuals; some may have harmful intentions.
- Beware of Fake Information: Develop skills to distinguish genuine news from fake on social networks. Validate before believing or sharing.
- Play Safe: Be careful before sharing personal photos online.
(B) Be Reliable
- Think Before Uploading: Remember uploaded content remains on servers even if deleted. Avoid sharing sensitive or confidential files carelessly.
Data Protection

Protecting data in today's digital world chiefly means safeguarding the privacy of electronically stored information. Sensitive data includes biometric data, health records, financial information, and other personal files that could cause harm or unfairness if compromised. Encryption, authentication, and other secure techniques ensure data is accessible only to authorised users for legitimate purposes.
Different countries enforce data protection laws to regulate sensitive information processing, storage, and transmission, aiming to protect it from unauthorised access or disclosure.
Intellectual Property Rights (IPR)
Intellectual property denotes ownership of inventions, literary and artistic works, designs, symbols, names, and logos. The owner is entitled to recognition and monetary benefits from their creation. IPR is safeguarded legally through copyrights, patents, and trademarks.
(A) Copyright
Copyright protects original creative works including writings, photographs, audio-visual recordings, software, and artistic pieces. For example, Rudyard Kipling’s novel "The Jungle Book" is copyrighted; its contents cannot be used without permission.
Activity:
- Suggesting a Stronger Password:. stronger password could be "T3chn0l0gy!2023," combining uppercase letters, numbers, and a special character.
- Importance of Mentioning Sources: Citing sources prevents plagiarism, gives credit to creators, and maintains academic integrity.
Executing IPR for Software:
- Copyright: Protects the software’s code and grants the creator exclusive rights to reproduce and distribute it.
- Patent: Protects the functional ideas behind the software, allowing exclusive commercialisation.
- Trademark: Protects the software’s name and logo from misuse or confusion.
Copyright Basics
- Copyright is automatically granted to original work creators.
- It grants exclusive rights including reproduction, creation of derivatives, distribution, and public performance.
- These prevent unauthorised use, copying, or selling of the work.
- Licenses are required to legally use copyrighted materials.
(B) Patent
- A patent protects inventions upon application and grants exclusive use rights for 20 years.
- Post expiration, inventions enter the public domain, allowing free use.
- This system encourages innovation by rewarding inventors.
(C) Trademark
A trademark identifies a brand or product through names, logos, slogans, or symbols. For example, only Nike can use its trademark for shoes or clothing, preventing confusion from similar brands like "Nikke."
Violation of IPR
(A) Plagiarism
Plagiarism is presenting someone else’s work or ideas as one’s own without proper credit. It includes copying content without source mention or claiming a derived idea as new. Proper attribution is essential to avoid ethical breaches and academic dishonesty.
(B) Copyright Infringement
Using copyrighted work without permission, even with attribution, constitutes infringement. For example, downloading and using an image without author consent, despite mentioning the source, is illegal.
(C) Trademark Infringement
Unauthorised use of registered trademarks can lead to legal action by the owner to protect their brand identity.
Public Access and Open Source Software
- Open licenses allow others to use and build upon copyrighted works, fostering collaboration and innovation without needing individual permissions.
- Popular licenses include GNU General Public License (GPL) for software and Creative Commons (CC) for creative content, enabling free sharing, modification, and distribution under conditions.
- GPL allows charging for software copies, unlike freeware that permits only personal use but prohibits commercial distribution.
- Free and Open Source Software (FOSS) such as Linux, LibreOffice, and Mozilla Firefox offer source code access for contribution and improvement.
- Software piracy involves unauthorized copying or distribution of software, violating copyright laws. It harms software performance, the industry, and the economy.
Cyber Crime
Cyber crime comprises illegal activities using digital systems either as targets or tools, affecting individuals, organisations, and nations by causing physical, financial, or psychological harm.
Cyber criminals exploit technology to damage data/services, spread malware, and steal information for blackmail. Common cyber crimes include hacking, ransomware, DoS attacks, phishing, email and banking fraud, and identity theft.

Hacking
Hacking is unauthorized access to computers or networks by exploiting vulnerabilities.
- Ethical Hacking: Conducted with permission to identify and fix security flaws, helping prevent attacks.
- Non-Ethical Hacking: Illegal access intending theft or damage.
Cyber crime uses computers as targets (hacking, phishing, spamming) or tools (extortion, data breaches, theft).
Click on the image to view the video on Cyber Crimes
Cyber Crime and Cyber Safety
Cyber crime involves crimes where a computer is either targeted or used as a tool.
- 1. Crime where the computer is the target:
- Hacking: Unauthorized access to steal or destroy data.
- Denial of Service (DoS) attacks: Overloading systems to cause denial of access.
- Virus and malware attacks: Malicious programs damaging or taking control.
- Phishing: Deceptive attempts to obtain sensitive data.
- Identity theft: Fraudulent use of personal information.
- 2. Crime where the computer is used as a tool:
- Cyberstalking: Harassment using digital means.
- Online fraud: Scams such as auction fraud and credit card fraud.
- Intellectual property theft: Unauthorized use of patents and copyrights.
- Cyberbullying: Online harassment causing emotional distress.
(A) Cyber Safety
Cyber safety involves precautions to protect oneself from digital threats. Key practices include:
- Strong Passwords: Use complex, unique passwords and avoid guessable information.
- Two-Factor Authentication: Add verification steps for account security.
- Be Cautious with Emails: Avoid opening suspicious emails or links.
- Secure Wi-Fi Networks: Use password-protected Wi-Fi, avoid public networks for sensitive tasks.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep software and antivirus updated for security patches.
- Be Mindful of Personal Information: Limit sharing on social media and adjust privacy settings.
- Use Reputable Security Software: Install and scan regularly against malware.
- Backup Data: Maintain backups to recover data if needed.
Following these helps reduce cyber crime risks and ensures safer online experiences.
Ransomware
Ransomware is a cyber crime where attackers restrict access to a computer’s data, often via encryption, demanding ransom to restore access. They may also threaten to release sensitive information if demands are not met. Ransomware is distributed through malicious websites, email attachments, or software downloads.
Combatting and Preventing Cyber Crime
To reduce cyber crime risks, follow these safety measures:
- Regularly backup important data.
- Use and update antivirus software.
- Avoid pirated software and download only from secure sources.
- Keep system software and browsers up to date.
- Avoid untrusted websites and heed browser security alerts.
- Use strong, unique passwords and change them periodically.
- When using others’ computers, avoid saving passwords and use private browsing modes.
- Utilise digital signatures issued by Certified Authorities for secure document authentication.
- Carefully consent to cookie use on websites.
- Perform online transactions only on known, secure websites.
Indian Information Technology Act (IT Act)
With the rapid Internet growth, cyber crimes, frauds, attacks, and cyberbullying have increased. To combat these evolving threats, many countries have enacted laws to protect personal data and Internet users' rights. In India, the Information Technology Act, 2000, amended in 2008, guides data processing, storage, and transmission.
Cyber Cells and Legal Framework
- Most Indian states have police cyber cells for cyber crime reporting.
- The IT Act recognises electronic records and digital signatures, and defines cyber crimes and their penalties.
Cyber Appellate Tribunal
- Designed to resolve cyber crime disputes involving:
- Tampering with computer source documents.
- Computer hacking.
- Unauthorized use of passwords.
- Publishing sensitive personal data without consent.
Importance of the IT Act
- Enables secure online transactions, preventing misuse.
- Allows government bodies to accept, create, and store digital official documents.
Impact on Health
With increasing use of digital devices like mobile phones, laptops, desktops, televisions, gaming consoles, and music players, we spend more time in front of screens. Improper posture during use can harm our physical and mental health. Excessive Internet time can also cause addiction, adversely affecting overall well-being.
Health impacts can be reduced by paying attention to device positioning and maintaining proper posture. Ergonomics, a scientific discipline, deals with designing workplaces and equipment to maximise safety and comfort, reducing body strain, fatigue, and injury risks from prolonged use.
Activities like watching, typing, chatting, or gaming expose our eyes to screen glare for extended periods, especially on small devices, leading to common complaints of eye strain among users.

|
33 docs|11 tests
|
FAQs on Societal Impact Chapter Notes - Computer Science for Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What are digital footprints and why are they important? |  |
| 2. How does the digital society influence the behavior of netizens? |  |
| 3. What measures can individuals take to protect their data online? |  |
| 4. What are common types of cyber crimes, and how can they affect individuals? |  |
| 5. What is the Indian Information Technology Act (IT Act), and what societal impacts does it have? |  |



















