Revision Notes: Universal Declaration of Human Rights | History and Civics Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
Universal Declaration of Human Rights

Human rights are the basic freedoms and entitlements that every person should have, regardless of their background, such as caste, class, gender, or religion. These rights include fundamental aspects like the right to live, the right to express oneself freely, the right to be treated equally, and the right to receive an education, among others.
Main Features of Human Rights
- Inalienable Rights: Human rights cannot be taken away, except in specific situations. For instance, the right to liberty can only be restricted if a person is found guilty of a crime by a court.
- Interdependence and Indivisibility: Human rights are interconnected. To achieve one set of rights, others must be recognized first. For example, without civil and political rights, individuals cannot claim economic, social, and cultural rights.
- Equality and Non-Discrimination: Human rights should be granted to everyone without discrimination based on gender, caste, class, or religion.
- Obligations of States: States have a duty under international law to respect, protect, and fulfill human rights. They must also safeguard citizens from human rights violations.
Historical Background
- One of the primary goals of the United Nations (UN) was to promote fundamental human rights.
- In 1946, the UN established a commission to develop key human rights policies within the organization.
- Led by Eleanor Roosevelt, the commission worked on defining essential rights and freedoms. On December 10, 1948, the UN General Assembly adopted the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR). This day is now celebrated worldwide as Human Rights Day.
The UDHR consists of an introduction (Preamble) and 30 articles outlining various human rights.
The Covenants
- Two significant legally binding human rights agreements under the United Nations are the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights and the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights.
- These two categories of rights, along with the Universal Declaration, constitute the International Bill of Rights.
- India has ratified nearly all the major United Nations Covenants, including those related to human rights.
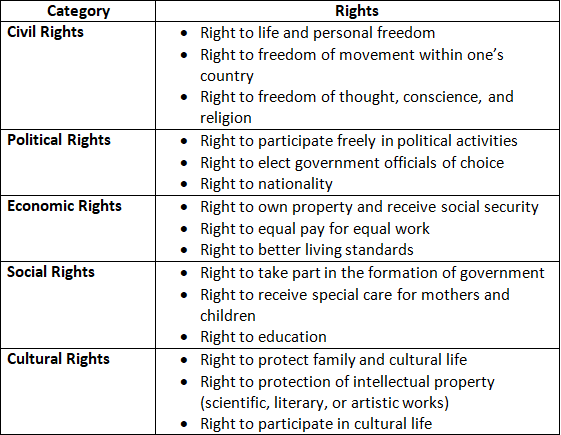
Categories of Human Rights
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights encompasses both civil and political rights, which can be categorized into five main groups:
Articles 1 and 2—Foundation of All Rights
Articles 1 and 2 are regarded as the foundation of all rights.
- Article 1: Every human being is born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are gifted with reason and conscience and should treat each other with a spirit of brotherhood.
- Article 2: Everyone is entitled to all the rights and freedoms mentioned in this Declaration, without any discrimination based on race, colour, sex, language, religion, political or other opinions, national or social origin, property, birth, or any other status.
These rights emphasize the following aspects of freedom:
- Inherent Freedom: All human beings are born free, and rights are inherent to humans by nature.
- Equality of Rights: Everyone should have the same rights, without any discrimination.
- Reason and Conscience: Humans have the ability to reason, which helps them distinguish between right and wrong. It is the duty of every individual to promote harmony and brotherhood.
- Prohibition of Discrimination: There should be no discrimination against any person based on colour, caste, class, sex, or religion.
- Universal Application of Rights: These rights are applicable to all territories, not just to self-governing states.
Significance of the Human Rights Declaration
- The Declaration of Human Rights establishes a universal benchmark for all countries to follow. Nations are required to eliminate political and social disabilities and inequalities in accordance with the declaration's guidelines.
- Member countries must uphold and enforce the rights outlined in the Declaration of Human Rights.
- Violations of human rights are a matter of global concern and require international attention.
- The Constitutions of several countries drafted after World War II have been influenced by the principles set forth in the Declaration of Human Rights.
The Constitution of India

- The Constitution of India guarantees rights and equality to all its citizens. The Preamble to the Constitution of India contains objectives of the Constitution of India. It secures justice, social, economic and political rights, liberty of thought, expression, belief, faith and worship. Equality and fraternity assure the dignity of individual and unity of the nation. Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles of state policy make India the largest democracy in the world.
Human Rights and Monitoring Agencies
- The Declaration of Human Rights holds moral authority but lacks legal enforcement. Various non-governmental organizations (NGOs) play a crucial role in monitoring and addressing human rights abuses.
- Amnesty International is one such organization based in London, dedicated to monitoring and reporting human rights violations globally.
Violation of Human Rights
- Violation of human rights refers to the denial of basic human rights to the people. Some examples of human rights violation include genocide, medical experimentation, forced labour, forcible relocations, torture, slavery, discriminations on the basis of religion, race, ethnicity, race or gender.
- Massacres and genocide are some gravest violations of the right to life. Genocide refers to the selective killing of the people belonging to particular racial, ethnic or religious groups.
- Many human rights violations take place during wars. War crimes include taking hostages, firing at civilians, hospitals and schools.
- Women and girls are most vulnerable to human rights violations. It includes rape, sexual assaults, humiliation, prostitution, domestic violence and denial of political rights.
- Children are also denied rights when they are used as soldiers, as well as when they are subject to child labour, child torture, inhuman conditions in juvenile homes and physical and sexual violence.
Introduction Human Rights are the basic rights and freedoms that belong to every person in the world, from birth until death. These rights are based on shared values like dignity, fairness, equality, respect, and independence. Human rights are usually protected by law, making it illegal for people to harm or violate these rights.
Human Rights Violation Human Rights Violation occurs when someone’s basic rights and freedoms are not respected or protected. This can happen in various ways, such as through discrimination, violence, or unfair treatment by the government or other individuals.
Need for Awareness Need for Awareness Human Rights violation can be checked by creating awareness among people about what constitutes a human rights violation. When people are aware of their rights and the rights of others, they are more likely to stand up against violations and report instances of abuse. Awareness can be built through various means, such as :
- Education : Incorporating human rights education in schools and colleges to inform students about their rights and the importance of safeguarding them.
- Campaigns : Organizing public awareness campaigns, workshops, and seminars to educate people about human rights and the consequences of violations.
- Media : Utilizing social media, television, radio, and print media to spread information about human rights issues and encourage people to take action.
- Community Engagement : Involving local communities in discussions and activities related to human rights to foster a culture of respect and protection for everyone’s rights.
Examples of Human Rights Violation Examples of Human Rights Violation Discrimination : Treating someone unfairly because of their race, gender, religion, or other characteristics.
- Police Brutality : Excessive force used by law enforcement officers against individuals, often violating their right to safety and dignity.
- Censorship : Suppressing free speech by restricting what people can say or publish, infringing on their right to express themselves.
- Child Labor : Forcing children to work in hazardous conditions, violating their right to a safe and healthy childhood.
- Refugee Crisis : Denying basic rights to refugees, such as safety and access to resources, violating their right to seek asylum and protection.
|
28 videos|103 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Universal Declaration of Human Rights - History and Civics Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What is the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR)? |  |
| 2. Why was the Universal Declaration of Human Rights created? |  |
| 3. How many articles are there in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights? |  |
| 4. What are some examples of violations of human rights? |  |
| 5. How does the Universal Declaration of Human Rights influence national laws? |  |















