Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry Class 10 ICSE > Revision Notes: Study of Compounds - Ammonia and Nitric Acid
Revision Notes: Study of Compounds - Ammonia and Nitric Acid | Chemistry Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Study of Compounds – Nitric Acid |

|
| Nitric Acid |

|
| Laboratory Preparation of Nitric Acid |

|
| Properties of Nitric Acid |

|
| Uses of Nitric Acid |

|
Study of Compounds – Nitric Acid
Nitric Acid
- Molecular formula: HNO3
- Relative molecular mass: 63
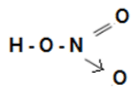
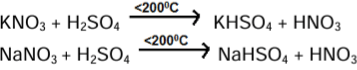
Laboratory Preparation of Nitric Acid
Reactions:
Properties of Nitric Acid
(A) Physical Properties
- Pure acid (98% conc.) is colourless, suffocating and sour to taste.
- It is heavier than water, with a specific gravity of 1.54.
- Boiling point is 86°C, and freezing point is −42°C
(B) Chemical Properties
- Pure nitric acid is colourless, unstable and decomposes slightly even at room temperature and in the presence of sunlight.
4HNO3 → 4NO2 + 2H2O + O2 - Nitric acid is a very strong monobasic acid and ionises almost completely in aqueous solution.
HNO3 ⇌ H+ + NO3− - Nitric acid neutralises alkalis to form salt and water.
CaO + 2HNO3 → Ca (NO3)2 + H2O
CuO + 2HNO3 → Cu (NO3)2 + H2O
NaOH + HNO3 → NaNO3 + H2O - Nitric acid reacts with carbonates and bicarbonates to produce salt, water and carbon dioxide.
Na2CO3 + 2HNO3 → 2NaNO3 + H2O + CO2
NaHCO3 + HNO3 → NaNO3 + H2O + CO2 - Nitric acid oxidises carbon, sulphur and phosphorus to their highest oxides or oxy-acids such as carbon dioxide, sulphuric acid and phosphoric acid.
C + 4HNO3 → 2H2O + 4NO2 + CO2
S + 6HNO3 → H2SO4 + 2H2O + 6NO2
P4 + 20HNO3 → 4H3PO4 + 4H2O + 20NO2 - Cold and dilute nitric acid oxidises metals to their nitrates and liberates nitric oxide.
3Cu + 8HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2H2O + 2NO2
3Zn + 8HNO3 → 3Zn (NO3)2 + 4H2O + 2NO2 - Concentrated nitric acid liberates nitrogen dioxide.
Cu + 4HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2H2O + 2NO2
Zn + 4HNO3 → Zn (NO3)2 + 2H2O + 2NO2 - Nitric acid (1 part by volume) mixed with conc. hydrochloric acid (3 parts by volume) produces a mixture called aqua regia.
HNO3 + 3HCl → NOCl + 2H2O + 2[Cl]
Aqua regia contains nascent chlorine and reacts with noble metals such as gold and platinum to produce chlorides.
Pt + 4[Cl] → PtCl4
Au +3[Cl] → AuCl3
Uses of Nitric Acid
- To etch designs on copper and brassware because it acts as a solvent for several metals except the noble metals.
- To purify gold with impurities of Cu, Ag and Zn which dissolve in nitric acid.
- It acts as a rocket fuel oxidant.
- In preparation of fertilisers such as Ca(NO3)2 and NH4NO3.
- In the preparation of aqua regia, which dissolves noble metals.
The document Revision Notes: Study of Compounds - Ammonia and Nitric Acid | Chemistry Class 10 ICSE is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry Class 10 ICSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
40 videos|140 docs|14 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Study of Compounds - Ammonia and Nitric Acid - Chemistry Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What is the laboratory preparation method of nitric acid? |  |
Ans. Nitric acid can be prepared in the laboratory by heating a mixture of sodium nitrate (NaNO3) and concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4). The reaction produces nitric acid, nitrogen dioxide, and sodium bisulfate. The chemical equation for this reaction is:
\[ \text{NaNO}_3 + \text{H}_2\text{SO}_4 \rightarrow \text{HNO}_3 + \text{NaHSO}_4 \]
| 2. What are the physical properties of nitric acid? |  |
Ans. Nitric acid is a colorless liquid with a strong, acrid smell. It has a boiling point of 83°C and is highly soluble in water. It exhibits strong acidic properties and can act as both an oxidizing and a nitrating agent. The density of concentrated nitric acid is approximately 1.5 g/cm³.
| 3. What are the chemical properties of nitric acid? |  |
Ans. Nitric acid is a strong acid that can ionize completely in water to produce hydrogen ions (H+) and nitrate ions (NO3-). It can react with metals, nonmetals, and bases. For example, it reacts with metals like copper to form metal nitrates and releases nitrogen dioxide gas. The general reaction with metals can be expressed as:
\[ \text{Metal} + \text{HNO}_3 \rightarrow \text{Metal Nitrate} + \text{NO}_2 + \text{H}_2\text{O} \]
| 4. What are the main uses of nitric acid? |  |
Ans. Nitric acid is primarily used in the production of fertilizers, explosives, and dyes. It is also used in the manufacture of nitrous oxide, in metal etching, and in the production of various chemicals. Additionally, it serves as a strong oxidizing agent in chemical reactions.
| 5. Why is nitric acid considered a hazardous substance? |  |
Ans. Nitric acid is considered hazardous due to its corrosive nature, which can cause severe burns upon contact with skin or eyes. It also produces toxic fumes, particularly nitrogen dioxide, which can be harmful if inhaled. Proper safety precautions, such as wearing gloves and goggles, should be taken when handling nitric acid.
Related Searches














