Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry Class 10 ICSE > Revision Notes: Study of Compounds – Sulphuric Acid
Revision Notes: Study of Compounds – Sulphuric Acid | Chemistry Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Study of Compounds – Sulphuric Acid |

|
| Sulphuric Acid |

|
| General Methods of Preparation |

|
| Manufacture of Sulphuric Acid [Contact Process] |

|
| Properties of Sulphuric Acid |

|
| Uses of Sulphuric Acid |

|
Study of Compounds – Sulphuric Acid
Sulphuric Acid
Molecular formula: H2SO4
Relative molecular mass: 98
Structure:
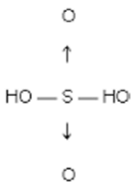
General Methods of Preparation
- By the action of heat on nitric acid and sulphur.
S + 6HNO3 → 6NO2 + 2H2O + H2SO4 - By passing chlorine through an aqueous solution of sulphur trioxide.
Cl2 + SO2 + 2H2O →2HCl + H2SO4 - By dissolution of sulphur trioxide in water.
SO3 + H2O → H2SO4 - By hydrolysis of sulphuryl chloride.
SO2Cl2 + 2H2O → H2SO4 + 2HCl
Manufacture of Sulphuric Acid [Contact Process]
Steps involved in the contact process
- Production of sulphur dioxide
SO2 is produced by roasting metallic sulphides in air.
4FeS2 +11O2 → 2Fe2O3 + 8SO2 - Purification of gases
To enhance the efficiency of a catalyst, various impurities present in the mixture of sulphur dioxide and air are first removed. - Catalytic oxidation of sulphur dioxide
Oxidation of SO2 to SO3 at 450°C in the presence of catalyst vanadium pentaoxide.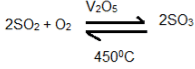
- Absorption of sulphur trioxide in sulphuric acid
Sulphur trioxide vapours are absorbed by a stream of conc. sulphuric acid.
SO3 + H2SO4 → H2S2O7 (oleum or pyrosulphuric acid) - Dilution of oleum to obtain sulphuric acid
A calculated amount of water is added to obtain sulphuric acid of desired strength.
H2S2O7 + H2O → 2H2SO4
Properties of Sulphuric Acid
(A) Physical Properties
- Colourless, odourless with slight sour taste.
- It is highly corrosive in nature and chars the skin black.
- It is heavier than water and soluble in water.
- Boiling point is 338°C, and melting point is 10.4°C.
(B) Chemical Properties
Properties of Dilute Sulphuric Acid
- Dilute sulphuric acid reacts with metals to form metallic sulphate and hydrogen.
Mg + H2SO4 → MgSO4 + H2
Fe + H2SO4 → Fe2SO4 + H2 - It neutralises bases to form salts and water.
NaOH + H2SO4 → NaHSO4 + H2O - It liberates carbon dioxide from metallic carbonates and bicarbonates.
Na2CO3 + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O + CO2
2KHCO3 + H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2H2O +2CO2 - It evolves hydrogen sulphide from metal sulphides.
Na2S + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2S
ZnS + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2S - It evolves sulphur dioxide from sulphites and hydrogen sulphites.
Na2SO3 +H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O + SO2
2NaHSO3 + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2H2O + 2SO2
Properties of Conc. Sulphuric Acid
- Non-volatile nature
It has a high boiling point so it is used to prepare volatile acids such as HCl, HNO3 and acetic acid from their salts.
NaCl + H2SO4 → NaHSO4 + HCl
NaNO3 + H2SO4 → NaHSO4 + HNO3 - As an oxidising agent
C + 2H2SO4 → CO2 + 2H2O + 2SO2
Cu + 2H2SO4 → CuSO4 + 2H2O + SO2
2HBr + H2SO4 → Br2 + 2H2O + SO2 - As a dehydrating agent
H2SO4 has a great affinity for water, and therefore, it acts as a dehydrating agent.
C2H5OH C2H4 + H2O
C2H4 + H2O
C6H12O6 6C + 6H2O
6C + 6H2O
Uses of Sulphuric Acid
- In the preparation of halogens, CO, CO2 and SO2.
- Extraction of metals: Leaching of metallic compounds produces sulphates which give the metal in pure form on electrolysis.
- Pickling of metals: Removes metallic impurities from the surface of metals before galvanising.
- Industrial uses:
i. In the manufacture of fertilisers such as ammonium sulphate [(NH4)2SO4] and superphosphate of lime [Ca (H2PO4)2 + CaSO4].
ii. In the manufacture of explosives such as trinitrotoluene and picric acid.
The document Revision Notes: Study of Compounds – Sulphuric Acid | Chemistry Class 10 ICSE is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry Class 10 ICSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
39 videos|85 docs|14 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Study of Compounds – Sulphuric Acid - Chemistry Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What is the Contact Process for the manufacture of Sulphuric Acid? |  |
Ans. The Contact Process is the primary method for the industrial production of sulphuric acid. It involves three main steps:
1. The combustion of sulfur or sulfide ores to produce sulfur dioxide (SO₂).
2. The conversion of sulfur dioxide to sulfur trioxide (SO₃) by reacting it with oxygen in the presence of a vanadium pentoxide (V₂O₅) catalyst at high temperatures.
3. The absorption of sulfur trioxide in water or oleum to produce sulphuric acid. This process is efficient and produces concentrated sulphuric acid.
| 2. What are the physical and chemical properties of Sulphuric Acid? |  |
Ans. Sulphuric acid (H₂SO₄) is a colorless, odorless, and viscous liquid. It is highly soluble in water, releasing heat during the process. Chemically, it is a strong acid and a powerful dehydrating agent. It can react with metals, non-metals, and organic compounds, often resulting in the release of gases like hydrogen or carbon dioxide. It also has a high boiling point (approximately 338°C) and can conduct electricity due to its ionization in solution.
| 3. What are the major uses of Sulphuric Acid? |  |
Ans. Sulphuric acid has a wide range of applications, including:
1. In the manufacture of fertilizers, particularly phosphoric acid and ammonium sulfate.
2. In the petroleum industry for refining crude oil and in the production of synthetic detergents.
3. In the metal industry for ore processing and in the production of lead-acid batteries.
4. As a dehydrating agent in the production of various chemicals and dyes.
5. In laboratories for various analytical and synthetic processes.
| 4. What safety precautions should be taken when handling Sulphuric Acid? |  |
Ans. When handling sulphuric acid, it is essential to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, goggles, and lab coats to prevent skin and eye contact. Work in a well-ventilated area or fume hood to avoid inhaling vapors. In case of a spill, neutralize the acid with a suitable base before cleaning up. Always add acid to water, never the reverse, to prevent exothermic reactions that can cause splattering.
| 5. Why is Sulphuric Acid known as the "king of chemicals"? |  |
Ans. Sulphuric acid is often referred to as the "king of chemicals" due to its extensive use in various industrial processes and its importance in chemical reactions. It is one of the most produced industrial chemicals globally and serves as a key ingredient in the manufacture of fertilizers, explosives, and other chemicals. Its versatility and strong acidic properties make it invaluable in both laboratory and industrial settings.
Related Searches















