Revision Notes: Photosynthesis - Provider of Food for All | Biology Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
Photosynthesis
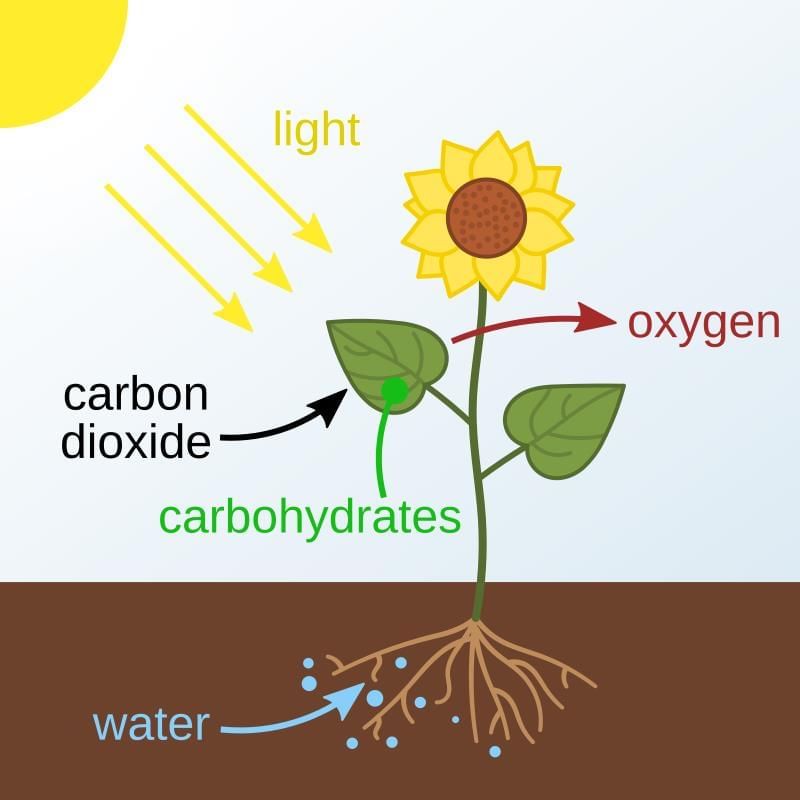
Photosynthesis is a process carried out by plant cells containing chlorophyll, where food is produced in the form of carbohydrates using carbon dioxide, water, and light energy. During this process, oxygen is released as a byproduct.
Chlorophyll - The Essential Plant Pigment
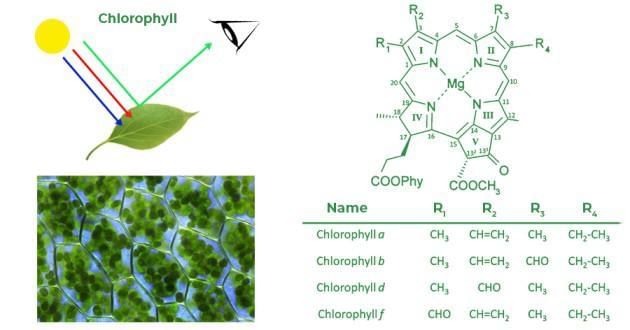
Chlorophyll is the green pigment found in green plants, and it plays a crucial role in photosynthesis. This pigment is located in a cell organelle called the chloroplast. Chlorophyll absorbs light predominantly in the red and blue wavelengths while reflecting light in the green wavelength, which is why leaves appear green.
Chloroplast
The chloroplast is an oval-shaped cell organelle bound by a membrane. It is enclosed by a double membrane, and its interior contains tightly packed, flattened sacs known as thylakoids. Chlorophyll is present in these thylakoids. The thylakoids are organized into stacks called grana, which are situated in a colourless matrix called stroma.
Regulation of Stomatal Opening
Stomata are tiny openings found in the epidermal layers of leaves. They play a crucial role in the exchange of gases during photosynthesis.
There are two theories that explain how stomata open and close:
- Sugar Concentration Theory: During the daytime, when guard cells carry out photosynthesis and produce sugar, these cells become turgid (swollen with water). This increase in turgor pressure causes the stomata to open.
- K+ Ion Concentration Theory: The opening and closing of stomata depend on the generation of a potassium ion (K+) gradient. An increase in K+ ion concentration inside the guard cells leads to stomatal opening.
Process of Photosynthesis
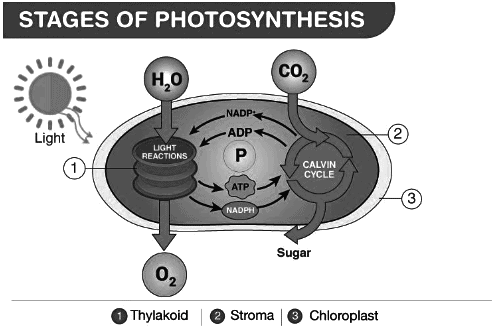
The palisade layer is the primary site for photosynthesis in leaves. Here, light energy is captured by the chlorophyll present in the mesophyll cells of the palisade layer.
The chemical equation for photosynthesis is: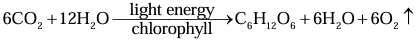
There are two main phases involved in the process of photosynthesis: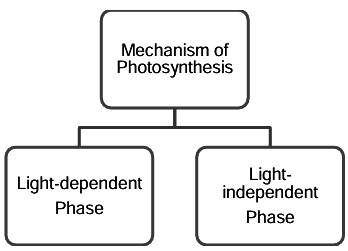
Light-dependent Phase
- Also known as the Hill reaction or photochemical phase.
- Takes place in the thylakoids of the chloroplasts.
- When exposed to light, chlorophyll absorbs light energy and becomes excited.
- This energy is used to split water molecules into hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH−).
- The hydrogen ions are captured by NADP+, reducing it to NADPH.
- Molecular oxygen (O2) is released as a byproduct during this phase.
Light-independent Phase
- This phase does not directly involve light and is also known as the Calvin cycle.
- It takes place in the stroma of the chloroplasts.
- During this phase, ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent phase are used to convert carbon dioxide (CO2) into glucose (C6H12O6).
Inter-conversion of Glucose and Starch
- When glucose is formed during photosynthesis, several molecules of glucose are combined to produce one molecule of starch through a process called polymerization.
- At night, starch is broken down into soluble glucose, which is then transported to other parts of the plant through the phloem. This process of transporting sugar to different parts of the plant is known as translocation.
Adaptations in Leaf for Photosynthesis

- Large Surface Area: Leaves are broad with large surface area
- Leaf Arrangement: Leaves are at right angle to the light source to obtain maximum light.
- Cuticle and Upper Epidermis: Cuticle and upper epidermis are transparent.
- Numerous Stomata: A large number of stomata allow the rapid exchange of gases.
- Thinness of Leaves: The thinness of leaves facilitates rapid transport.
- Chloroplasts: Chloroplasts are concentrated in the upper layers of the leaf.
- Extensive Vein System: An extensive vein system allows rapid transport to and from the mesophyll cells.
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis

External Factors
- Light Intensity: The rate of photosynthesis increases with light intensity up to a certain point and then levels off.
- Carbon Dioxide: The rate of photosynthesis rises with higher concentrations of carbon dioxide up to a limit, after which it stabilizes.
- Temperature: Photosynthesis generally increases with rising temperatures, typically up to an optimal range around 35°C.
- Water Content: Insufficient water due to excessive transpiration or reduced absorption by roots decreases the rate of photosynthesis.
Internal Factors
- Chlorophyll: Higher amounts of chlorophyll enhance the rate of photosynthesis.
- Protoplasm: Dehydration of protoplasm or excessive carbohydrate buildup in protoplasm can reduce the rate of photosynthesis.
- Leaf Structure: Factors like cuticle thickness, stomatal distribution, and leaf size affect the rate of photosynthesis.
Experiments on Photosynthesis
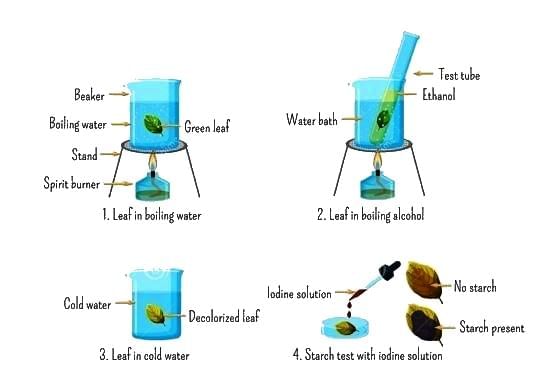
Destarching
- Before conducting experiments on photosynthesis, plants need to be destarched 24 to 48 hours in advance. This process ensures that all the starch in the leaves is removed, making them show no presence of starch initially.
- In the context of these experiments, a blue-black color indicates the presence of starch, while a brown color signifies its absence.
Necessary Factors for Photosynthesis
- Photosynthesis requires chlorophyll, sunlight, and carbon dioxide.
Importance of Photosynthesis
- Provides Food: Photosynthesis is crucial because it is the primary source of food for all animals, either directly or indirectly. Plants produce food through this process, and animals rely on plants for their sustenance.
- Provides Oxygen: Photosynthesis is responsible for releasing oxygen into the atmosphere. This free oxygen is essential for almost all organisms, as they need it for respiration.
Understanding the Carbon Cycle
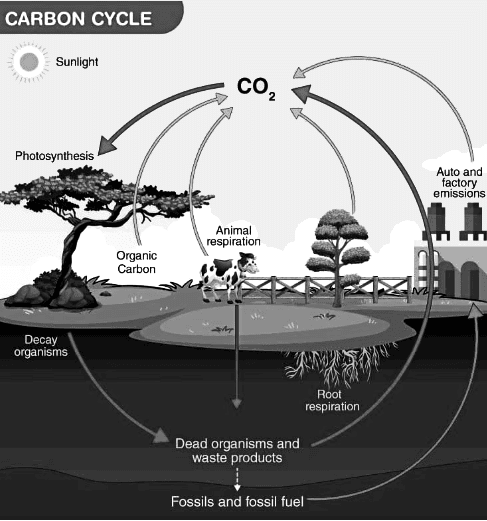
The carbon cycle involves a sequence of chemical processes where carbon is taken from the atmosphere as carbon dioxide (CO2), utilized by living organisms for various bodily functions, and eventually released back into the atmosphere.
|
55 videos|110 docs|21 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Photosynthesis - Provider of Food for All - Biology Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What are the main stages of photosynthesis? |  |
| 2. What external factors affect the rate of photosynthesis? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the destarching process in photosynthesis experiments? |  |
| 4. How do internal factors influence photosynthesis? |  |
| 5. What role does chlorophyll play in photosynthesis? |  |
















