Forms of Legal Entities Chapter Notes | Legal Studies for Class 12 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Types of Legal Entities in India |

|
| Comparative Analysis of Different Business Entities |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Introduction
When considering starting or expanding a business, it is crucial to understand the various forms of organizations available. The choice of legal structure should align with the entity's goals and comply with local and central laws.
In India, the primary types of business frameworks include: (a) Sole Proprietorship (b) Partnership (c) Company (public or private) Over time, hybrid and innovative variations, such as limited liability partnerships, have emerged. Each business form comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Objective of Law Regulation of Legal Entities
The objective of regulating the legal forms of entities is to establish a framework for the creation, management, and dissolution of various types of organizations, including corporations, partnerships, and sole proprietorships. These regulations aim to:
- Protect the rights and interests of stakeholders, such as shareholders, employees, customers, and creditors.
- Ensure the fair and transparent functioning of these entities within the legal and economic system.
- Promote competition and prevent fraud and misconduct.
- Provide a clear understanding of responsibilities and liabilities.
Types of Legal Entities in India
Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is a common and suitable form of business organization for small enterprises, especially during their initial stages. In a sole proprietorship, an individual owns, manages, and controls the business, receiving all profits and bearing all risks. The term "sole" means "only," and "proprietor" refers to "owner," indicating that a sole proprietor is the exclusive owner of the business.
Establishing or dismantling a sole proprietorship is straightforward due to minimal government regulation. This simplicity makes it a popular choice for individual business owners, self-contractors, and consultants. Many small businesses begin as sole proprietorships and either remain in this form or expand into limited liability entities or corporations. Sole proprietorships are especially prevalent in sectors providing personalized services, such as beauty salons, hairdressers, and small retail shops within local communities.
Key Features of Sole Proprietorship
- No Separate Entity: The law does not differentiate between the owner and the business.
- Formation: There is no specific law governing the formation, and the business is owned by a single person without the need for formal registration.
- Number of Members: Minimum and maximum members required is one.
- Liability: The owner has unlimited liability, meaning they are responsible for all losses, debts, and liabilities.
- Profit: The owner enjoys all the profits if the business is successful.
- Control & Decision Making: The sole proprietor has the exclusive right to run the business and make all decisions.
- Limited Life of the Business: The business's existence is tied to the owner; events like death, insanity, imprisonment, physical or mental incapacity, or bankruptcy can lead to its closure.
- Confidentiality: The sole decision-making authority allows the proprietor to keep all business operation information confidential.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Sole Proprietorship
Advantages:
- Quick Decision Making: The owner can make decisions swiftly without consulting others.
- Confidentiality: Business information can be kept private, as there are no partners or shareholders.
- Profit Retention: The owner receives all profits without having to share with partners.
- Full Control: The owner has complete control over the business and its operations.
- Ease of Formation: It is the simplest and least expensive form of business ownership to set up.
- Tax Benefits: The business does not pay separate taxes; income is taxed at the owner's personal tax rate.
Disadvantages:
- Unlimited Liability: The owner is personally liable for all business debts and obligations.
- Limited Fundraising: Raising funds can be challenging, as options are limited compared to other business structures.
- Lack of Legal Status: The business does not have a separate legal identity from the owner.
- Resource Constraints: Access to resources may be limited compared to larger businesses.
- Skill Limitations: The skills and managerial abilities of the owner may restrict business growth and operations.
Partnership
A partnership, as defined by the Indian Partnership Act of 1932, is a relationship between individuals who have agreed to share the profits of a business carried out by all or any one of them acting on behalf of all. Individuals in a partnership are referred to as "partners" and collectively as "a firm," with the name under which the business operates called the "firm-name."
The limitations of sole proprietorship in terms of financing and managing a growing business led to the emergence of partnership as a viable alternative. A partnership addresses the need for increased capital investment, diverse skills, and risk-sharing.
A successful partnership can significantly benefit a business by allowing partners to combine their efforts and resources. However, joining a partnership also involves risks, as partners share not only profits but also responsibilities for losses or debts incurred by other partners.
Strategic partnerships involve two or more businesses or individuals collaborating to achieve common goals and enhance their respective brands. By co-branding and pooling resources, strategic partnerships can offer advantages such as increased brand visibility, improved brand trust, and access to new markets and customers. Notable examples of successful strategic partnerships include Spotify and Google, Sherwin-Williams and Pottery Barn, and McDonald's and Coca-Cola, which have contributed to the growth and success of both companies in their respective markets.
In professions such as law and medicine, individuals with expertise in their fields often form partnerships with other specialists to enhance knowledge, expand reach, combine various sub-specializations, increase trustworthiness, and provide comprehensive solutions to clients.
Salient features of a partnership are as follows: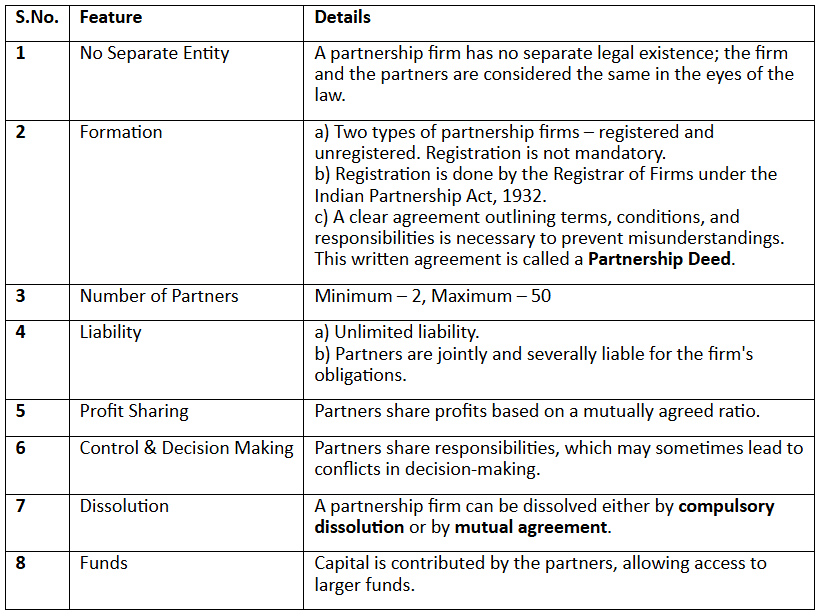
Advantages of Partnership
- Easy to Establish: Partnerships are simple to set up, although a partnership agreement is necessary.
- Liability Protection: Partnerships have a separate legal status, which protects partners from personal liability.
- Complementary Skills: Partners may bring different skills that complement each other.
- Low Startup Costs: The cost to start a partnership is relatively low.
- Increased Capital: Partnerships can raise more capital for the business.
Disadvantages of Partnership
- Joint Liability: Partners are individually and collectively responsible for the actions of other partners.
- Profit Sharing: Profits must be divided among partners.
- Shared Decision-Making: Decision-making can be divided, which may lead to conflicts.
- Risk of Poor Agreement: If a detailed partnership agreement is not in place, the business may suffer.
Limited Liability Partnership
A Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) is a type of business structure that combines the benefits of limited liability with the operational flexibility of a partnership. It is governed by the Limited Liability Partnership Act of 2008 in India.
In an LLP, the partners have limited liability, meaning their personal assets are protected from the business’s debts and liabilities. This structure is particularly suitable for professionals, entrepreneurs, and small businesses that want to limit their personal risk while enjoying the operational flexibility of a partnership.
The key features of an LLP include:
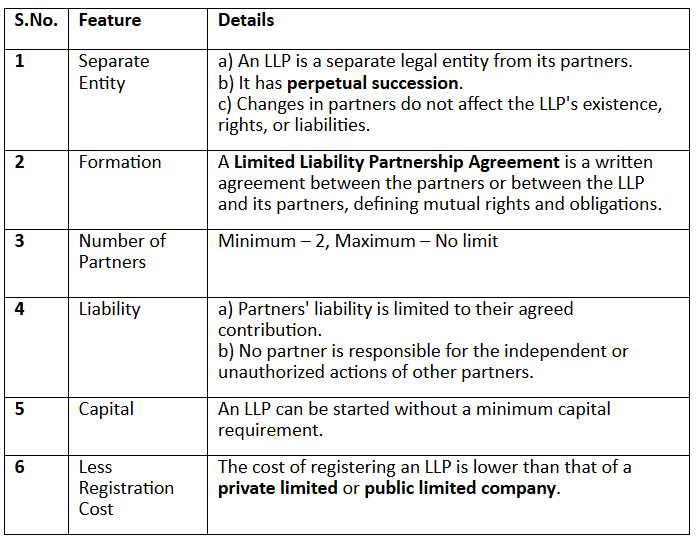 Advantages of Limited Liability Partnership
Advantages of Limited Liability Partnership
- Flexibility: The terms of an LLP are based on a mutually agreed LLP agreement, providing greater flexibility and ease of operation.
- Lower Registration Costs: Registering an LLP is more affordable compared to incorporating a public or private limited company.
- Limited Liability: Partners are only liable up to their agreed contribution, and there is no joint liability for the actions of another partner.
- Simpler Registration Process: The registration process for an LLP is less complex than that of a company.
- Clear Terms: Aspects such as remuneration, voting rights, and other terms are clearly defined in the LLP agreement, with no restrictions on partner remuneration as long as it is authorized by the agreement.
- Legal Protection: The LLP can sue and be sued in its own name, protecting partners from personal liability for the LLP’s debts.
- Flexibility in Partnership: There is greater flexibility in becoming a partner, leaving the LLP, or transferring interest in the LLP.
- Higher Credit-Worthiness: The LLP enjoys better credit-worthiness compared to a partnership, although it is lower than that of a company.
- No Mandatory Auditing: There is no requirement for mandatory auditing of accounts, and the LLP can raise funds from private equity investors and financial institutions.
Disadvantages of Limited Liability Partnership
- Binding Actions: Actions taken by one partner without the consent of others can bind the LLP, and in some cases, partners may be personally liable for the LLP’s debts.
- Lengthy Winding-Up Process: The winding-up process, as per the Limited Liability Partnership (Winding Up and Dissolution) Rules, 2012, can be time-consuming and costly.
Private Limited Company
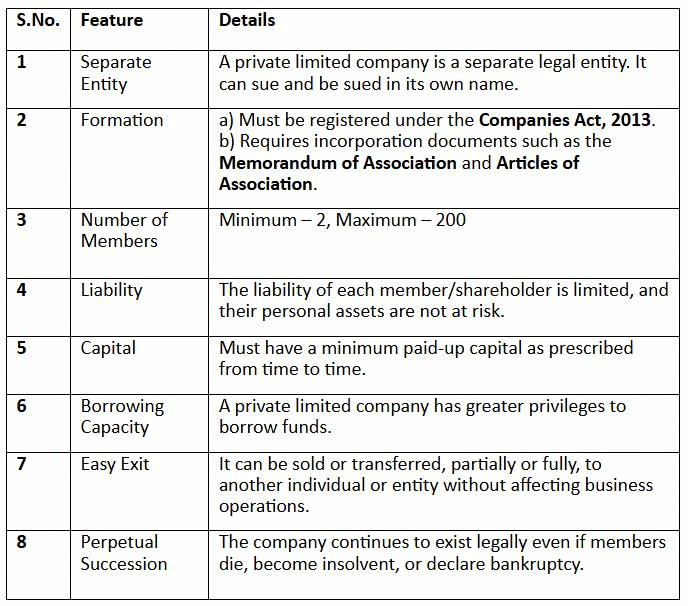
A Private Limited Company is a widely favored business structure, especially among growing businesses and companies. It is registered under the Companies Act, 2013, and is considered a separate legal entity. This type of business entity is owned by a small group of individuals and is established for specific business purposes. Private Limited Companies are particularly popular among startups and businesses with high growth potential due to the limited liability protection they offer to shareholders and the flexibility in ownership and management structures.3

Here are the key features of a Private Limited Company:
 Public Limited Company
Public Limited Company
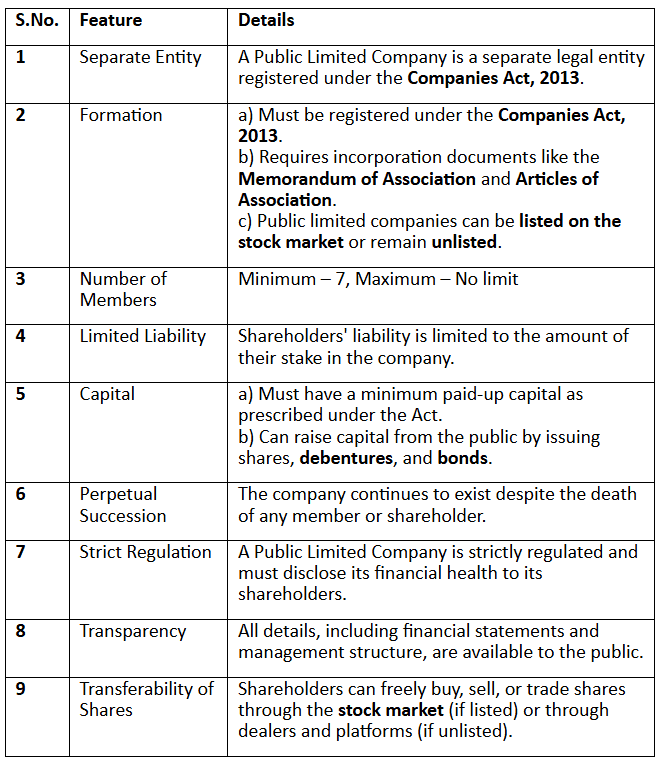
A public limited company is defined under Section 2(71) of the Companies Act, 2013, as a company that is not a private company. This type of company is recognized as a separate legal entity from its owners, meaning it can enter into contracts and agreements in its own name. The company operates independently of its owners, who are referred to as shareholders or stakeholders.
The ownership of a public limited company is divided into shares, which can be held by multiple individuals or corporations. This structure allows the company to raise capital by selling shares to the public. Shareholders have limited liability, meaning their responsibility for the company’s debts and obligations is limited to the amount they invested in shares.
The key features of a public limited company include:
Examples of public limited companies in India include:
- Indian Oil Corporation Ltd.
- Bharat Petroleum Corporation Ltd.
- State Bank of India
Compared to sole proprietorships and partnerships, companies have greater financial resources and can attract capital from the public as well as through loans from banks and financial institutions, allowing for larger expansion potential.
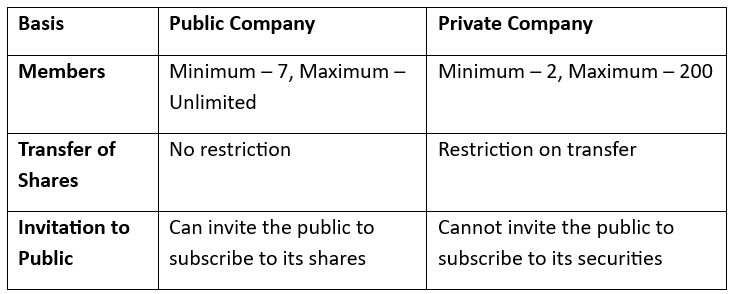
Difference between Public and Private Company
One Person Company (OPC)

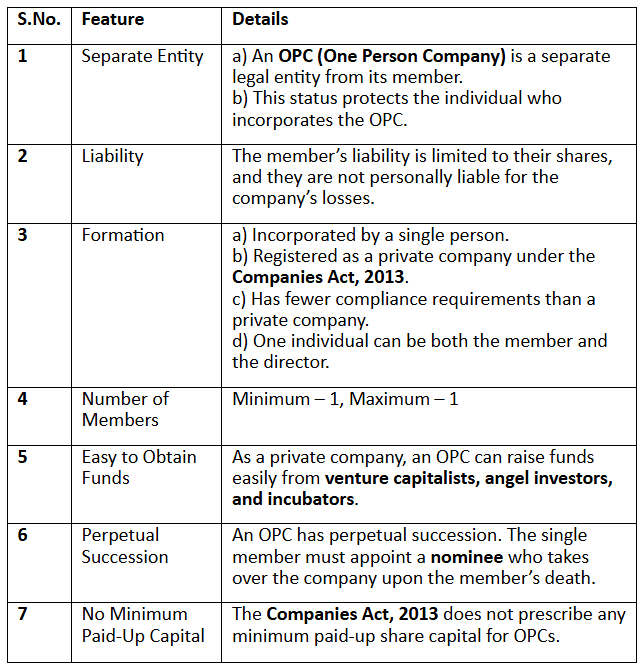
Concept of One Person Company:
According to Section 2(62) of the Companies Act 2013, a "one person company" refers to a company with a single member. This concept was introduced to empower entrepreneurs to establish and manage companies independently.
Comparative Analysis of Different Business Entities
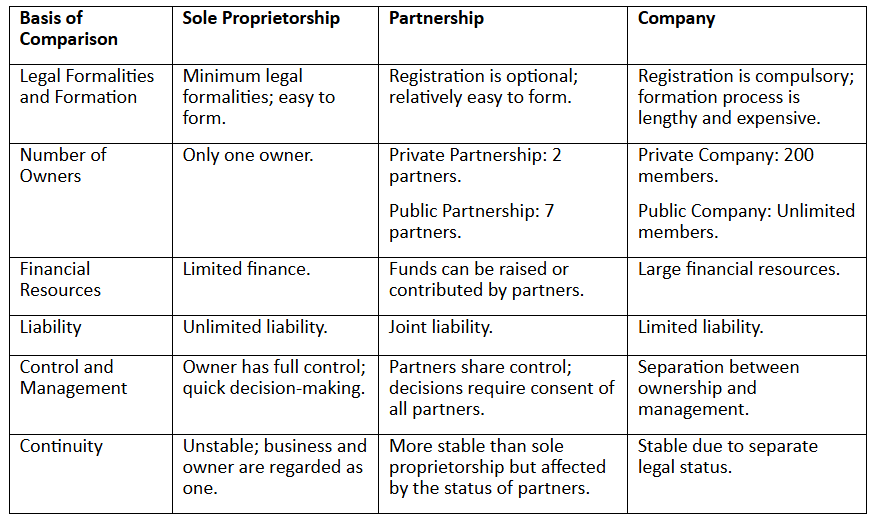
Conclusion
A legal entity is any business or organization that is recognized by law as having certain rights and responsibilities, like the duty to pay taxes. These entities can enter into contracts as a vendor or supplier and have the ability to sue or be sued in court.
Choosing the right business structure is crucial as it affects taxes, funding, paperwork, and personal liability. It’s important to make this decision before registering a business.
|
98 videos|69 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on Forms of Legal Entities Chapter Notes - Legal Studies for Class 12 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What are the different types of legal entities recognized in India? |  |
| 2. How does a Sole Proprietorship differ from a Private Limited Company? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of forming a Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) in India? |  |
| 4. What factors should be considered when choosing a business entity in India? |  |
| 5. How does the taxation of a Private Limited Company differ from that of a Partnership Firm? |  |















