Revision Notes: United Nations | History and Civics Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
The United Nations

The United Nations (UN) was established after the Second World War with the aim of creating a more effective organization than the League of Nations. World leaders recognized the need for a powerful body to maintain peace and prevent future conflicts.
Reasons for the Formation of the United Nations

- Impact of the World Wars
The two World Wars in the twentieth century caused immense suffering, with millions of casualties and widespread economic depression. This devastation highlighted the urgent need for a robust international organization to prevent future wars. - Failure of the League of Nations
The League of Nations was established after the First World War to promote peace but failed to prevent the Second World War. This failure underscored the necessity for a more effective organization capable of maintaining global peace and security. - Cold War Tensions
After the Second World War, the world was divided into two armed blocs: the capitalist bloc led by the United States and the communist bloc led by the Soviet Union. The potential for conflict between these blocs made the establishment of an impartial organization like the UN crucial for resolving disputes peacefully. - Threat of Destructive Weapons
The use of atomic bombs during the Second World War demonstrated the catastrophic potential of such weapons. In the aftermath, countries began amassing more destructive arsenals. The UN was created to mitigate the threat posed by these lethal weapons and to protect humanity and the planet from their devastating effects.
Origin of the UN
- During the War: Even while the Second World War was ongoing, leaders from Allied governments, including U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt and British Prime Minister Winston Churchill, recognized the dangers of war. They engaged in discussions about the need for a post-war organization to maintain peace.
- Formation of the Idea: Through their discussions, Roosevelt and Churchill, along with other leaders, concluded that a new international organization was essential to prevent future conflicts and promote global cooperation.
- Drafting the Charter: The Charter of the United Nations was drafted in June 1945 during a conference in San Francisco. This document outlined the principles and structure of the new organization.
- Official Establishment: The UN officially came into existence on October 24, 1945, when the Charter was ratified by 29 nations. This date is now celebrated annually as United Nations Day.
Aims and Objectives of the UN
- To maintain international peace and security.
- To develop friendly relations among nations.
- To achieve international cooperation in resolving international, economic, social, cultural and humanitarian problems.
Many Conferences and discussions finally led to the San Francisco Conference in 1945. It was in this Conference that the Charter of the UN was drafted.
To work diligently for establishing peaceful relations among countries and for achieving the aims of the UN.
Principles of the UN

- To respect the sovereign equality of all its members.
- All obligations should be fulfilled by member nations in good faith.
- Member nations should neither threaten nor use force against any other nation.
- Member nations should support and assist the UN in every action which is taken by it.
- The UN should not interfere in internal affairs of any country.
Some Facts about the United Nations
- Headquarters of all the organs of the United Nations are based in New York, USA except the International Court of Justice which is located at the Hague in the Netherlands.
- Its flag is light blue, and in the middle is the polar map of the world embraced by olive branches. The flag was adopted on 20 October 1947.
- Expenditures of the UN are met by the contributions made by member countries.
- There are 193 member countries of the United Nations.
- India is an original member of the UN as it participated in the San Francisco Conference. India was represented by Jawaharlal Nehru.
Organs of the UN
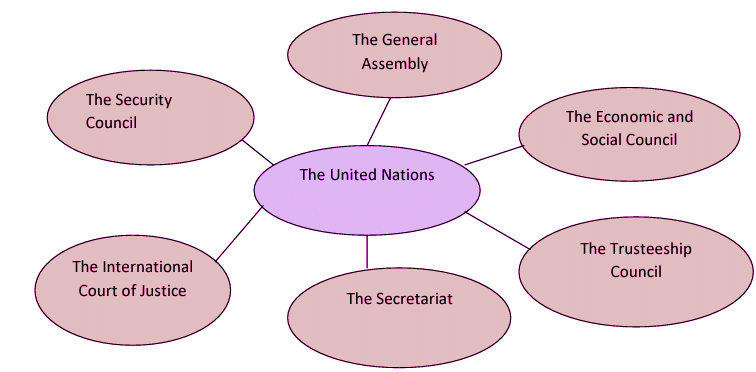
The General Assembly
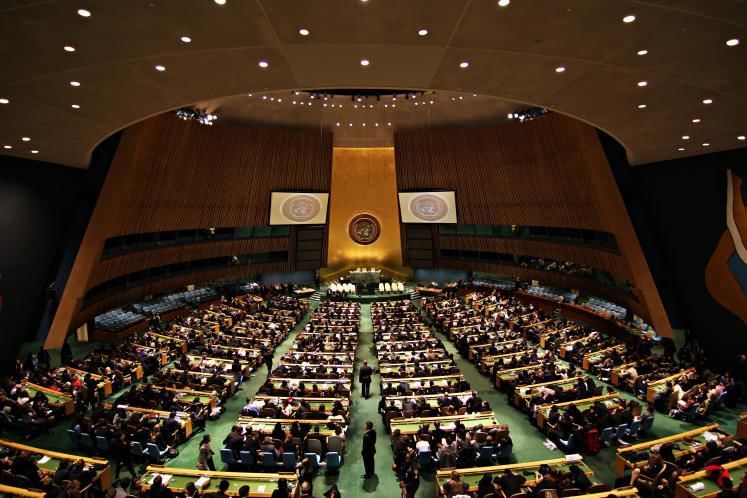

- The General Assembly is the primary organ of the United Nations (UN), and all UN member countries are also members of the General Assembly.
- Each country has an equal voice with one vote. The regular sessions of the General Assembly start every year on the third Tuesday of September and last until the third week of December. A new President is chosen for each session.
- Important decisions, such as those regarding the budget, expulsion of members, and admission of new members, require a two-thirds majority of the member nations.
Powers and Functions of the General Assembly
- To make recommendations on the principles of cooperation while ensuring peace and security.
- To discuss any issues related to international peace and security.
- To consider and make recommendations on any matters that may impact the powers and functions of other UN organs.
- To receive and review reports from the Security Council and other UN bodies.
- To approve the budget of the United Nations.
- To elect non-permanent members of the Security Council, the Economic and Social Council, and the Trusteeship Council, as well as the judges of the International Court of Justice.
The Security Council
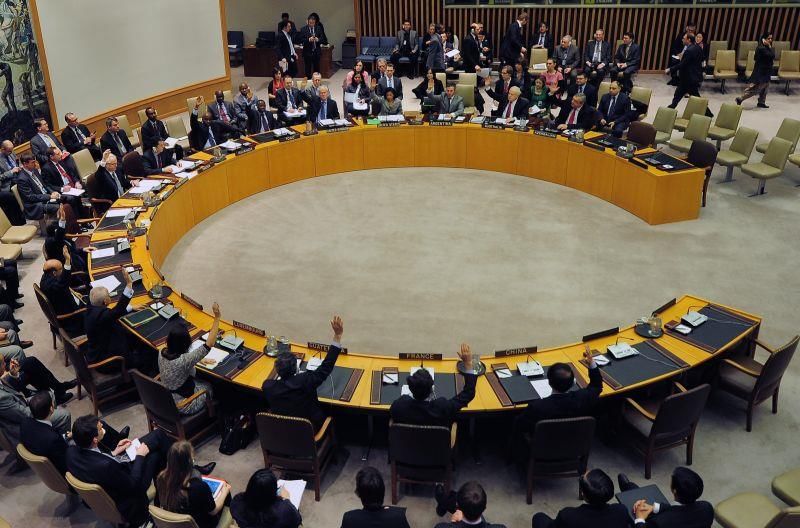

- The Security Council is an executive body of the United Nations responsible for maintaining international peace and security. It is composed of 15 members, including five permanent members: China, France, Russia, Britain, and the United States.
- The ten non-permanent members are elected from different regions: five from Afro-Asian countries, two from Latin American countries, two from Western European countries, and one from Eastern European countries. Each member has one vote, and decisions require at least nine votes in favor, including those of the permanent members.
- The permanent members have veto power, meaning that if any one of them votes against a decision, it does not pass.
Functions and Powers of the Security Council
- To maintain international peace and security.
- To investigate disputes or situations that may lead to international tension or conflict.
- To establish plans for regulating armaments.
- To take military action against an aggressor.
- To recommend the admission of new members to the United Nations.
- To recommend the appointment of the Secretary-General and, together with the General Assembly, elect the judges of the International Court of Justice.
International Court of Justice
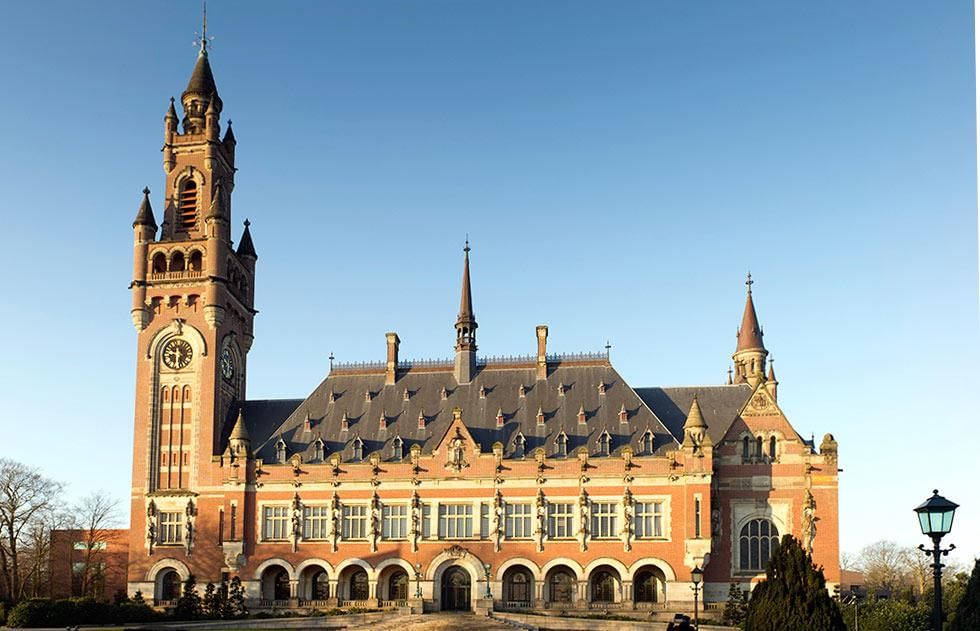

- The International Court of Justice (ICJ) is the main judicial body of the United Nations, located in The Hague, Netherlands. It is responsible for settling legal disputes between countries and providing advisory opinions on legal questions.
- The ICJ is composed of 15 judges elected for nine-year terms by the UN General Assembly and Security Council. The Court makes decisions based on international treaties, customs, and legal principles.
Functions and Powers
The Court has both voluntary and compulsory jurisdiction. Voluntary jurisdiction allows the Court to decide cases referred by member nations. Compulsory jurisdiction includes cases where treaties mandate submission to the Court, disputes over international law interpretation, and cases related to breaches of international obligations.
- The Court can give advisory opinions at the request of member nations and plays a role in codifying international law and recommending peaceful dispute resolution measures.
The Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC)

The Economic and Social Council is tasked with promoting higher living standards, ensuring full employment, and advancing economic and social progress.
The Trusteeship Council

The Trusteeship Council oversees territories that were administered before the Second World War.
The Secretariat

The Secretariat serves as the chief administrative office of the United Nations and is headed by the Secretary-General. The Secretary-General is responsible for coordinating and supervising the activities of the various UN organs.
|
28 videos|104 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: United Nations - History and Civics Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What is the origin of the United Nations? |  |
| 2. What are the main organs of the United Nations? |  |
| 3. How does the United Nations maintain international peace and security? |  |
| 4. What role does the General Assembly play in the United Nations? |  |
| 5. Why is the United Nations important for global cooperation? |  |















