Selina Textbook Solutions: Cell - The Structural and Functional Unit of Life | Biology Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
Very Short Answer Type
Q1: Identify the cellular structures with the help of the following clues:
(a) It synthesizes the respiratory enzymes.
(b) It is made up of lipoprotein.
(c) A non-living rigid layer surrounding the plasma membrane.
(d) Supportive framework for the cell.
(e) It consists of cisternae, vesicles and vacuoles.
(f) It destroys foreign substances.
(g) It gives turgidity to the plant cells.
(h) It is made up of DNA threads.
(i) It contains chromatin fibres.
(j) It initiates and regulates cell division.
Ans: (a) Mitochondria
(b) Cell membrane/plasma membrane
(c) Cell wall
(d) Endoplasmic reticulum
(e) Golgi apparatus
(f) Lysosomes
(g) Vacuoles
(h) Chromatin fibres
(i) Nucleus
(j) Centrosome
Q2: Give two examples of each:
(a) Unicellular animals
(b) Unicellular plants
(c) Cell organelles
(d) Cell inclusions
(e) Stains which make the nucleus distinct.
Ans: (a) Unicellular animals — Amoeba, Paramecium
(b) Unicellular plants — Chlamydomonas, Diatoms
(c) Cell organelles — Mitochondria, Nucleus
(d) Cell inclusions — Pigments, Granules
(e) Stains which make the nucleus distinct — Iodine, Eosin.
Q3: Name the following:
(a) A plastid without pigment.
(b) A pigment which is not found in plastids.
(c) The orange-red pigment found in the chromoplast.
(d) Scattered Golgi complex, found in plant cells.
(e) Amoeboid blood cells of human body.
(f) The smallest cell of human body.
(g) Bean-shaped cells of stomata.
(h) The part of cytoplasm which is devoid of the organelles.
(i) The folds/finger-like projections from the inner wall of the mitochondria.
(j) The tubules of Golgi complex.
Ans: (a) Leucoplast
(b) Anthocyanin
(c) Carotene
(d) Dictyosomes
(e) White blood cells (WBCs)
(f) Red blood cells (RBCs)
(g) Guard cells
(h) Cytosol
(i) Cristae
(j) Cisternae
Descriptive Type
Q1: Define the following terms:
(a) Cell
(b) Organelles
(c) Cytoplasm
(d) Protoplasm
(e) Nucleus
Ans: (a) Cell — Cell is the structural and functional unit of life capable of independent existence. All cells are basically alike in chemical composition and metabolic processes and arise from a pre-existing cell.
(b) Organelles — Organelles are specialized and membrane-bound, living structures in a cell concerned with definite functions.
(c) Cytoplasm — Cytoplasm is the part of the cell which is inside the cell membrane and outside the nucleus. It is a semi-liquid substance and contains several organelles, each concerned with a specific function.
(d) Protoplasm — The living parts of the cell which consist of cytoplasm, nucleus and other living bodies collectively constitute protoplasm or protoplast.
(e) Nucleus — Nucleus is a large spherical body lying nearly in the centre of the cytoplasm. It is surrounded by a double layered nuclear membrane with nuclear pores.
Q2: Distinguish between the following pairs:
(a) Plant cell and animal cell
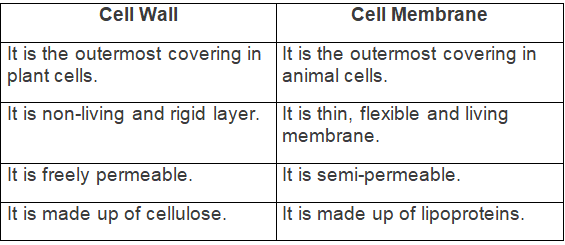
(b) Cell wall and cell membrane
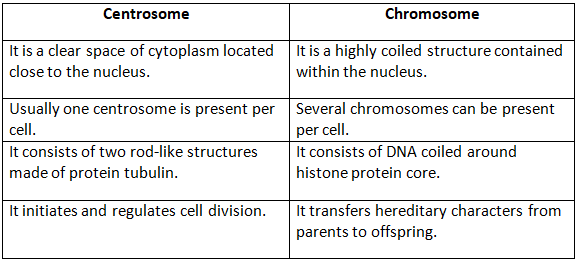
(c) Centrosome and chromosome
(d) Chloroplast and chromoplast
Ans: 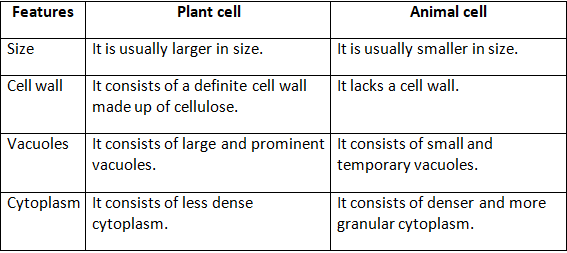
(b) Cell Wall and Cell Membrane
Ans:
(c) Centrosome and Chromosome
Ans:
(d) Chloroplast and Chromoplast
Ans: 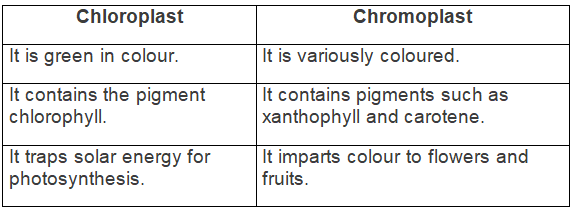
|
55 videos|113 docs|21 tests
|
FAQs on Selina Textbook Solutions: Cell - The Structural and Functional Unit of Life - Biology Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What is a cell and why is it considered the basic structural and functional unit of life? |  |
| 2. What are the main components of a cell and their functions? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? |  |
| 4. How do plant cells differ from animal cells? |  |
| 5. Why are cells often referred to as the "building blocks of life"? |  |





















