Revision Notes: Non-Conventional Sources of Energy | Geography Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Solar Energy |

|
| Wind Energy |

|
| Nuclear Power |

|
| Biogas |

|
Introduction
Non-conventional sources of energy, also referred to as renewable or alternative energy sources, have gained prominence as viable alternatives to traditional non-renewable energy sources. Examples of these sources include wind energy, solar energy, geothermal energy, tidal energy, and biogas. Non-conventional resources are often considered the energy resources of the future.
Some of the Non-Conventional Sources of Energy are:
- Solar Energy
- Wind Energy
- Tidal Energy
- Geothermal Energy
- Nuclear Power
- Biogas
Solar Energy

India, being a tropical country, receives ample sunlight throughout the year, with most regions experiencing around 300 clear sunny days annually. This makes solar energy a viable and abundant resource for generating electricity and heat.
Solar Cells
Solar cells, also known as photovoltaic cells, are made from thin wafers of semiconductor materials like silicon and gallium. When sunlight falls on these cells, they generate electricity.
- Solar cells are commonly used in devices such as calculators, electronic watches, street lighting, traffic signals, and water pumps.
- When a group of solar cells is connected together, they form a solar panel, capable of generating a large amount of solar energy.
Solar Cookers
Solar cookers utilize solar heat by reflecting solar radiation onto a glass sheet covering a black insulated box.
- Raw food is placed in the black insulated box, which is designed to retain heat.
- The heated box emits infrared radiation, which is trapped by the opaque glass, ensuring that a significant amount of energy remains inside the cooker.
- Recently, spherical reflectors have been preferred over plain mirrors in solar cookers due to their improved heating effect and efficiency.
Solar Water Heaters
Solar energy can be harnessed to heat water using solar water heaters. These systems typically use flat plate collectors, which are shallow rectangular trays filled with water.
- The collectors consist of an insulated box painted black on the inside, with a glass lid to capture and store solar heat.
- Inside the box, there is a black-painted copper coil through which cold water flows. As the coil heats up, the water is warmed and directed into a storage tank.
- Many housing societies have begun installing solar panels on rooftops to provide lighting for common areas and to heat water for various purposes.
Benefits of Solar Energy
- Solar energy is a clean and renewable source of power.
- It can be used for various purposes, such as generating electricity in areas without access to the energy grid and distilling water in regions with limited clean water supplies.
- Solar energy systems require minimal maintenance.
- They help conserve fossil fuels like coal and petroleum and reduce energy bills.
Wind Energy

Wind energy is an affordable, dependable, and cleaner source of power.
Production of Wind Energy
- Electricity is generated using windmills, which harness the wind's force to rotate their blades. This rotational motion drives various machines, including water pumps, flour mills, and electric generators.
- Wind farms, which consist of several windmills installed in a specific pattern, are typically located in coastal areas, open grasslands, and hilly regions.
- India has the fifth-largest wind programme in the world, with its largest wind farm cluster situated from Nagarcoil to Madurai in Tamil Nadu. Other significant wind farms are found in states such as Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Kerala, Lakshadweep, and Maharashtra.
Advantages of Wind Energy
- Wind energy is a renewable power source.
- It does not produce pollution, making it a cleaner alternative.
- Wind energy reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
- Wind turbines can be installed on existing agricultural farms, benefiting rural economies where most optimal wind sites are located.
- Landowners can generate additional income by installing wind turbines on their land.
Tidal Energy

Tidal energy is generated from the periodic rise and fall of ocean waters caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and the sun. This phenomenon creates a substantial amount of energy known as tidal energy.
How Tidal Energy is Generated
- Tidal energy is harnessed through the construction of a tidal barrage.
- During high tide, seawater flows into the reservoir of the barrage, turning turbines connected to generators to produce electricity.
- During low tide, the stored seawater in the barrage reservoir flows back into the sea, turning the turbines in the process.
Potential Sites for Tidal Energy in India
- Gulf of Kutch
- Gulf of Cambay
- Sunderbans
- Lakshadweep Islands
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
Advantages of Tidal Energy
- Predictability: Water in the oceans moves in highly predictable patterns, making it easy to harness tidal energy.
- Renewable and Inexhaustible: Tidal energy is a renewable and inexhaustible source of energy.
- Cleaner Source: Tidal energy is a cleaner source of energy compared to fossil fuels.
- Low Maintenance Cost: Although the initial cost of setting up tidal energy systems is high, the maintenance cost is extremely low.
- Efficiency: Tidal energy can be produced even with slow-moving water.
Geothermal Energy

Geothermal Energy is the energy produced by using the heat of the earth, which is stored in the core of the earth. The core of the earth is very hot and it heats the surrounding rocks and soil. This energy can be used to generate electricity.
Generation of Geothermal Energy
- Geothermal energy is generated by using the extremely high temperatures found in the deeper geothermal reservoirs.
- Hot water is pumped from deep underground through a well under high pressure.
- When the water reaches the surface, the pressure is reduced, causing the water to turn into steam.
- The steam spins a turbine, which is connected to a generator that produces electricity.
- After passing through the turbine, the steam cools off in a cooling tower and condenses back into water.
- The cooled water is then pumped back underground to repeat the process.
- Geothermal energy is widely distributed and easily accessible.
- It is environmentally friendly due to low emissions of sulfur, carbon dioxide, and greenhouse gases.
- Geothermal energy is not affected by weather or seasonal changes.
- It operates independently of external supply and demand factors and fluctuations in exchange rates.
Distribution of Geothermal Energy in India
- India has the potential to produce around 12,000 MW of geothermal energy.
- Geothermal plants in India are located in Manikaran (Himachal Pradesh) and Puga Valley (Ladakh).
- Hot springs in these areas have been grouped into different geothermal provinces, including:
- Himalayan Geothermal Province
- Naga-Lushai Geothermal Province
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands Geothermal Province
- Cambay Graben
- Son-Narmada-Tapti Graben
- West Coast
- Damodar Valley
- Mahanadi Valley
- Godavari Valley
Nuclear Power

Nuclear power comes from the energy stored in the nuclei of atoms of naturally occurring radioactive elements like uranium, thorium, and plutonium.
Generation of Nuclear Energy
- Nuclear fission is the process where a large nucleus splits into two smaller nuclei, releasing a significant amount of energy.
- This energy produces heat, which is used to heat water and generate steam.
- The steam drives a turbine connected to a generator, producing electricity.
There are two main types of reactors used to generate electricity:
- Pressurized Water Reactors (PWR) : In these reactors, water is kept under high pressure, preventing it from boiling. The heated water is circulated through tubes in generators, turning the turbine.
- Boiling Water Reactors (BWR) : In BWRs, the water is boiled by the heat from the nuclear reaction, turning into steam to drive the turbine.
- Water is reused in both systems.
Nuclear Power in India
- Nuclear power is the fourth largest source of electricity in India.
- India has 21 nuclear reactors using uranium and thorium for power generation.
- The Monazite sands of Kerala are rich in thorium, which is also used for nuclear power.
Advantages of Nuclear Energy
- Nuclear energy is renewable and reduces dependence on fossil fuels.
- It saves on raw material costs, and its transportation and handling costs are minimal.
- Nuclear power initiates a continuous process of energy production, generating electricity for about 90% of the year.
- It also helps reduce the price volatility of other fuels, such as petrol.
Biogas
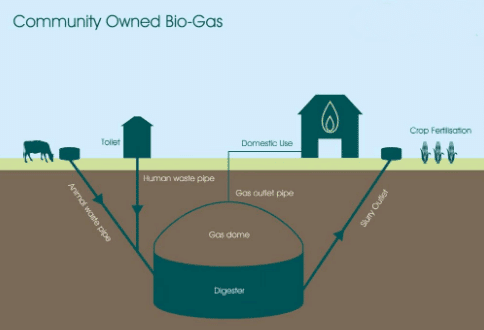
Biogas is a renewable energy source produced by the anaerobic degradation of organic matter, such as plant and animal wastes, in the presence of water and absence of oxygen. It consists mainly of methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and hydrogen sulfide.
Generation of Biogas
- A biogas digester involves placing a digester tank underground, where a mixture of dung and water is fed into the tank.
- Inside the tank, bacteria break down the organic material, producing biogas, which is collected and used for cooking and lighting.
- The leftover slurry is rich in nutrients and can be used as fertilizer.
- Biogas is a clean, non-polluting, and affordable source of energy, with the added benefit of not requiring storage due to direct supply from the plant.
- The sludge left behind after biogas production is a valuable fertilizer containing bacterial biomass.
- In India, the Ministry of Non-Conventional Energy Sources has been promoting biogas production by setting up biogas plants across the country.
|
33 videos|86 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Non-Conventional Sources of Energy - Geography Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What are the main advantages of tidal energy? |  |
| 2. How is nuclear energy generated? |  |
| 3. What is biogas and how is it produced? |  |
| 4. What are the distribution methods for renewable energy sources? |  |
| 5. What are the challenges associated with biogas production? |  |















