Revision Notes: Cell - The Structural and Functional Unit of Life | Biology Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
Introduction

- Cells are the basic building blocks of all living organisms. They are both the structural and functional units of the body.
- Every living being comes from a single cell, which then divides and multiplies to form more cells. This is the fundamental principle of life.
- The concept of the cell was first introduced by Robert Hooke in 1665 when he looked at the cells in cork tree bark through a microscope.
- According to the Cell Theory, all living organisms start their life as a single cell, and each cell has the ability to perform various metabolic processes necessary for life.
Cell Number
Organisms can be classified based on the number of cells they possess:
- Unicellular Organisms: These organisms are made up of a single cell that carries out all the necessary functions for life. An example of a unicellular organism is Amoeba, which lives in water and can change its shape to move and capture food.
- Multi-cellular Organisms: These organisms consist of many cells that are specialized to perform different functions. For instance, plants have cells that are adapted for photosynthesis, while human beings have cells that perform various tasks such as digestion, circulation, and movement. Examples of multi-cellular organisms include plants, animals, and humans.
Cell Size
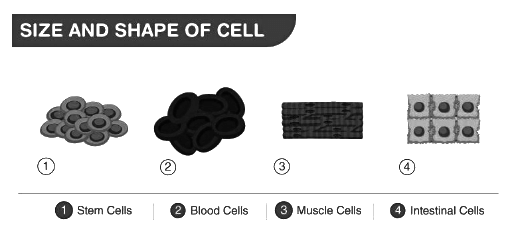
- The size of cells can vary greatly, ranging from 1/10th to 1/1000th of a millimeter.
- Largest Cell: The largest cell in the world is the egg of an ostrich, which can be several centimeters in diameter.
- Smallest Cell: The smallest known cell is Mycoplasma gallisepticum, a type of bacteria that can be as small as 0.2 micrometers in diameter.
- Largest Human Cell: The largest cell in the human body is the female ovum (egg cell), which is about 100 micrometers in diameter.
- Smallest Human Cell: The smallest cell in the human body is the red blood cell, which is about 6-8 micrometers in diameter. However, some consider the sperm cell to be the smallest due to its size and the length of its tail.
- Longest Cell: The longest cell in the human body is the nerve cell (neuron), which can extend several feet in length, especially in the case of neurons that run from the spinal cord to the limbs.
Cell Shape: The shape of a cell is often related to its function. For example:
- Red Blood Cells: These cells are circular and biconcave (dented in the middle) to allow for easy passage through blood capillaries and to maximize their surface area for oxygen transport.
- White Blood Cells: These cells have an amoeboid shape, meaning they can change shape and have extensions called pseudopodia. This allows them to squeeze through blood capillaries and engulf pathogens.
- Nerve Cells: These cells are long and slender, with a long axon, which allows them to transmit electrical impulses over long distances.
- Guard Cells: These cells are bean-shaped and are found in plant leaves. They control the opening and closing of stomata, which are small pores that allow gas exchange.
Microscope: A microscope is a tool used to make small objects appear larger, allowing scientists and researchers to study cells and other tiny structures in detail.
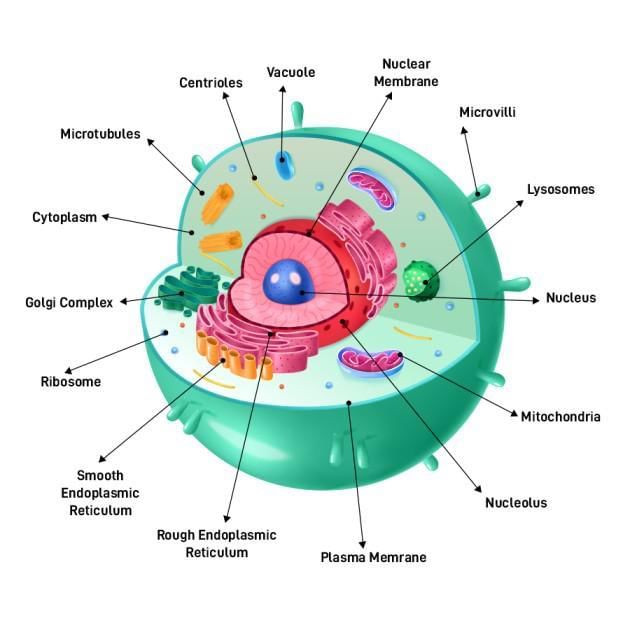
Cell Structure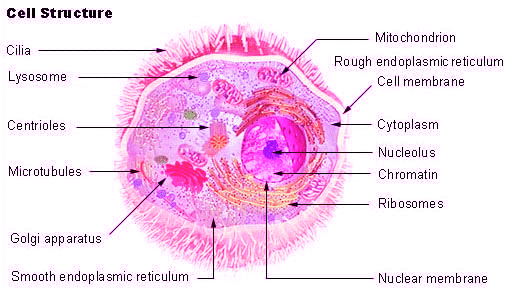
(a) Plant Cell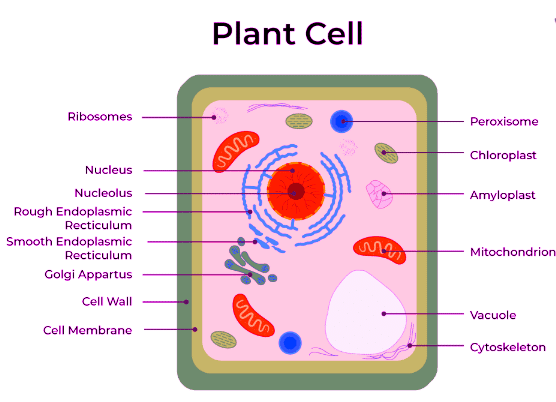 (b) Animal Cell
(b) Animal Cell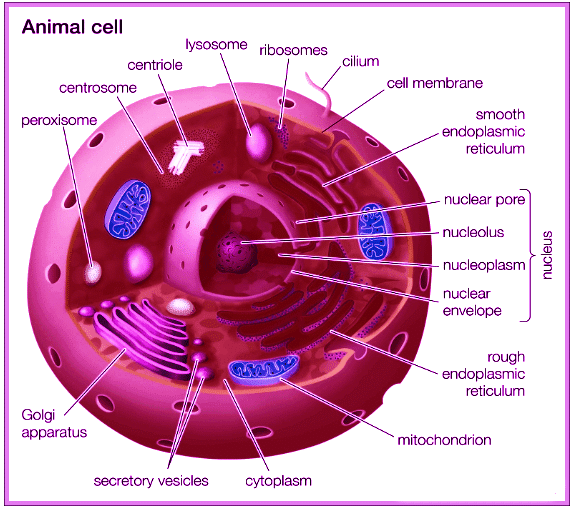
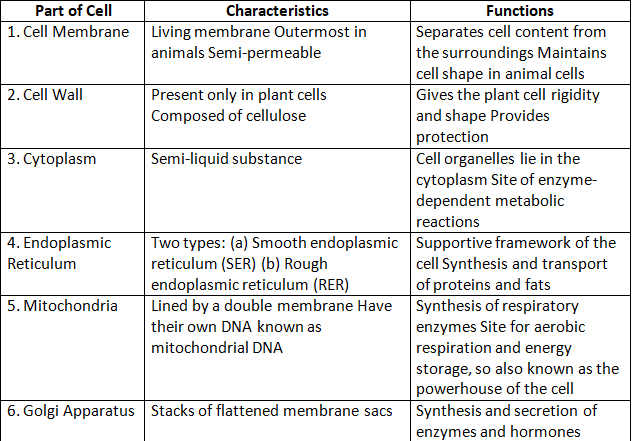
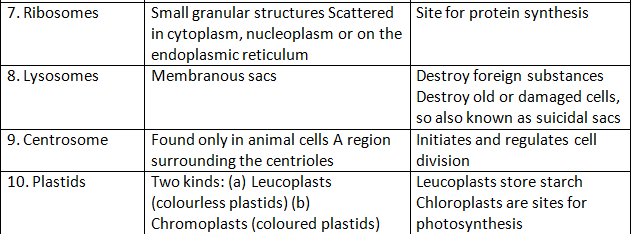
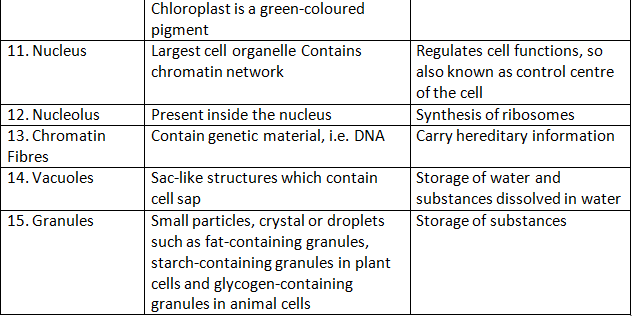
Functions of Cell Organelles
1. Nucleus: It is the control centre of the cell and is responsible for the following functions:
- It contains the genetic material (DNA) which carries the information for the synthesis of proteins.
- It regulates the activities of the cell by controlling the expression of genes.
- It plays a crucial role in cell division by ensuring the proper distribution of genetic material to the daughter cells.
- It is involved in the production of ribosomes which are essential for protein synthesis.
2. Ribosomes: Ribosomes are the protein factories of the cell and are responsible for the following functions:
- They synthesize proteins by translating the information carried by mRNA (messenger RNA).
- They play a crucial role in the assembly of amino acids into polypeptide chains which then fold into functional proteins.
- They are involved in the quality control of proteins by ensuring that only properly folded proteins are released into the cytoplasm.
3. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): The endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for the following functions:
- It is involved in the synthesis of lipids and proteins.
- It plays a crucial role in the transport of proteins and lipids to various parts of the cell.
- It is involved in the detoxification of drugs and harmful substances.
- It plays a role in the storage of calcium ions which are essential for various cellular processes.
4. Golgi Apparatus: The Golgi apparatus is responsible for the following functions:
- It modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for transport to their final destinations.
- It plays a crucial role in the secretion of proteins and lipids outside the cell.
- It is involved in the formation of lysosomes which are responsible for the degradation of cellular waste.
- It plays a role in the synthesis of certain polysaccharides and glycoproteins.
5. Mitochondria: Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell and are responsible for the following functions:
- They generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate) which is the primary energy currency of the cell.
- They play a crucial role in cellular respiration by converting glucose and oxygen into ATP, carbon dioxide, and water.
- They are involved in the regulation of cellular metabolism by controlling the levels of various metabolites.
- They play a role in the apoptosis (programmed cell death) by releasing certain factors that trigger the apoptotic pathway.
6. Lysosomes: Lysosomes are the waste disposal system of the cell and are responsible for the following functions:
- They degrade and recycle cellular waste, damaged organelles, and foreign substances.
- They play a crucial role in the removal of harmful substances from the cell.
- They are involved in the processing of certain nutrients and the release of certain metabolites.
7. Cell Membrane: The cell membrane is responsible for the following functions:
- It acts as a barrier between the cell and its external environment, controlling the entry and exit of substances.
- It is involved in the communication between the cell and its environment by facilitating the transport of signals and molecules.
- It plays a crucial role in maintaining the homeostasis of the cell by regulating the levels of various ions and metabolites.
- It is involved in the recognition of certain cells and the formation of certain tissues.
Comparison between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Microscopic Examination of Onion Peel:
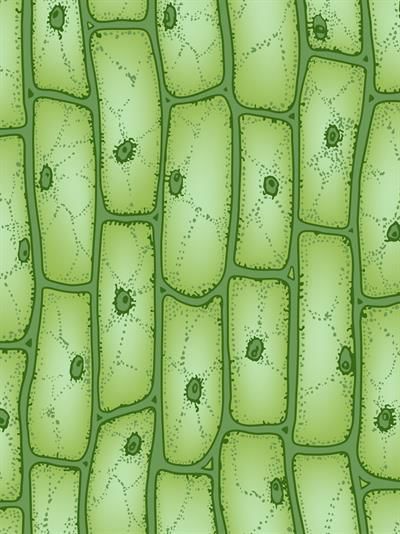
Observations:
- The cells in the onion peel are tightly packed together, indicating a strong adhesion between them.
- The nucleus of each cell is located towards one side of the cell, which is a common characteristic of plant cells.
Nucleus is Essential for Normal Life:
Importance of Nucleus:
- The nucleus is a vital organelle for the survival and normal functioning of cells.
- It contains the genetic material (DNA) that regulates all cellular activities and is responsible for the inheritance of traits.
- The nucleus plays a crucial role in cell division, ensuring the accurate replication and distribution of genetic material to daughter cells.
Experiments Demonstrating the Importance of Nucleus:
- Amoeba Division: Amoeba, a single-celled organism, divides by normal cell division (mitosis). If the nucleus is removed from an amoeba, it cannot survive because the essential genetic instructions for life processes are missing.
- Nucleus Transplant: If the nucleus from a healthy amoeba is transplanted into an enucleated (nucleus-free) amoeba, the recipient amoeba can survive and divide because it receives the necessary genetic instructions. Meanwhile, the donor amoeba, lacking a nucleus, dies.
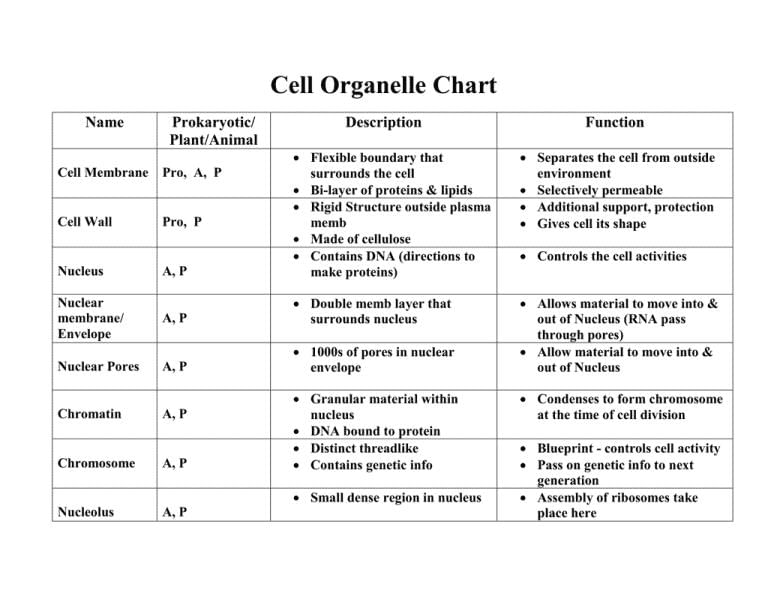
Differences between Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic Cells
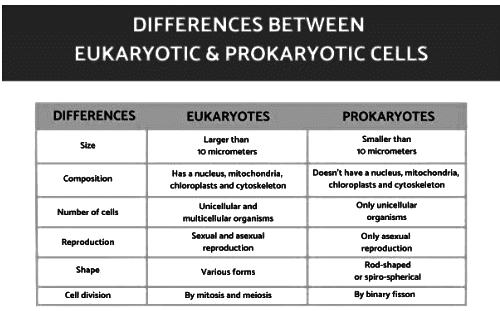
Eukaryotic Cells
- Membrane-bound cell organelles are present.
- The contents of the nucleus are separated from the cytoplasm.
- Examples include animal cells and plant cells.
Prokaryotic Cells
- Membrane-bound cell organelles are absent.
- Nuclear material lies in the cytoplasm.
- Example: Bacteria
|
55 videos|113 docs|21 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Cell - The Structural and Functional Unit of Life - Biology Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What is the basic difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? |  |
| 2. Why is the nucleus considered essential for the normal life of a cell? |  |
| 3. How do plant cells differ from animal cells in terms of structure? |  |
| 4. What are the main functions of cell organelles? |  |
| 5. How is the microscopic examination of onion peel used to study cells? |  |
















