Revision Notes: Waste Management-I | Geography Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Waste |

|
| Need for Management of Wastes |

|
| Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming |

|
| Depletion of the Ozone Layer |

|
| Acid Rain |

|
Waste

Waste refers to any material that is discarded because it is no longer useful. According to the Environment Protection Act of 1990, waste includes scrap materials, effluents, and unwanted surpluses that result from various processes. There are three main types of waste: solid, liquid, and gaseous.
- Solid Waste: This includes items like garbage, food leftovers, decaying fruits and vegetables, cans, bottles, and ashes.
- Liquid Waste: This refers to sewage discharged from households, hospitals, restaurants, offices, and factories. Oil spills also fall under liquid waste.
- 3Gaseous Waste: This includes fuel exhausts containing gases like carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and sulfur dioxide. Smog is an example of gaseous waste.
Waste can also be classified into toxic and non-toxic categories:
- Toxic Wastes: These are hazardous wastes that pose serious health risks to humans and animals. They are often produced from industrial processes, the use of chemical fertilizers, biomedical waste from hospitals, and nuclear activities. Examples include chlorinated solvents, asbestos, organochlorine pesticides, waste paints, and the release of large amounts of sulfur and nitrogen.
- Non-toxic Wastes: These wastes do not pose significant health risks and are usually domestic in nature. Examples include food leftovers, fruit and vegetable peels, and other household waste.
Sources of Wastes
Wastes are classified based on their origin into the following categories:
Domestic Wastes
- Domestic wastes are generated from household activities and include items such as:
- Polythene bags
- Toilet sewage
- Batteries
- Expired medicines
- Scrap metals
Industrial Wastes
- Industrial wastes come from various large and small-scale industries and can be categorized based on the type of industry:
- Mining: Mining activities generate wastes that include harmful chemicals and liquids, leading to the degradation of land and water resources.
- Cement Industry: These industries produce fine dust particles that pose serious health risks.
- Oil Refineries: Oil refineries contribute to environmental problems by generating wastes such as organic sulphur compounds, hydrocarbons, and organic acids.
- Construction Sites: Wastes from construction sites include bricks, plastics, pipes, and roofing and insulating materials.
- Paper Industry: Effluents from paper industries contain sulphur dioxide and chlorine, which can be harmful to aquatic life.
- Textile Industry: Wastes from the textile industry include effluents resulting from the boiling and processing of fibres.
- Chemical Industries: This category includes manufacturing industries as well as fertiliser and pesticide industries.
- Metal Industries: Metal industries produce wastes containing harmful substances like copper, lead, acids, chromium, and zinc, which can adversely affect aquatic life.
Agricultural Wastes

Agricultural waste refers to the waste produced by the agricultural sector, which is inclusive of agricultural activities such as planting, harvesting, and processing of agricultural products. Agricultural waste includes plant, animal, and agro-processing waste.
Agricultural waste is classified into the following:
1. Plant Remains or Crop Residues
Field Residues:
- These are the wastes left in agricultural fields after harvesting.
- Examples include the straw of barley, wheat, sorghum, and rye.
Process Residue:
- These are the remains discarded after the processing of crops.
- Examples include husks, seeds, and bagasse.
2. Animal Wastes
Slurry:
- A mixture of water and animal excrement, often used as fertilizer.
Poultry Litters:
- Waste material from poultry farms, including bedding and droppings.
3. Processing Wastes
Agro-Based Industries:
- Industries that process agricultural products often produce waste.
Examples:
- Stalks: Remains of plants after harvesting, used in various applications.
- Press Mud: A byproduct of sugar purification, consisting of dirt and color removed from sugar.
4. Fertilizer Components
Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium:
- Essential nutrients found in fertilizers, used to enhance soil fertility and crop yield.
5. Pesticides and Insecticides
Dangerous Chemicals:
- Pesticides and insecticides often contain harmful chemicals such as nitrogen, sulfur, and DDT.
Impact on Humans:
- These chemicals can affect humans by entering the food chain, leading to potential health risks.
Municipal Wastes

Municipal waste refers to the waste generated within a municipality or local area, typically from sources such as shops, offices, banks, hospitals, and schools. This type of waste can be categorized into several types, including sewage.
Sewage is a specific type of municipal waste that consists of liquid waste discharged from various facilities, including kitchens, bathrooms, lavatories, laundries, and laboratories. Sewage contains a mix of mineral and organic matter, wastewater, and human excreta. Due to the high levels of nitrogen and organic matter present in municipal sewage, untreated sewage can have a detrimental impact on the ecosystem.
Degradable and Non-Degradable Wastes
Biodegradable Pollutants:
- Biodegradable wastes are those that can decompose naturally into the soil. These wastes do not pose a significant environmental challenge because they break down over time.
- Examples of biodegradable wastes include paper, egg shells, leaves, and vegetable peels. These materials can be easily broken down by natural processes.
Non-biodegradable Pollutants:
- Non-biodegradable pollutants, on the other hand, take a long time to decompose or may never decompose at all. These wastes pose a serious environmental challenge because they accumulate in the environment and do not return to the soil.
- Examples of non-biodegradable pollutants include metal cans and plastic products, such as plastic bags and bottles. These materials can persist in the environment for many years.
Biodegradable wastes can be further classified into two categories:
- Simple Biodegradable Wastes : These are materials that can be easily broken down by natural processes. Examples include leaves, fruit peels, and vegetable scraps.
- Complex Biodegradable Wastes : These are materials that are more difficult to decompose. Examples include leather shoes, tin cans, and other items that take longer to break down.
Biomedical Wastes
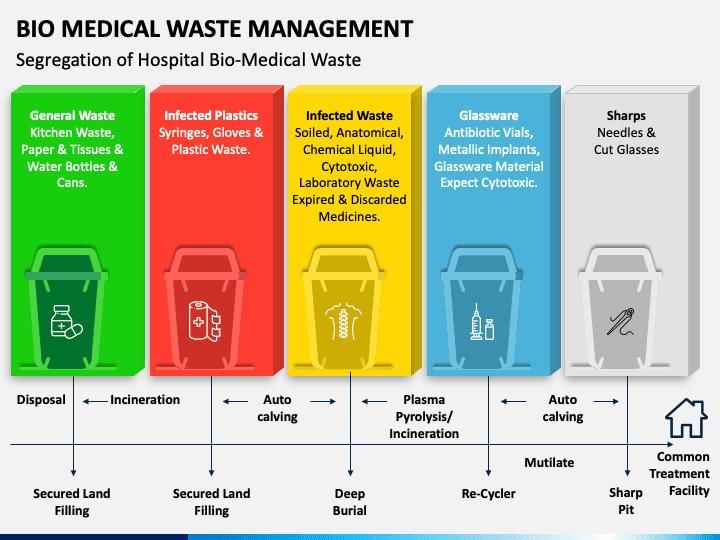
Biomedical wastes refer to the waste materials generated during the medical treatment, diagnosis, and immunization of humans and animals. This category also includes waste produced during research and experiments conducted in laboratories. Examples of biomedical wastes are needles, syringes, tissues, body parts, chemicals used in pathological tests, and polythene bags.
Nuclear Waste

Nuclear waste consists of radioactive materials generated from nuclear reactors, nuclear power plants, trident submarines, and X-ray machines. Among all types of waste, nuclear waste is considered the most hazardous due to its emission of harmful radiation, which can lead to various diseases, including cancer and genetic disorders. For instance, medical X-rays account for about 18% of the artificial radiation used in radiotherapy for diagnostic purposes.
Need for Management of Wastes
Waste on Lands
- Waste management is crucial because improper disposal can lead to the spread of various diseases.
- Accumulation of waste on land and in water bodies poses a significant health risk as it creates breeding grounds for disease-causing insects and organisms.
- Houseflies are known to spread diseases such as typhoid, diarrhoea, dysentery, and cholera.
- Sand flies can transmit diseases like kala-azar and sand fly fever.
- Tsetse flies are responsible for spreading sleeping sickness.
- Mosquitoes are vectors for diseases such as malaria, yellow fever, chikungunya, and dengue.
- Rodents can spread diseases like plague and salmonellosis.
- Dogs can transmit rabies and hydatid diseases.
Wastes in Water
- Industrialisation and urbanisation contribute to water pollution in several ways:
- Sewage contains pathogenic agents, which are microorganisms capable of causing diseases.
- Effluents discharged by industries may contain metal salts and complex organic chemicals that are harmful to water quality.
- Fertilisers and pesticides used in agriculture can run off into water bodies, contaminating water resources.
- Radioactive substances released into the environment can have severe health impacts, including damage to reproductive organs, cancer, and genetic disorders.
Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming
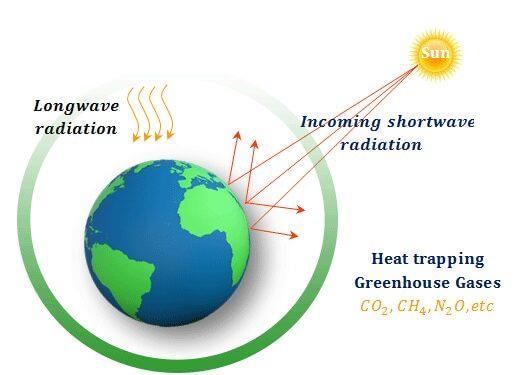
The Earth receives sunlight, which keeps it warm. However, the Earth does not absorb all the heat; it emits some of it back into space. This process helps maintain a uniform temperature on the Earth's surface. A greenhouse, where plants are grown, works on a similar principle. The glass building absorbs the Sun's heat but prevents it from escaping, thereby increasing the temperature inside. Similarly, greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, absorb the Sun's energy and do not reflect it back into space, leading to an increase in the Earth's temperature. Four gases are mainly responsible for creating the greenhouse effect on Earth : carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxide, and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). Many human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, have contributed to global warming.
Effects of Global Warming
The Earth's temperature is expected to rise by 2°C to 5°C in the next hundred years. This increase in temperature will lead to several significant impacts:
- Melting of Polar Ice: The warming will cause the snow in the polar regions to melt, resulting in a rise in sea levels. This rise in sea levels could submerge coastal areas.
- Changes in Climate: The increase in temperature will alter climatic conditions worldwide by affecting wind and rainfall patterns.
- Groundwater Depletion: Higher temperatures will lead to increased rates of transpiration, which could deplete groundwater resources.
Depletion of the Ozone Layer
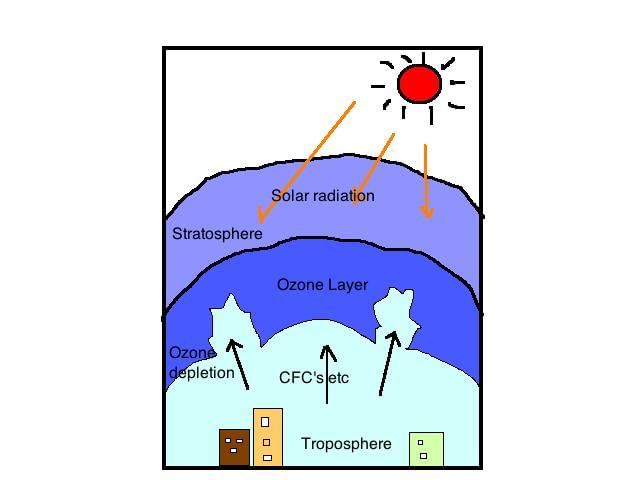
- The ozone layer, located in the stratosphere, plays a crucial role in protecting the Earth by absorbing the Sun's harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays. However, this layer has been declining due to the release of nitrogen oxide and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
- Supersonic jets contribute to this depletion by emitting nitrogen gas, which harms the ozone layer. CFCs, commonly used in various materials such as paints, foam, and thermal insulation, escape into the atmosphere during their application and further damage the ozone layer.
- A significant breach in the ozone layer has been identified over Antarctica. The absence of a healthy ozone layer increases the risk of diseases in humans, including skin cancer and cataracts, due to heightened exposure to UV rays. Additionally, these rays can cause genetic disorders and disrupt the ecological balance, particularly in marine ecosystems.
Acid Rain
Acid rain occurs when pollutants like sulfuric acid and nitrogen oxides, released from the burning of fossil fuels and industrial activities, combine with water droplets in the air and fall as rain.
The effects of acid rain include:
- Harm to the human nervous system, potentially leading to neurological diseases.
- Negative impact on aquatic life.
- Corrosion of buildings, monuments, and bridges.
- Increased soil acidity, resulting in reduced soil fertility.
Soil Pollution

Acid rain can lead to soil pollution, which negatively impacts the processes of mineralization and decomposition in the soil. This, in turn, reduces soil fertility and soil aeration. Therefore, it is crucial to prevent the accumulation of waste and minimize soil pollution to maintain healthy soil conditions.
Waste Management

Effective waste management is essential to protect our environment.
One of the simplest ways to manage waste is by following the 3-R system : reduction, reuse, and recycling.
- Reduction: We should reduce the use of resources by avoiding overuse and overexploitation.
- Reuse: Materials should be used multiple times to conserve resources.
- Recycling: Materials like glass and paper should be recycled to create new products. This practice helps in protecting our environment by reducing the demand for new resources and minimizing waste.
|
33 videos|148 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Waste Management-I - Geography Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What is waste management and why is it important? |  |
| 2. What are the main types of waste that need management? |  |
| 3. How does waste contribute to the greenhouse effect and global warming? |  |
| 4. What is the relationship between waste management and the depletion of the ozone layer? |  |
| 5. What are the causes and effects of acid rain, and how does it relate to waste management? |  |




















