Revision Notes: Public Expenditure | Economics Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Types of Public Expenditure |

|
| Reasons for the Growth of Public Expenditure |

|
| Goals of Public Expenditure |

|
Introduction
Public expenditure refers to the money spent by the government for various activities aimed at the welfare and development of the nation. This includes spending on infrastructure like roads, education, irrigation, and maintaining law and order.
Types of Public Expenditure
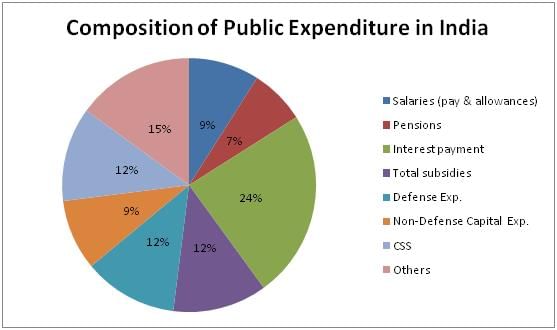
- Protective and Commercial Expenditures
- Primary and Secondary Expenditures
- Optional and Obligatory Expenditures
- Direct and Transfer Expenditures
- Constant and Variable Expenditures
- Revenue and Capital Expenditures
- Developmental and Non-developmental Expenditures
- Productive and Unproductive Expenditures
Protective and Commercial Expenditures
Protective Expenditure: This type of expenditure is aimed at safeguarding the country from external threats and maintaining internal order. It includes spending on:- Defence: Protecting the nation’s borders and sovereignty.
- Police: Ensuring law and order within the country.
- Jails: Managing and overseeing correctional facilities.
Commercial Expenditure: This expenditure is related to promoting and supporting commercial activities within the country, such as:
- Industrial Exhibitions: Showcasing industrial products and innovations.
- Bounties: Financial incentives to encourage specific commercial activities.
Primary and Secondary Expenditures
Primary Expenditure: This includes essential spending on:- Law and Order: Ensuring public safety and security.
- Civil Administration: Managing government operations and services.
- Debt Services: Paying interest and principal on government debt.
Secondary Expenditure: This includes spending on important services such as:
- Health: Providing healthcare services to the public.
- Education: Ensuring access to educational facilities and programs.
- Unemployment Support: Assisting those without jobs.
- Transport and Communication: Developing and maintaining infrastructure for transport and communication.
- Poor Relief: Providing assistance to those in financial need.
Optional and Obligatory Expenditures
Optional Expenditure: This refers to spending that the government can choose to incur, such as:- Health: Investments in health services and facilities.
- Education: Funding for educational programs and institutions.
- Poor Relief: Social safety nets for the underprivileged.
Obligatory Expenditure: This includes mandatory spending that the government must undertake, such as:
- Defence: National security and military expenses.
- Contractual Payments: Obligations arising from contracts and agreements.
Direct and Transfer Expenditures
Direct Expenditure: This involves government spending on goods and services that contribute to the current national output, such as:- Defence Goods: Purchasing equipment and supplies for the military.
- Capital Goods for Industrial Expansion : Investing in infrastructure to support industrial growth.
Transfer Expenditure: This type of expenditure does not correspond to any specific productive service and includes payments such as:
- Old-age Pensions: Financial support for retired individuals.
- Sickness Benefits: Assistance for individuals unable to work due to illness.
Constant and Variable Expenditures
Constant Expenditure: This type of expenditure remains constant regardless of usage and includes:
Defence Spending: Costs incurred for national security, irrespective of the number of users.
Variable Expenditure: This expenditure increases with the level of public service usage, such as:
- Postal Services: Costs associated with mail delivery services.
- Telephone Services: Expenses related to telecommunications services.
Revenue and Capital Expenditures
- Revenue Expenditure: This type of expenditure is used to run government departments and does not create any capital assets. While government funds decrease with this spending, their liability does not reduce. Revenue expenditure is essential for maintaining services but does not promote economic development. Examples include spending on defence forces, public health, and education.
- Capital Expenditure: Capital expenditure is incurred to create capital assets and leads to the formation of capital stock. This type of spending reduces both government funds and liability and promotes the economic development of the nation. Examples include building infrastructure such as dams, roadways, and railways.
Developmental and Non-developmental Expenditures
- Developmental Expenditure: This refers to spending on projects aimed at economic and social development, such as transport and communication infrastructure. Developmental expenditure is crucial for enhancing the overall development and welfare of society.
- Non-developmental Expenditure: Non-developmental expenditure is incurred on administrative services, including police and defence. These expenditures are necessary for maintaining law and order and national security but do not directly contribute to economic or social development.
Productive and Unproductive Expenditures
- Productive Expenditure: This type of expenditure increases the production of goods and services in a nation. Productive expenditures involve investments in physical assets, such as machinery, and human capital, such as education and health. By enhancing production capacity, these expenditures contribute to economic growth and development.
- Unproductive Expenditure: Unproductive expenditure does not increase the productivity of a nation. This type of spending includes activities such as maintaining law and order, which, while necessary, do not directly contribute to increasing the output of goods and services. Unproductive expenditures are essential for ensuring stability and security but do not have a direct impact on economic productivity.
Reasons for the Growth of Public Expenditure
Political and Social Causes:- Democracy and Socialism: Public expenditure increases with the growth of democracy and socialism worldwide.
- Administrative Expansion: Growth in public spending is linked to the expansion of administrative machinery and efforts to maximize social and economic welfare.
- Welfare Benefits: Increased spending is necessary for providing salaries and benefits such as old-age pensions, sickness benefits, accident benefits, and free education to industrial workers.
- Interest Payments: Public expenditure rises due to substantial interest payments on market borrowings.
Economic Causes:
- Rise in Prices: Following World War II, there was a consistent increase in price levels, requiring the government to spend more to acquire goods and services and to raise salaries for government employees.
- Rise in Urbanization: Increased urbanization has led to higher public spending on civil administration, education, water supply, and parks.
Goals of Public Expenditure
The purpose of public expenditure is to enhance the social and economic welfare of the economy. It aims to reduce income and wealth disparities within the society.Importance of Public Expenditure in Economic Growth
- Investment by the government in infrastructure boosts the production efficiency of industries and creates more job opportunities.
- It promotes private businesses by establishing state-owned financial and banking institutions that offer low-interest loans.
- Public expenditure helps increase the production of essential goods to prevent private monopolies and supports the establishment of public enterprises.
- It reduces income inequality through welfare programs such as education and healthcare services.
- When public expenditure rises, aggregate demand also increases. This encourages producers to ramp up production levels. The higher demand leads to quicker depletion of goods in stock, prompting producers to expand their production capacity. This, in turn, generates greater demand for capital and labor, resulting in higher production levels and increased employment within the economy.
|
18 videos|50 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Public Expenditure - Economics Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What is public expenditure and why is it important for the economy? |  |
| 2. How does public expenditure affect inflation? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of public expenditure? |  |
| 4. How is public expenditure funded? |  |
| 5. What are the challenges associated with increased public expenditure? |  |















