Revision Notes: Aids to Health | Biology Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Immunity |

|
| Immune System |

|
| Toxins and Antitoxins/Antibodies |

|
| Vaccination and Immunisation |

|
| Antiseptics and Disinfectants |

|
| Antibiotics |

|
| First Aid |

|
Health refers to a condition of complete physical, mental, and social well-being, and not just the absence of disease or weakness.
Immunity

Immunity is the capability of an organism to fend off the invasion of antigens or pathogens. Harmful substances like pollutants and pathogens can enter our bodies in various ways. Our body’s defense mechanism operates on two levels:
(A) Local Defence System: This system acts as the first line of defense, preventing the entry of germs into the body.
(B) Immune System: This system comes into play once the germs have breached the body’s initial defenses and entered the body tissues.
Local Defence System
1. Protective Mechanical Barriers
- Skin: The skin is made of a protein called keratin, which is largely impermeable to germs. However, any scratch or cut in the skin can provide an entry point for germs. When the skin is injured, blood clotting helps to plug the cut and prevent the entry of harmful microorganisms.
- Hair: Hair present inside the nostrils plays a crucial role in trapping dust particles that may carry germs, thereby preventing their entry into the body.
- Mucus: Mucus is a slimy secretion produced by the epithelial lining of various organs. It acts as a protective barrier by trapping bacteria and preventing their entry into the body.
2. Expulsion Mechanisms
- Coughing, Sneezing, and Vomiting: These are direct methods the body uses to expel germs or foreign particles that have entered the body.
3. Germ-killing Secretions
- Saliva, Sweat, Tears, and Nasal Secretions: These bodily secretions play a role in killing germs.
- Hydrochloric Acid: This acid is secreted by the stomach and is effective in killing germs that may enter the body along with food.
4. Germ-fighting White Blood Cells (WBCs)
- WBCs: White blood cells are crucial components of the immune system. They engulf and destroy germs through a process known as phagocytosis.
Merits of the Local Defence System
- Instantaneous Response: The local defence system acts immediately to prevent the entry of harmful agents.
- Broad Effectiveness: It is effective against a wide range of potentially infectious agents.
Immune System
Immunity can be classified into two main categories:
(A) Innate Immunity
It is inherited from the parents.
(I) Non-specific Innate Immunity : General natural resistance to all infections.
(II) Specific Innate Immunity : Natural resistance to a particular kind of germ.
(B) Acquired Immunity
Resistance to a disease is acquired during the lifetime of an organism.(I) Actively Acquired Immunity : Resistance is developed due to a previous infection.
(II) Passively Acquired Immunity : Immunity is provided from an outside source in the form of antibodies.
(a) Naturally Acquired Passive Immunity : Mother’s antibodies reach the foetus through the placenta.
(b) Artificially Acquired Passive Immunity : Antiserum injections are given to stimulate the production of antibodies.
Differences between Active Immunity and Passive Immunity
Active Immunity
- Produced by one’s own body.
- Induced by infections or by contact with immunogens.
- Provides effective and long-lasting protection.
Passive Immunity
- Received from an outside source.
- Readymade antibodies are provided.
- Protection is less effective and does not ensure protection against subsequent infections.
Antigen : It is a chemical found on the surface membranes of germ cells.
Toxins and Antitoxins/Antibodies
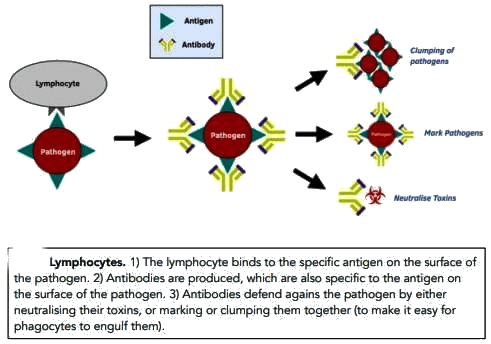
Toxins are harmful substances created by animals, plants, or bacteria. For instance, snake venom and the poisons from insect stings are examples of toxins.
An antibody is a protein found in blood serum that is produced in response to injected antigens. Antivenins for snake venoms are examples of antibodies.
Characteristics of Antibodies
- Antibodies are a type of protein known as immunoglobulins.
- They are produced by lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell.
- The body can produce a wide variety of antibodies.
- Antibodies are specific to particular antigens, meaning they can only act on specific antigens.
AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome)
Cause: AIDS is caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), which attacks the immune system by infecting T-cells.
How HIV Works: When HIV infects T-cells, it replicates itself, and when these cells die, they release new viruses that go on to infect more cells.
Transmission: HIV is transmitted through:
- Sexual intercourse
- Sharing contaminated needles
- Blood transfusion
- From infected mother to unborn fetus
Awareness: World AIDS Day is observed on December 1st to raise awareness about the seriousness of AIDS and the available protective measures.
Vaccination and Immunisation
Vaccination involves introducing dead or weakened germs into a living being's body to develop immunity against a specific disease.
There are different kinds of vaccines:
- Killed Germs: For example, the TAB Vaccine.
- Living Weakened Germs: For example, the BCG Vaccine.
- Living, Fully Poisonous Germs: For example, the Cowpox Vaccine.
- Toxoids: Vaccines that contain inactivated toxins.
Immunisation is the process of developing resistance to disease-causing germs or their toxins by introducing killed germs or germ substances to induce the production of specific antibodies.
Antiseptics and Disinfectants

Antiseptics
- Antiseptics are mild chemical substances that are used to kill germs when applied to the body.
- Examples of antiseptics include:
- Lysol (dilute)
- Carbolic acid
- Iodine
- Benzoic acid
- Mercurochrome
- Boric acid
Disinfectants
- Disinfectants are strong chemical substances that are applied to spots and places where germs thrive and multiply.
- Examples of disinfectants include:
- Cresol
- Phenol
- Lysol
- 40% formalin
- Lime
- Bordeaux mixture
- DDT
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are substances produced by microorganisms that can kill or inhibit the growth of other microorganisms.
The first antibiotic, penicillin, was discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1928.
Sources of Antibiotics
- Penicillin is produced commercially from the mold Penicillium chrysogenum.
- Streptomycin is obtained from the bacterium Streptomyces.
Uses of Antibiotics
- Antibiotics are used to fight infections in humans and animals.
- They are also used as food preservatives, to treat animal feed, and to control plant pathogens.
In 1930, a group of chemicals known as sulphonamides was discovered, which also have antibiotic properties.
First Aid

First aid refers to the prompt and initial care provided to an individual who has experienced an accident, sudden illness, or any other medical emergency, until professional help, such as an ambulance or a doctor, arrives.
1. Bleeding:
- Rinse the cut area with clean water.
- Apply pressure to the area using a piece of clean cotton wool.
- Use a mild antiseptic on the wound.
2. Fractures:
- Remove or loosen clothing around the injured area.
- For a fractured arm, use a sling to support the arm.
3. Eyes:
- If an object gets into the eyes, avoid rubbing them.
- Gently rinse the eyes with clean water.
4. Unconsciousness:
- If someone becomes unconscious, lay them down comfortably.
- Loosen their clothing.
- Ensure they have access to fresh air.
5. Heart Attack:
- Lay the person flat and ensure they have fresh air.
6. Burns:
- Rinse the burned area with cold water for several minutes.
- Apply burn ointment to the affected area.
7. Swallowing Poison:
- Attempt to induce vomiting.
8. Snake Bite:
- Extract some blood from the bite wound.
- Apply a tourniquet above the bite site to slow the spread of venom.
9. Stinging:
- Extract some blood to remove the venom.
- Apply an alkali substance like baking soda or lime.
10. Artificial Breathing:
- Position the victim flat on their back.
- Fold the victim’s arms and press them against their ribs.
- Mouth-to-mouth resuscitation is the most effective method for restoring breathing.
- In cases of drowning, pressing on the back can help expel water.
|
55 videos|189 docs|21 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Aids to Health - Biology Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What is the role of the immune system in protecting the body? |  |
| 2. How do vaccines strengthen the immune system? |  |
| 3. What are the differences between antiseptics and disinfectants? |  |
| 4. What are antibiotics, and how do they work? |  |
| 5. What are common first aid practices for treating minor injuries? |  |














