Revision Notes: Endocrine Glands - The Producers of Chemical Messengers | Biology Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Hormonal Control |

|
| Nervous Control |

|
| Hormones |

|
| Endocrine System |

|
| Feedback Mechanism |

|
Introduction

Multicellular organisms rely on two main systems—the nervous system and the endocrine system —to communicate and regulate their activities.
Hormonal Control
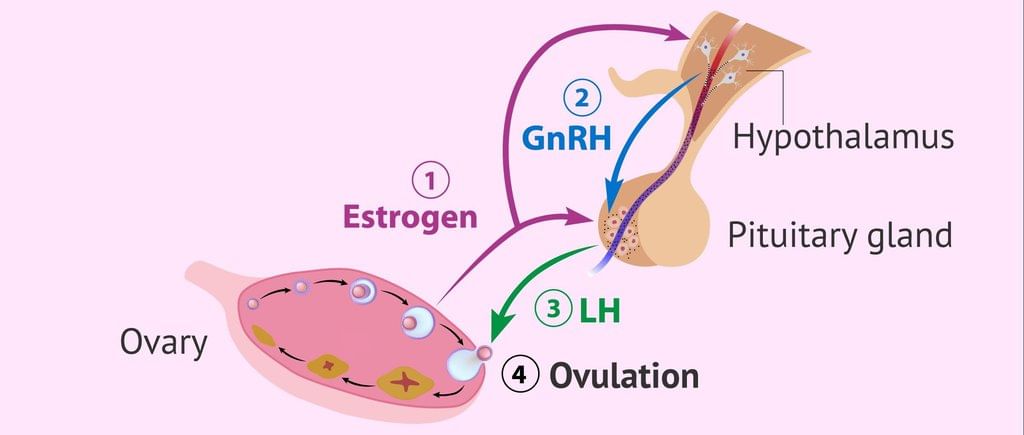
Hormonal control involves the release of chemical messengers called hormones into the bloodstream. This system can have long-lasting effects, and it plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism by bringing about specific chemical changes. Hormonal control can also affect growth, and its actions, while slower than those of the nervous system, can be either short-term or long-term.
Nervous Control
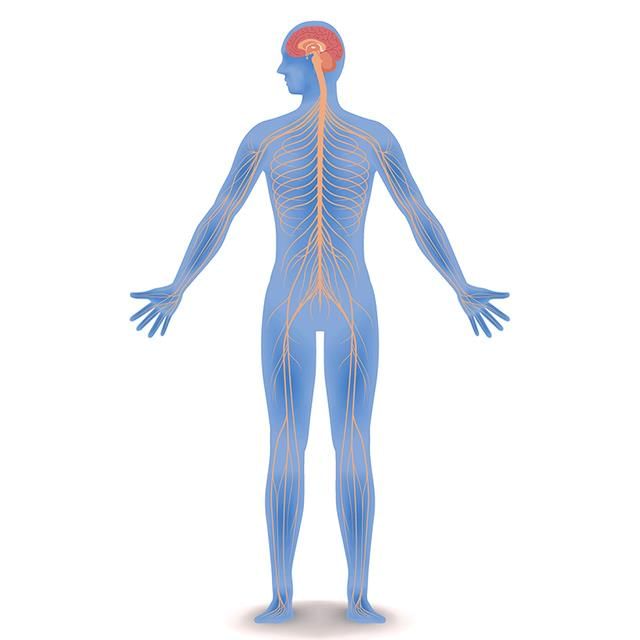
Nervous control, on the other hand, involves sending impulses to neurons to maintain and control the body’s internal environment. This system acts quickly, with immediate effects that are usually brief. Unlike hormonal control, nervous control does not influence growth or regulate metabolism through chemical changes.
Hormones
Hormones are chemical messengers secreted by glands in the body. These messengers travel through the bloodstream to target organs or cells, where they elicit specific responses. Most hormones are produced by specialized glands known as endocrine glands.
Key Characteristics of Hormones:
- Direct Secretion: Hormones are released by endocrine glands directly into the bloodstream.
- Small Quantities: Hormones are produced in very small amounts.
- High Biological Activity: Despite being secreted in small quantities, hormones are biologically very active.
- Target Specificity: Hormones act on specific target organs or cells, which are usually located away from the site of secretion.
Endocrine System
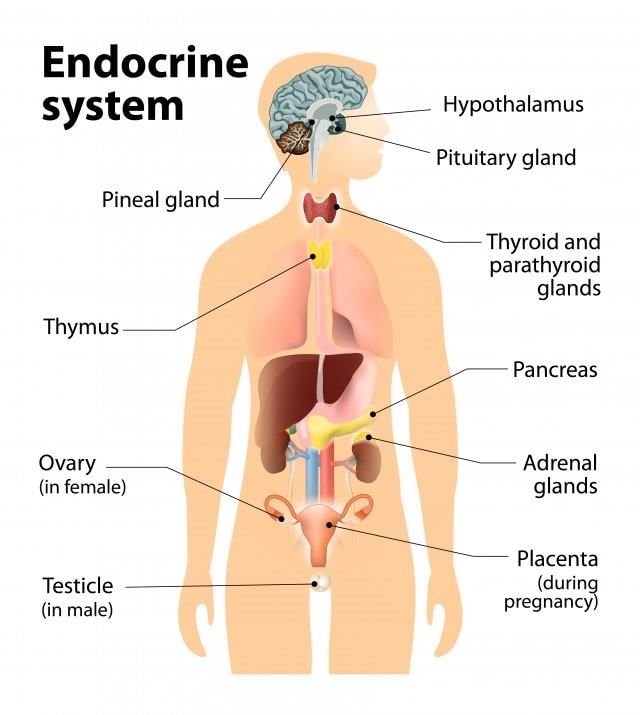
The endocrine system comprises various endocrine glands and tissues that secrete hormones to regulate different body functions.
Major Endocrine Glands:
- Adrenal Glands
- Pancreas
- Thyroid Gland
- Pituitary Gland
- Parathyroid Gland
- Thymus
- Gonads (Testes in males and Ovaries in females)
Adrenal Glands
The human body has two adrenal glands located on top of the kidneys; hence, they are also known as suprarenal glands.
Adrenal Cortex
- Mineralocorticoids: These hormones regulate mineral metabolism in the body.
- Glucocorticoids: These hormones regulate the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
Adrenal Medulla
- Adrenaline: This hormone prepares the body for the "fight or flight" response.
Effects of Adrenaline
- Heart: Beats faster and increases blood pressure, ensuring more glucose and oxygen are sent to the muscles.
- Muscles: Tense up, preparing the body for immediate action. This may cause a tense feeling or shivering.
- Liver: Converts glycogen to glucose, making glucose available in the blood for energy production.
Additional Effects of Adrenaline
- Dilation of pupils.
- Stimulation of uterine contractions during childbirth.
- Increase in blood clotting capacity.
Abnormal Secretions of Adrenal Glands
- Addison’s Disease: Caused by hyposecretion of the adrenal cortex.
- Cushing Syndrome: Caused by hypersecretion of the adrenal cortex.
Pancreas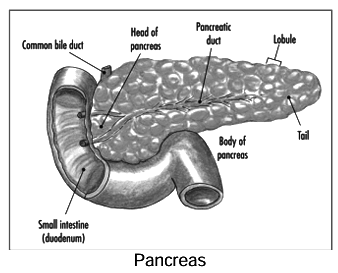
- The pancreas functions as both an exocrine and an endocrine gland.
Pancreas
(a) Exocrine Pancreas
- Secretes pancreatic juice into the duodenum via the pancreatic duct.
(b) Endocrine Pancreas: Islets of Langerhans
- Alpha Cells: Secrete glucagon, which stimulates the breakdown of glycogen into glucose in the liver.
- Beta Cells: Secrete insulin, which regulates blood sugar levels.
- Delta Cells: Secrete somatostatin, which controls the secretion of glucagon and insulin.
Disorders of Insulin Secretion
(a) Insufficient Insulin Secretion
- Causes diabetes mellitus
- Symptoms: High blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia), excessive urine production with high sugar content.
- Treatment: Diabetes cannot be cured, but blood sugar levels can be managed with insulin therapy.
(b) Over secretion of Insulin:
- Leads to low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia)
- Severe cases can cause insulin shock, where the patient becomes unconscious due to extremely low blood sugar levels.
Thyroid Gland
- The thyroid gland, shaped like a butterfly with two lobes connected by a narrow tissue called the isthmus.
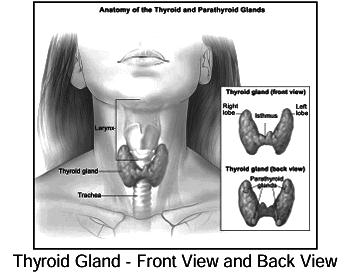
- Secretion: Produces thyroxine (regulates basal metabolism) and calcitonin (regulates calcium and phosphate levels in the blood).
- Disorders: Includes hypothyroidism, simple goitre, cretinism, myxoedema, hyperthyroidism, and exophthalmic goitre.
Pituitary Gland
- A small gland about the size of a pea.
Pituitary Gland: The Master Gland
The pituitary gland is often referred to as the master gland because it controls the secretions of all other endocrine glands. It is divided into three lobes, each responsible for producing different hormones.
1. Anterior Pituitary
- Growth Hormone: Essential for normal growth.
- Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH): Controls the activities of the thyroid gland.
- Gonadotropins (FSH/LH): Regulate the activities of the testes and ovaries.
- Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH): Regulates the activity of the adrenal cortex.
2. Intermediate Lobe
- Regulates the activity of the adrenal cortex.
3. Posterior Pituitary
- Anti-diuretic Hormone (Vasopressin): Regulates the amount of water excreted in urine. Deficiency of ADH can lead to diabetes insipidus.
- Oxytocin: Stimulates the contraction of uterine muscles during childbirth.
Feedback Mechanism
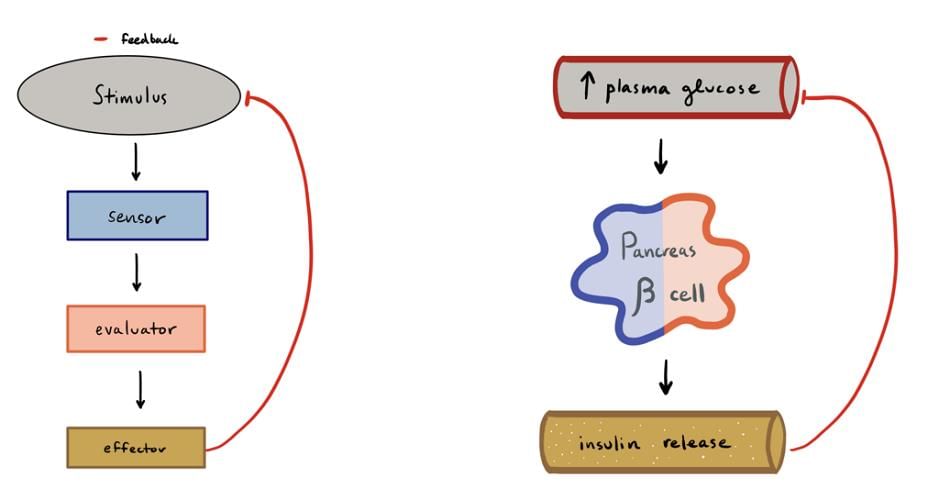
Negative Feedback Mechanism
- The body has systems in place to maintain a normal state.
- When there is a deviation from this normal state, signals are sent to either increase or decrease secretions to restore balance.
- If something falls below normal, secretions are increased; if it rises above normal, secretions are decreased.
- This process is known as a Negative Feedback Mechanism.
Gonads
1. Testes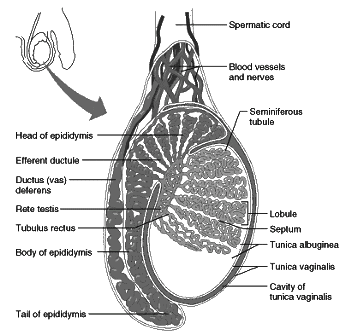
- The testes are found in males and are located in the scrotum.
- Interstitial cells within the testes produce testosterone.
- Testosterone plays a crucial role in the maturation of sperm and stimulates the growth and development of the male reproductive system.
2. Ovaries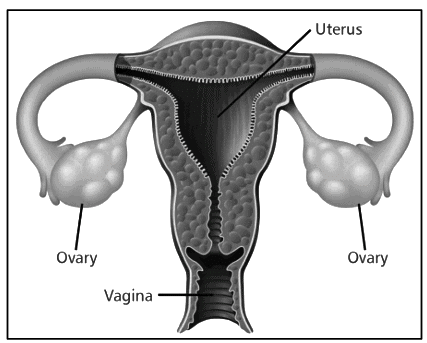
- Ovaries are the female gonads and are found in females.
- They secrete hormones such as oestrogen, progesterone, and relaxin.
- Oestrogen is responsible for the development of ovarian follicles.
- Progesterone plays a key role in the development of the corpus luteum and placenta.
- Relaxin helps to dilate the cervix towards the end of pregnancy.
Parathyroid Glands
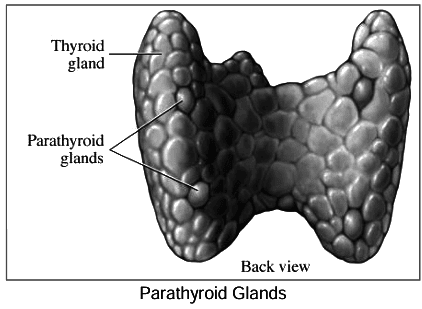
- The parathyroid glands consist of two pairs located on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland.
- These glands are responsible for secreting parathormone (PTH), a hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating calcium metabolism and maintaining a constant level of calcium in the blood.
- When PTH is secreted in insufficient amounts (hyposecretion), it can lead to a condition called tetany, characterized by muscle spasms and cramps due to low calcium levels. On the other hand, if PTH is secreted in excess (hypersecretion), it can result in the demineralization of bones, as the hormone promotes the release of calcium from bones into the bloodstream.
Thymus Gland
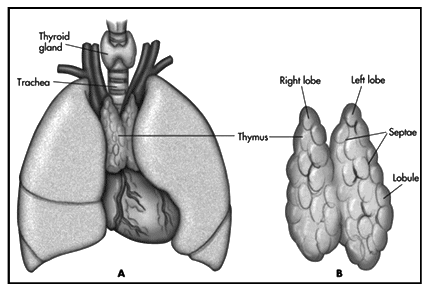 The thymus gland is a bilobed organ situated between the lungs. It produces various hormones, including thymic protein and thymosin.Functions of the Thymus Gland :
The thymus gland is a bilobed organ situated between the lungs. It produces various hormones, including thymic protein and thymosin.Functions of the Thymus Gland :
- Maturation and Distribution of Lymphocytes: The thymus gland plays a crucial role in controlling the maturation and distribution of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell essential for the immune response.
- Stimulation of Antibody Production: The hormones produced by the thymus gland also stimulate the production of antibodies, which are vital for combating infections and foreign substances in the body.
|
55 videos|189 docs|21 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Endocrine Glands - The Producers of Chemical Messengers - Biology Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What is the role of hormones in the endocrine system? |  |
| 2. How does hormonal control differ from nervous control? |  |
| 3. What are the main endocrine glands in the human body? |  |
| 4. What is a feedback mechanism in the context of the endocrine system? |  |
| 5. Can hormonal imbalances affect health? How? |  |















