Revision Notes: Conventional Sources of Energy | Geography Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Conventional Sources of Energy |

|
| Coal |

|
| Petroleum |

|
| Natural Gas |

|
| Hydel Power |

|
Conventional Sources of Energy
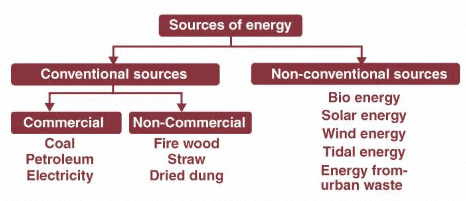
Conventional sources of energy refer to the energy sources that have been used for a long time and are still being utilized on a large scale. Examples of conventional sources of energy include coal and petroleum.
Coal

Coal is a significant mineral resource in India. It is found as a sedimentary rock alongside carbonaceous shale, sandstone, and fine clay. The formation of coal dates back approximately 300 million years when large land plants and trees were buried under the Earth's surface. Over time, sediments were deposited over these buried plants and trees, and the resulting heat and pressure led to physical and chemical changes, ultimately forming coal.
Coal can be classified into four main types based on its carbon content and moisture levels:
- Anthracite: This is the highest and hardest quality of coal. It burns slowly without producing much smoke and has a high heating value, leaving very little residue.
- Peat: Peat represents the first stage of wood transformation into coal. It is considered inferior to the other three varieties of coal.
- Lignite: Also known as brown coal, lignite is a lower-grade coal with about 40% carbon content and less combustible material.
- Bituminous: Bituminous coal is known for its high carbon content and heating value. It burns slowly and produces minimal smoke.
Distribution and Uses of Varieties of Coal in India
Anthracite
- Distribution: Found in Jammu and Kashmir.
- Uses: Ideal for domestic use as it is a smokeless fuel. Used in metallurgical processes and the iron and steel industry.
Bituminous
- Distribution: Found in Gondwana coal fields.
- Uses: Known as cooking coal, used to produce coke, coal gas, and steam coal. High-grade bituminous coal is also used for domestic purposes.
Lignite
- Distribution: Found in Tamil Nadu, Rajasthan, West Bengal, and Puducherry.
- Uses: Primarily used for the generation of electricity.
Peat
- Distribution: Found in the Nilgiri mountains, Kashmir valley, and swampy areas of coastal plains.
- Uses: Limited commercial use.
Advantages of Using Coal
- Power Generation: Coal is a crucial source of power for running machines, trains, ships, and dynamos.
- Manufacturing: Used in the manufacturing of iron and steel.
- Direct Heat: Source of direct heat for domestic purposes, burning of bricks, tiles, and in iron and brass factories.
- Chemical By-products: When burnt in a closed chamber, coal produces various chemicals such as ammonia and benzol as by-products.
Disadvantages of Coal in India
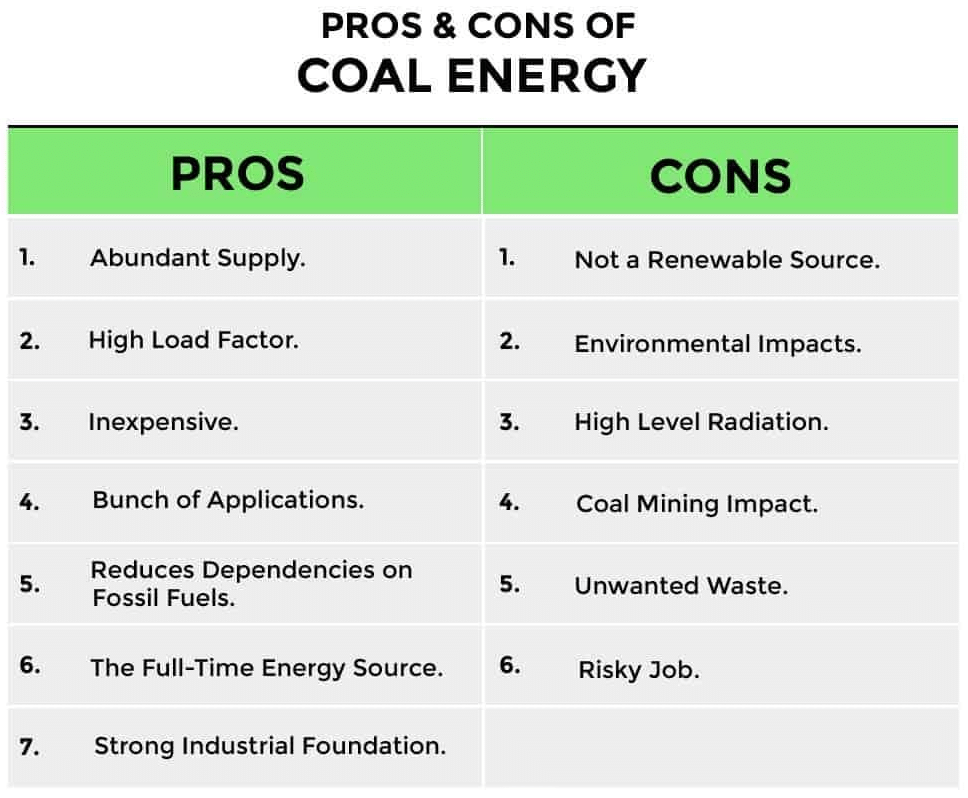
- Low Calorific Value: The coal found in India has a low calorific value, meaning it produces less energy per unit compared to higher-quality coal.
- Scattered and Limited Reserves: Coal reserves in India are not only limited but also scattered, making extraction and production more challenging and less efficient.
- High Production and Transportation Costs: The cost of producing and transporting coal in India is very high, which adds to the overall expense and reduces its competitiveness as an energy source.
- Environmental Pollution: Burning coal leads to large-scale pollution, contributing to environmental degradation and health issues.
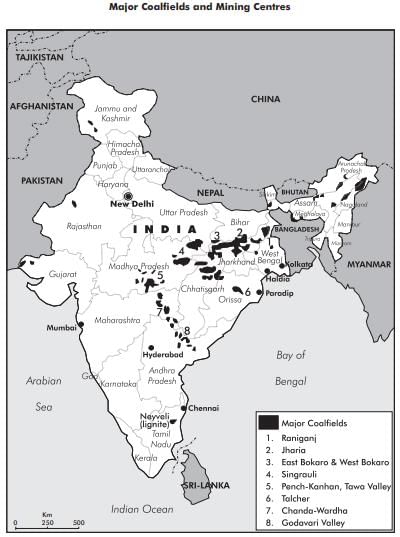
- Coalfields in India: There are two main types of coalfields in India:
- Gondwana Coalfields:These account for 98% of the total coal reserves in India. The Gondwana coalfields are primarily located in river valleys such as the Damodar, Mahanadi, and Godavari. These coalfields are found in several states, including:
- West Bengal
- Jharkhand
- Odisha
- Chhattisgarh
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Uttar Pradesh
- Andhra Pradesh
- Telangana
- Tertiary Coalfields:Coal found in these fields has a high moisture content. These coalfields are located in the northeastern states of India, including:
- Assam
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Meghalaya
- Nagaland
- Lignite Deposits: The Neyveli lignite field in Tamil Nadu is the largest lignite deposit in South India.
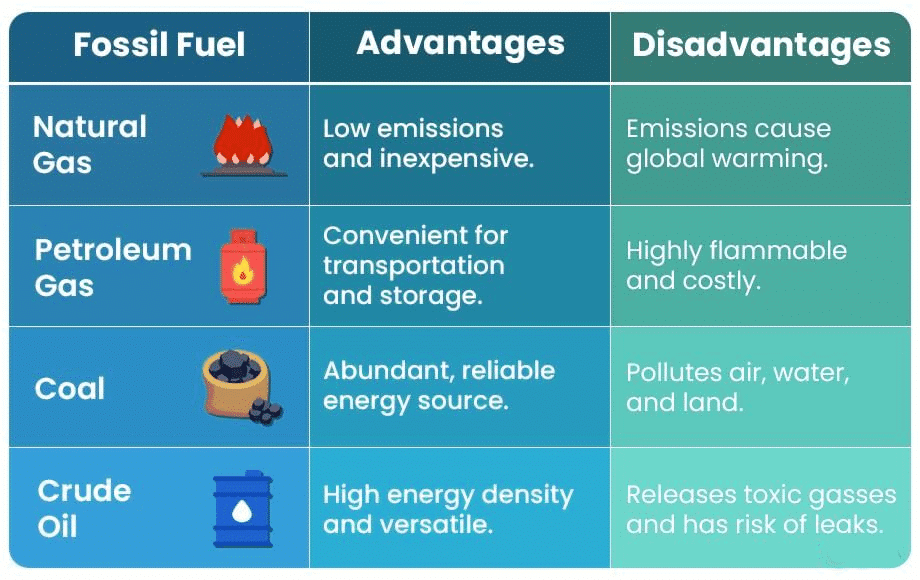
Petroleum
Petroleum is a crucial mineral resource, often referred to as 'liquid gold' because every part of crude petroleum is utilized without waste. It is found in underground reservoirs within sedimentary rock formations such as sandstone, shale, and limestone.
During the refining process, various products are obtained from petroleum, including petrol, diesel, kerosene, tar, liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), lubricants, and paraffin wax.
Advantages
- High Energy Density: Petroleum has a high energy density, with 1 kg of oil capable of generating 10,000 kcal of energy.
- Liquid Form: Being in liquid form, petroleum can be easily transported through pipelines or vehicles.
- Fuel Source: Petroleum is a primary fuel source, with its by-products such as diesel, gasoline, jet fuel, kerosene, and LPG being widely used as fuels.
- Petrochemical Production: After refining, petroleum is used to produce various petrochemical products, including synthetic rubber, synthetic fiber, PVC, phenol, varnishes, lubricating oil, and paraffin wax.
- Power Generation: Petroleum is also used for generating power.
Disadvantages
- Non-Renewable: Petroleum is a non-renewable energy source, making its availability limited. The increasing demand is rapidly depleting petroleum resources.
- Environmental Impact: The extraction and burning of petroleum produce greenhouse gases, contributing to environmental pollution and global warming.
- High Cost: Due to its limited supply and high demand, the cost of petroleum is high.
- Inflammability: Petroleum is highly inflammable, posing a fire risk.
- Oil Spills: Spilling oil in water not only pollutes oceans but also leads to the death of many marine animals.
Oil Refineries

Oil refineries play a crucial role in transforming crude oil into various useful products. During the refining process, crude oil is separated and processed into different fractions based on their boiling points. The main products obtained from this process include:
- Light Distillates: These include gasoline, liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), and naphtha. These products are used as fuels for vehicles, cooking, and as feedstock for petrochemical industries.
- Middle Distillates: This category includes diesel and kerosene, which are used for transportation, heating, and as aviation fuel.
- Heavy Products: These include bitumen (used in road construction), petroleum (used for various industrial applications), and petroleum coke (used as a fuel and in industrial processes).
Reliance Petroleum Limited at Jamnagar, Gujarat, was the first private sector refinery in India. Most refineries are strategically located near oilfields or coastal areas to reduce transportation costs.
ONGC Platform at Mumbai High Mumbai High is a prominent offshore oil field situated 176 km off the coast of Mumbai in the Arabian Sea. The name "Mumbai High" refers to the elevated syncline in the rock structure where oil reserves have been discovered. This field is known for its high productivity and substantial reserves, estimated at 50 million tonnes of oil.
Digboi Oil Field in upper Assam is recognized as the largest oilfield in India. Cambay Basin in Gujarat is another significant oil-bearing region, along with other noteworthy sites in the state, including Kalol, Koyali, Kosamba, Sanand, Ankleshwar, and Navgaon.
Natural Gas

Natural gas is a fossil fuel that is found in association with mineral oil. It is formed from the decomposed remains of dead plants and animals that were buried under the earth's surface.
Distribution
Natural Gas: More than three-fourths of India’s natural gas comes from Mumbai High. Other production areas include Assam, Tamil Nadu, Rajasthan, and Tripura.
Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG)
Compressed Natural Gas (CNG)
Advantages of Natural Gas
- Environmentally Friendly: Natural gas is primarily composed of methane, which produces fewer carbon emissions compared to other fossil fuels.
- Ease of Storage and Transportation: It can be stored and transported through pipelines, cylinders, and tankers, both on land and at sea.
- Cost-Effective: Natural gas is generally cheaper than diesel or gasoline.
- Industrial Uses: It is used in the production of hydrogen, ammonia (for fertilizers), paints, and plastics.
Disadvantages of Natural Gas
- Safety Concerns: Leaks in natural gas can be extremely dangerous, as they may lead to explosions and fires. Methane, the main component of natural gas, is more harmful than carbon dioxide when it comes to greenhouse gas emissions.
- Non-Renewable: Being a fossil fuel, natural gas is a non-renewable source of energy.
- High Infrastructure Costs: The setup for production and distribution of natural gas is very expensive.
- Mileage Issues: Vehicles running on natural gas typically provide less mileage compared to those running on gasoline.
Hydel Power
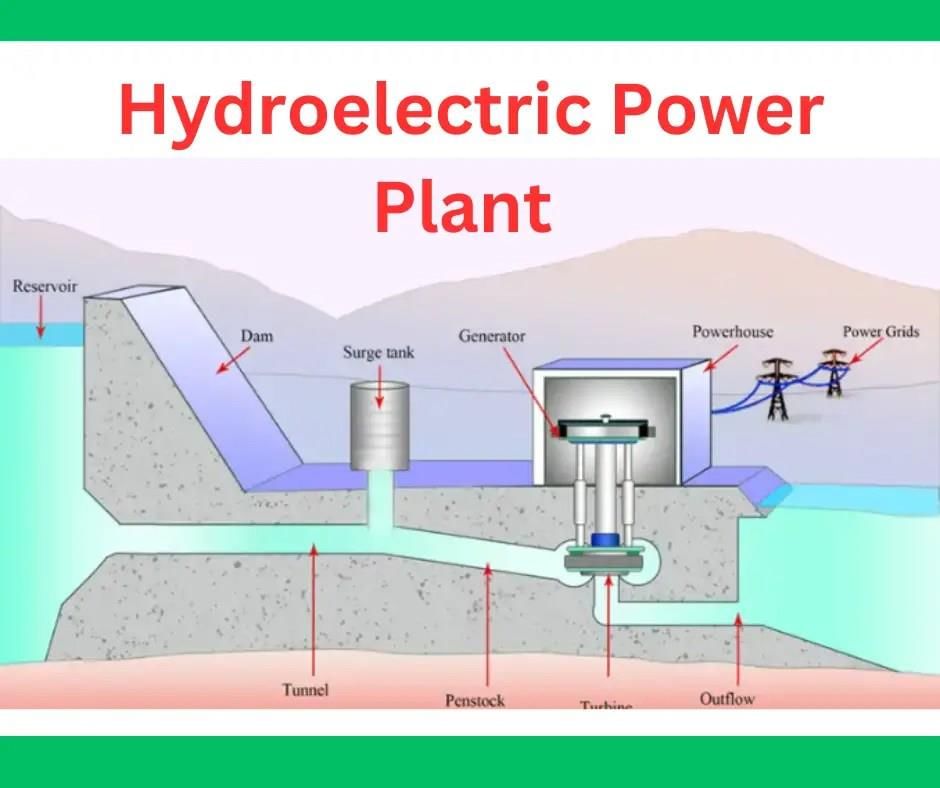
Hydel power, also known as hydroelectricity, is the generation of electricity from water. This process occurs when water stored in a dam falls from a great height onto a turbine, causing its blades to spin forcefully. This rotation drives a generator, producing electricity. Hydropower projects are considered multipurpose because they serve various functions, including irrigation, domestic and industrial water supply, and flood control.
- Clean and Non-Polluting: Hydel power is a clean source of energy as it does not release any toxic gases or pollutants into the atmosphere.
- Renewable Energy Source: Hydel power is renewable, meaning it can be used repeatedly without depleting the resource.
- Water Conservation: Dams built for hydroelectricity help in saving and restoring water resources.
- Economic and Sustainable: The cost of generating electricity from hydro power is cheaper compared to fossil fuels and nuclear power.
- High Initial Costs: The initial investment for constructing dams for hydroelectricity is extremely high.
- Environmental Impact: Building large dams can lead to the destruction and submergence of forests on a significant scale.
- Seismic Risks: The construction of massive dams may trigger earthquakes in the surrounding areas.
- Displacement of Communities: Dam construction can displace local communities from their villages, disrupting their livelihoods.
Bhakra Nangal Dam

The Bhakra Nangal Dam project is a collaborative effort involving the governments of Punjab, Haryana, and Rajasthan.
The Bhakra dam holds the distinction of being the second highest dam in India. Its reservoir, known as Gobind Sagar, has a storage capacity of 9.3 billion cubic meters, making it the third largest water reservoir in the country.
The Bhakra-Nangal project includes:
- The Bhakra Dam : This dam is not only the second highest in India but also features the third largest water reservoir in the country.
- The Nangal Dam : Located at Nangal on the Sutlej River in Punjab, this dam provides water to the Bhakra irrigation canal.
- Power Houses : The project includes four power houses for electricity generation.
- Bhakra Canal System : This system irrigates agricultural lands in Punjab, Haryana, and Rajasthan.
The objectives of the Bhakra Nangal project are:
- To provide water for irrigation purposes.
- To generate hydroelectric power.
- To prevent flooding in the Sutlej-Beas river basin.
Hirakud Dam
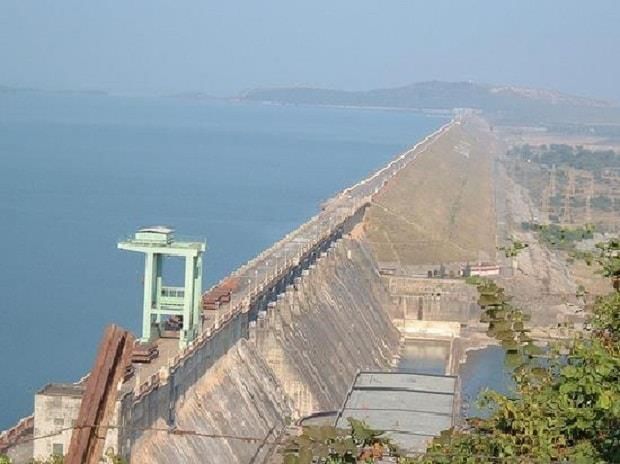

The Hirakud Dam is constructed across the Mahanadi River and was among the first multipurpose river projects initiated after India gained independence, with its construction completed in 1953. It holds the distinction of being the longest major earthen dam in Asia and also creates the largest artificial lake on the continent. The dam features two observational towers, known as Gandhi Minar and Nehru Minar, located on either side of the structure.
Benefits of the Hirakud Dam
- Flood Control: The dam plays a crucial role in controlling floods in the Mahanadi delta, protecting a delta area of 95,000 square kilometers in the districts of Cuttack and Puri.
- Irrigation: It irrigates 75,000 square kilometers of land, benefiting the kharif and rabi crops in the districts of Sambalpur, Bargarh, Bolangir, and Subarnpur.
- Power Generation: The dam has the capacity to generate up to 307.5 megawatts of electrical power through its two power plants located at Burla and Chiplima.
|
33 videos|148 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Conventional Sources of Energy - Geography Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What are the main types of conventional sources of energy? |  |
| 2. How do fossil fuels contribute to energy production? |  |
| 3. What are the environmental impacts of using conventional energy sources? |  |
| 4. What is the role of nuclear energy in conventional energy sources? |  |
| 5. How does hydroelectric power work as a conventional energy source? |  |















