Revision Notes: Population - The Increasing Numbers and Rising Problems | Geography for Grade 11 PDF Download
Introduction

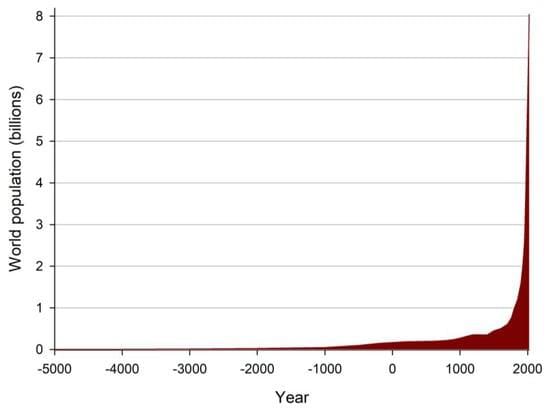
- The world population was about 1 million around 50,000 years ago.
- By 10,000 years ago, the population had increased to approximately 5.3 million.
- 11 July 1987: World population reached 5.0 billion.
- 1995: Population was nearly 5.6 billion.
- 12 October 1999: Population crossed 6 billion.
- 11 July: Observed as World Population Day.
- Current Birth Rate: More than 100,000 babies born every day.
Reasons for Rapid Population Growth
1. Industrial Revolution
- Marked a significant period in human population growth.
- Led to increased job opportunities and improved food production, making life more comfortable.
2. Advances in Medical Science
- The 20th century saw major breakthroughs in medical science, including the discovery of antibiotics and vaccines for various diseases.
- These advancements significantly reduced mortality rates, leading to a rapid increase in population growth.
Three Cultural Revolutions and Population Growth
- Each cultural revolution was followed by a period of rapid population increase, which eventually stabilized or rose slowly.
- Flattened Curves: Indicate stability in growth or a very slow rise.
- Wavy Gaps: Represent long periods of stability in growth or very slow rise.
Population Explosion – A Serious Global Concern
Six Main Reasons for a Sharp Rise in World Population in the Recent Past
- Better Healthcare
- Better Medical Aid
- Availability of Food
- Improved Nutrition
- Large-scale Immunisation
- More Number of Children Reaching Reproductive Age
With a fast-increasing world population, there are numerous problems
- Decreasing open spaces
- Shrinking of forests
- Increasing industrialisation causing air, water and soil pollution
- Rapid and intense shortage of drinking water and other resources
- Increasing health hazards
Population in India
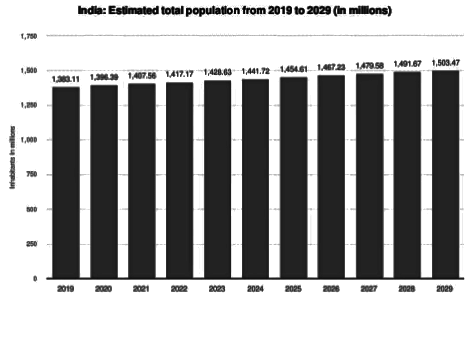
- The trend of increasing population in India is alarming.
- A few years ago, it was estimated that India’s population in 2001 would be about 760 million, but it has already crossed the 1 billion mark.
Factors Responsible for Population Explosion in India
- People from rural regions are illiterate and superstitious.
- More number of children in a family.
- High infant mortality results in more number of pregnancies.
- Poor standards of living and poverty provide no recreation other than sex.
Rising Population – Pressure on Natural Resources
- Food:
For an unchecked rise in population, food would be running short. - Land:
Man uses more and more land for cultivation and to build residential colonies, factories and industries.
Thus, usable land would become less and less available. - Forests:
Rise in population leads to deforestation.
Deforestation has led to serious problems such as droughts, flash floods, soil erosion and extinction of flora and fauna. - Water:
With an increase in population, the availability of clean and germ-free water for drinking purposes would become scarcer.
An increasing population leads to pollution of rivers, lakes, ponds etc. - Energy:
Reserves of fossil fuels are fast depleting.
The increasing population would need more non-conventional resources. Resources such as solar energy, wind energy and tidal energy must be used by humans to minimise the use of conventional resources.
Population Growth and Urbanization - Serious Pressure on Resources
Urbanization: The population is increasing rapidly. Villages are transforming into towns, towns are becoming cities, and cities are evolving into megacities. This process is known as urbanization.
Rising Living Standards of Growing Population
- Use of household equipment such as high-end gadgets and better furniture
- Use of more clothes
- Use of different modes of conveyance such as bike, car, bus, taxi etc.
The above-mentioned factors lead to the overuse of natural resources. Some also lead to pollution.
Need to Check Exploitative Use of Resources
It is necessary for individuals to become conscious and contribute to the sustainable use of natural resources.
Sustainable development
Sustainable development is a type of development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Sustainable development can be achieved by:
- Reduction in excessive use of natural resources
- Recycling and reuse of resources wherever possible
- Increased use of renewable resources such as solar energy and wind energy
Rate of Population Growth
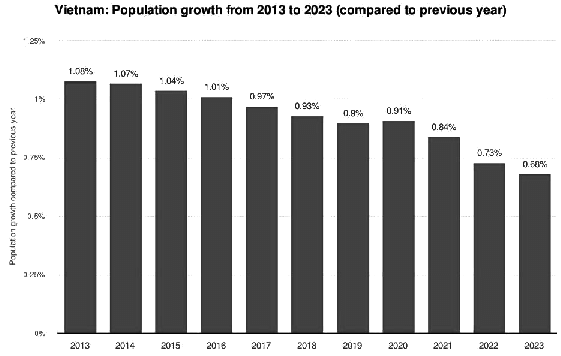
It is important to reduce the rate of population growth because it can lead to several positive outcomes, such as:
- Less burden on dwindling resources: A lower population growth rate means that the demand for limited resources, such as water, food, and energy, will be reduced. This can help ensure that these resources are available for future generations and prevent overexploitation.
- Better healthcare: With a smaller and more manageable population, healthcare systems can provide better services and access to medical care for individuals. This can lead to improved overall health and well-being.
- Better education: Reducing population growth can also lead to better educational opportunities for children. With fewer students to accommodate, schools can provide more personalized attention and resources, leading to better educational outcomes.
A Few Statistical Terms
Demography
Demography refers to the statistical study of human populations, focusing on aspects such as size, density, distribution, and other vital statistics. It involves analyzing data related to population characteristics and trends.
Population Density
Population density is the measurement of the number of individuals living per square kilometer at a specific point in time. It provides insights into how crowded or sparse a particular area is in terms of its population.
Birth Rate (Natality)
The birth rate, also known as natality, is the number of live births occurring in a population per 1,000 individuals per year. It is a key indicator of population growth and reproductive patterns.
Death Rate (Mortality)
The death rate, or mortality rate, is the number of deaths occurring in a population per 1,000 individuals per year. This statistic helps assess the mortality levels within a population and can impact overall population growth.
Growth Rate of Population
The growth rate of a population is determined by the difference between the birth rate and the death rate.
- If the birth rate exceeds the death rate, the population grows.
- Conversely, if the birth rate is lower than the death rate, the population declines.
Importance of Implementing Control Measures
When a country's population exceeds its capacity, it leads to various issues such as:
- Decrease in per capita income
- Reduction in natural resources like land, minerals, wood, and fuels
- Deterioration of general health
- Decline in overall quality of life
Population Education and Control

Given the current population growth, it is essential to educate people about the necessity of controlling population growth and the measures that can be taken.
Awareness should be raised regarding population-related issues.
People need to understand the benefits of having small families and the drawbacks of having many children.
Family Welfare
Family welfare is indicated by an inverted red triangle.
Family welfare centres
These centres, marked with the symbol, offer assistance and advice on family planning.
Three Key Aspects of Family Welfare
- Family Planning: Emphasizing the importance of having a small family.
- Total Welfare: Ensuring the well-being of small families, including the diet and nutrition of children and pregnant mothers.
- Child Care: Providing subsequent care for children, such as immunization and oral rehydration therapy, to guarantee the survival of young ones.
Methods of Contraception

1. Hormonal Method
- Hormonal contraceptives are available in the form of tablets or pills, commonly referred to as contraceptive pills.
2. Barrier Methods
I. Condom
- Condoms are a barrier method used by men to prevent sperm from entering the vagina during sexual intercourse.
II. Diaphragm
- The diaphragm is a flexible, dome-shaped barrier that can be inserted deep into the vagina to cover the cervix, preventing sperm from entering the uterus.
III. Spermicidals
- Spermicidal agents are chemicals placed in the vagina near the cervix to kill sperm and prevent them from reaching the egg.
3. Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
- Intrauterine devices such as Lippe’s Loop and Copper T are commonly used in India.
- These devices are fitted inside the uterus and work by preventing the implantation of a fertilized egg (blastocyst) in the uterine lining.
4. Surgical Methods
I. Tubectomy
- Tubectomy is a surgical procedure performed on women to prevent pregnancy.
- During this procedure, the abdomen is opened, and the fallopian tubes are either cut or tied with a nylon thread, closing the passage for the ovum (egg) to travel from the ovary to the uterus.
II. Vasectomy
- Vasectomy is a surgical procedure performed on men as a method of permanent contraception.
- During this procedure, a small cut is made in the scrotum, and the vas deferens (the tube that carries sperm from the testicles) is ligated (tied off).
- A small piece of the vas deferens is removed between the two ligatures, preventing sperm from being released during ejaculation.
- It is often recommended that the husband undergo vasectomy in a couple.
5. Induced Abortion
- Induced abortion, also known as Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP), is an option for couples who do not wish to continue with an unintended pregnancy.
- Abortion is legally permitted and can be requested by any woman at government hospitals without any cost.
FAQs on Revision Notes: Population - The Increasing Numbers and Rising Problems - Geography for Grade 11
| 1. What are the main reasons for rapid population growth globally? |  |
| 2. How does population growth affect urbanization and resource management? |  |
| 3. What is the current population situation in India, and what challenges does it face? |  |
| 4. Why is it important to implement population control measures? |  |
| 5. What are some common methods of contraception, and how do they contribute to population control? |  |















