Case Based Questions: Circle | Mathematics (Maths) Class 10 PDF Download
Q1: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
The discus throw is an event in which an athlete attempts to throw a discus. The athlete spins anti-clockwise around one and a half times through a circle, then releases the throw. When released, the discus travels along the tangent to the circular spin-orbit.
In the given figure, AB is one such tangent to a circle of radius 75cm. Point O is the centre of the circle and ∠ABO = 30°. PQ is parallel to OA.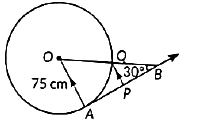
i. Find the length of AB. (1 mark)
ii. Find the length of OB. (1 mark)
iii. Find the length of AP. (1 mark)
iv. Find the value of PQ. (1 mark)
Ans:
i. Given, ∠ABO = 30°, OA = 75 cm
In ΔOAB, tan30° = OA / AB
⇒ 1 / √3 = 75 / AB ⇒ AB = 75√3 cm
ii. In ΔOAB, sin30° = OA / OB
⇒ 1 / 2 = 75 / OB ⇒ OB = 150 cm
iii. In ΔOAB, PQ || OA
QB / QO = BP / AP
⇒ (150 - 75) / 75 = AB / AP - 1
⇒ 2 = (75√3) / AP
⇒ AP = 75 × (√3 / 2)
⇒ AP = (75√3) / 2 cm
iv. OA = OQ = 75 cm (∵ Radius)
In ΔOAB,
We have, PQ || OA
In ΔBQP and ΔBOA
∠BQP = ∠BOA (corresponding angles)
∠B = ∠B (common)
∴ ΔBQP ~ ΔBOA (By AA similarity)
∴ BQ / BO = QP / OA = BP / BA
PQ / 75 = (AB - AP) / AB
⇒ PQ / 75 = 1 - AP / AB
⇒ PQ / 75 = 1 - (75√3) / (2 × 75√3)
⇒ PQ / 75 = 1 / 2
∴ PQ = 75 / 2 = 37.5
∴ PQ = 37.5 cm
Q2: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
In a math class-IX, the teacher draws two circles that touch each other externally at point M with centres A and B and radii 5 cm and 4 cm respectively as shown in the figure.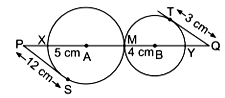
i. Find the value of PX. (1 mark)
ii. Find the value of QY. (1 mark)
iii. Show that PS2 = PM-PX. (1 mark)
iv. Show that TQ² = YQ.MQ (1 mark)
Ans:
i. Here, AS = 5 cm and BT = 4 cm (∵ radii of circles)
Since, radius at point of contact is perpendicular to tangent.
∴ AS ⊥ PS
⇒ ∠ASP = 90°
In right-angled ΔASP,
PA² = PS² + AS² (by Pythagoras theorem)
⇒ PA² = (12)² + (5)²
⇒ PA = √(144 + 25) = √169 = 13 cm
∴ PX = PA - XA
⇒ PX = 13 - 5 = 8 cm (∵ radius, XA = 5 cm)
ii. ∴ BT ⊥ TQ
∠BTQ = 90°
In right-angled ΔBTQ,
BQ² = TQ² + BT² (by Pythagoras theorem)
⇒ BQ² = (3)² + (4)²
⇒ BQ = √(9 + 16) = √25 = 5 cm
∴ QY = BQ - BY
⇒ QY = 5 - 4 = 1 cm (∵ radius, BY = 4 cm)
iii. In right-angled ΔASP,
PS² = PA² - AS²
= PA² - AM² [∵ AS = AM (radii)]
= (PA + AM)(PA - AM)
= (PA + AM)(PA - AX)
= PM × PX [∵ AM = AX (radii)]
Hence proved.
iv. TQ² = BQ² - TB²
= (BQ - TB)(BQ + TB) (∵ TB = MB (radii))
= (BQ - MB)(BQ + MB)
= (BQ - BY) × MQ [∵ MB = BY (radii)]
= YQ × MQ [∵ BQ + MB = MQ, BQ - BY = YQ]
Hence proved.
Q3: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
If a tangent is drawn to a circle from an external point, then the radius at the point of contact is perpendicular to the tangent.i. In the given figure, O is the centre of two concentric circles. From an external point P tangents PA and PB are drawn to these circles such that PA = 6 cm and PB = 8 cm. If OP = 10 cm, then find the value of AB. (1 mark)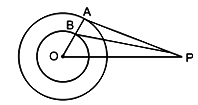 ii. The diameter of two concentric circles are 10 cm and 6 cm. AB is a diameter of the bigger circle and BD is the tangent to the smaller circle touching it at D and intersecting the larger circle at P on producing. Find the length of BP. (1 mark)
ii. The diameter of two concentric circles are 10 cm and 6 cm. AB is a diameter of the bigger circle and BD is the tangent to the smaller circle touching it at D and intersecting the larger circle at P on producing. Find the length of BP. (1 mark)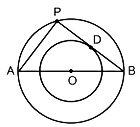 iii. Two concentric circles are such that the difference between their radii is 4 cm and the length of the chord of the larger circle which touches the smaller circle is 24 cm. Then f ind the radius of the smaller circle. (1 mark)
iii. Two concentric circles are such that the difference between their radii is 4 cm and the length of the chord of the larger circle which touches the smaller circle is 24 cm. Then f ind the radius of the smaller circle. (1 mark)
iv. If AB is a chord of a circle with centre O, AOC is a diameter and AT is the tangent at A as shown in figure. Prove that <BAT = <ACB.
(1 mark)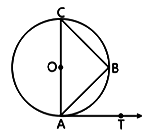
Ans:
i. Since, radius is perpendicular to the tangent.
∴ OB ⊥ BP and OA ⊥ AP
Now in right-angled ΔOBP and ΔOAP,
Here, OP² - PB² = OB² and OP² - PA² = OA² (by Pythagoras theorem)
∴ OB = √(100 - 64) = √36 = 6 cm
(∵ OP = 10 cm and PB = 8 cm)
and OA = √(100 - 36) = √64 = 8 cm
(∵ PA = 6 cm)
∴ AB = OA - OB = 8 - 6 = 2 cm
ii. Since, radius is perpendicular to the tangent
∴ OD ⊥ BP
Given, AB = 10 cm
⇒ OB = 10 / 2 = 5 cm and OD = 6 / 2 = 3 cm
Now in right-angled ΔODB,
OB² = OD² + BD² ⇒ BD = √(OB² - OD²) (by Pythagoras theorem)
⇒ BD = √(25 - 9) = √16 = 4 cm
Since, chord BP is bisected by radius OD.
∴ BP = 2 × BD = 2 × 4 = 8 cm.
iii. Let x be the radius of smaller circle, then (x+4) be the radius of larger circle,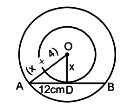
Since, radius is perpendicular to the tangent.
∴ OD ⊥ AB
Now in right-angled ΔODA,
OA² = OD² + AD² (by Pythagoras theorem)
⇒ (x + 4)² = x² + 12²
⇒ x² + 8x + 16 = x² + 144
⇒ 8x + 16 = 144
⇒ x = 16 cm
iv. Since, AC is a diameter, so the angle in a semi-circle will be 90°.
In ΔABC,
∠ABC = 90°
∠CAB + ∠ABC + ∠ACB = 180° (sum of interior angles of a triangle)
= ∠CAB + ∠ACB = 180° - 90° - 90°
= 0° (1)
Since, the diameter of the circle is perpendicular to the tangent.
i.e., CA ⊥ AT
∴ ∠CAT = 90°
⇒ ∠CAB + ∠BAT = 90° ...(2)
From (1) and (2), we get
∠CAB + ∠ACB = ∠CAB + ∠BAT
∠ACB = ∠BAT
Hence proved.
Q4: Read the source below and answer the questions that follow:
Circles play an important part in our life. When a circular object is hung on the wall with a chord at nail N, the chords NA and NB work like tangents. Observe the figure, given that <ANO = 30° and OA = 5 cm.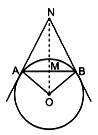
i. Find the distance AN. (1 mark)
ii. Find the measure of <AOB. (1 mark)
iii. Find the total length of chords NA, NB and the chord AB. Name the type of quadrilateral OANB. Justify your answer. (2 marks)
Ans:
i. Here, OA ⊥ AN
∴ ∠OAN = 90°
Given, ∠ANO = 30° and OA = 5 cm.
In right-angled ΔOAN,
tan ∠ANO = OA / AN ⇒ tan 30° = 5 / AN
⇒ 1 / √3 = 5 / AN
⇒ AN = 5√3 cm
ii. ∴ ∠ANO = ∠BNO = 30°
= ∠ANB = 2 × ∠ANO = 2 × 30° = 60°
∴ OA ⊥ AN and OB ⊥ BN
∴ ∠OAN = ∠OBN = 90°
Now in quadrilateral OANB,
∠AOB + ∠OAN + ∠OBN + ∠ANB = 360°
= ∠AOB + 90° + 90° + 60° = 360°
∴ ∠AOB = 360° - 240° = 120°
iii. In ΔAOB,
OA = OB (radii of circle)
∴ ∠OAB = ∠OBA (Say)
∴ ∠OAB + ∠OBA + ∠AOB = 180° (by angle sum property)
= 0 + 0 + 120° = 180° (∵ ∠AOB = 120°)
⇒ 2θ = 60°
⇒ θ = 30°
∴ ∠OAB = ∠OBA = 30°
∴ ∠OAN = ∠OAB + ∠BAN
= 90° = 30° + ∠BAN
⇒ ∠BAN = 90° - 30° = 60°
Similarly, ∠ABN = 60°
∴ ∠ANB = ∠BAN = ∠ABN = 60°
∴ ΔANB is an equilateral triangle.
∴ Total length of chords = NA + NB + AB
(∵ AN = BN = AB = 5√3 cm)
= 5√3 + 5√3 + 5√3
= 15√3 cm
From above parts,
∠OAN = ∠OBN = 90°
But ∠AOB = ∠ANB
Also, AN = BN = 5√3 cm
(the length of two tangents drawn from an external point of a circle are equal.)
and OA = OB = 5 cm (Radii)
In quadrilateral OANB,
longer diagonal ON bisects shorter diagonal AB perpendicularly.
(: the perpendicular from the centre of a circle to a chord bisects the chord)
Hence, the special name of quadrilateral OANB is kite.
|
127 videos|584 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Case Based Questions: Circle - Mathematics (Maths) Class 10
| 1. What are the key properties of a circle? |  |
| 2. How do you calculate the area of a circle? |  |
| 3. What is the relationship between the diameter and the radius of a circle? |  |
| 4. What is the formula for the circumference of a circle? |  |
| 5. How do you find the length of an arc in a circle? |  |
















