Introduction to Problem Solving NCERT Solutions | Computer Science for Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Q1: Write pseudocode that reads two numbers and divide one by another and display the quotient.
Ans:
Input number_1Input number_2
IF number_2 == 0 Then
Print "Division by ZERO is not allowed"
ELSE
quotient = number_1 / number_2
Print quotient
END IF
Ans:
SET p1 = 0SET p2 = 0
For i in range(5):
INPUT coin_number
IF coin_number is 1 THEN
p1 = p1 + 1
ELSE IF coin_number is 2 THEN
p2 = p2 + 1
IF p1 > 2 THEN
PRINT "Player 1 wins"
Break
ELIF p2 > 2 THEN
PRINT "Player 2 wins"
Break
Q3: Write the pseudocode to print all multiples of 5 between 10 and 25 (including both 10 and 25).
Ans:
FOR number = 10 to 25
IF number MOD 5 == 0 THEN
Print number
END IF
Q4: Give an example of a loop that is to be executed a certain number of times.
Ans:
FOR number = 11 to 25
Print number
Q5: Suppose you are collecting money for something. You need ₹ 200 in all. You ask your parents, uncles and aunts as well as grandparents. Different people may give either ₹ 10, ₹ 20 or even ₹ 50. You will collect till the total becomes 200. Write the algorithm.
Ans:
SET CollectMoney = 0
WHILE CollectMoney < 200 DO
INPUT money
CollectMoney = CollectMoney + money
END LOOP
Q6: Write the pseudocode to print the bill depending upon the price and quantity of an item. Also print Bill GST, which is the bill after adding 5% of tax in the total bill.
Ans:
Input price_per_unit
Input quantity
Bill_without_GST = price_per_unit * quantity
Print Bill_without_GST
gst = Bill_without_GST * 5/100
Bill_with_GST = Bill_without_GST + gst
Print Bill_with_GST
Q7: Write pseudocode that will perform the following:
(a) Read the marks of three subjects: Computer Science, Mathematics, and Physics, out of 100
(b) Calculate the aggregate marks
(c) Calculate the percentage of marks
Ans:
Input CS_Marks
Input Math_Marks
Input Physics_Marks
Aggr_Marks = CS_Marks + Math_Marks + Physics_Marks
Print Aggr_Marks
percentage = Aggr_Marks/300 * 100
Print percentage
Q8: Write an algorithm to find the greatest among two different numbers entered by the user.
Ans:
Input num_1
Input num_2
IF num_1 > num_2 THEN
Print num_1
ELSE IF num_1 < num_2 THEN
Print num_2
Q9: Write an algorithm that performs the following:
Ask a user to enter a number. If the number is between 5 and 15, write the word GREEN. If the number is between 15 and 25, write the word BLUE. if the number is between 25 and 35, write the word ORANGE. If it is any other number, write that ALL COLOURS ARE BEAUTIFUL.
Ans:
Input num_1
IF num_1 >= 5 AND num_1 <= 15 THEN
Print "GREEN"
ELSE IF num_1 > 15 AND num_1 <= 25 THEN
Print "BLUE"
ELSE IF num_1 > 25 AND num_1 <= 35 THEN
Print "ORANGE"
ELSE
Print "ALL COLOURS ARE BEAUTIFUL"
Q10: Write an algorithm that accepts four numbers as input and find the largest and smallest of them.
Ans:
Input n1
Input n2
Input n3
Input n4
IF n1 > n2 AND n1 > n3 AND n1 > n4 THEN
Print n1
ELSE IF n2 > n1 AND n2 > n3 AND n2 > n4 THEN
Print n2
ELSE IF n3 > n1 AND n3 > n2 AND n3 > n4 THEN
Print n3
ELSE IF n4 > n1 AND n4 > n2 AND n4 > n3 THEN
Print n4
Q11: Write an algorithm to display the total water bill charges of the month depending upon the number of units consumed by the customer as per the following criteria:
- for the first 100 units @ 5 per unit
- for next 150 units @ 10 per unit
- more than 250 units @ 20 per unit
Also add meter charges of 75 per month to calculate the total water bill .
Ans:
Input number_of_units
bill = 0
IF number_of_units <=100 THEN
bill = number_of_units * 5
ELSE IF number_of_units > 100 AND number_of_units <=250 THEN
bill = (number_of_units-100) * 10 + 500
ELSE IF number_of_units > 250 THEN
bill = (number_of_units - 250) * 20 + 2000
bill = bill + 75
Print bill
Q12: What are conditionals? When they are required in a program?
Ans: Conditional statements in Python are required to execute the code based on the output of the condition. They help check possibilities in a program. The program evaluates one or more conditions and performs operations depending on whether the condition is true or false.
Q13: Match the pairs Ans:
Ans: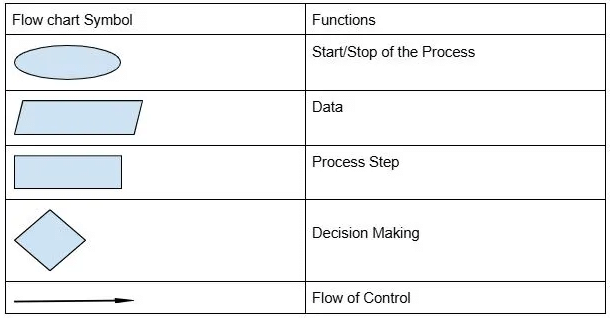
Q14: Following is an algorithm for going to school or college. Can you suggest improvements in this to include other options?Reach_School_Algorithm
(a) Wake up
(b) Get ready
(c) Take lunch box
(d) Take bus
(e) Get off the bus
(f) Reach school or college
Ans:
(a) Wake up
(b) Thank GOD for the beautiful morning
(c) Brush teeth
(d) Wear uniform
(e) Eat breakfast
(f) Take lunch box
(g) Take I-Card
(h) Say Bye to Parents
(i) Go to Bus Stop
(j) Take bus
(k) Get off the bus
(l) Reach school or college
Q15: Write a pseudocode to calculate the factorial of a number (Hint: Factorial of 5, written as 5! = 5 × 4 ×3 ×2×1) .
Ans:
Factorial=1
input Num1
IF(Num1==0) THEN
Factorial=1
ELSE
WHILE(Num1!=0) DO
Factorial=Factorial*Num1
Number=Number-1
END WHILE
END IF
Print Factorial
Q16: Draw a flowchart to check whether a given number is an Armstrong number. An Armstrong number of three digits is an integer such that the sum of the cubes of its digits is equal to the number itself. For example, 371 is an Armstrong number since 3**3 + 7**3 + 1**3 = 371.
Ans: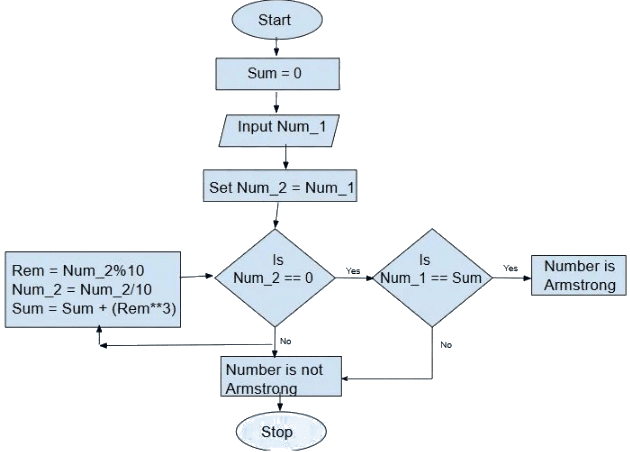
Q17: Following is an algorithm to classify numbers as
“Single Digit”, “Double Digit” or “Big”.
Classify_Numbers_Algo
Verify for (5, 9, 47, 99, 100 200) and correct the algorithm if required
Ans:
Verification for Input Numbers:
For 5:
Output: “Single Digit” #Correct Output
For 9:
Output: “Double Digit” #Wrong Output
For 47:
Output: “Double Digit” #Correct Output
For 99:
Output: “Big” #Wrong Output
For 100:
Output: “Big” #Correct Output
For 200:
Output: “Big” #Correct Output
Correct Algorithm is given below:
INPUT Number
IF Number ≤ 9
"Single Digit"
Else IF Number ≤ 99
"Double Digit"
Else
"Big"
Q18: For some calculations, we want an algorithm that accepts only positive integers upto 100.
Accept_1to100_Algo
INPUT Number
IF (0<= Number) AND (Number <= 100)
ACCEPT
Else
REJECT
(a) On what values will this algorithm fail?
(b) Can you improve the algorithm?
Ans:
(a) Algorithm will fail for value 0(ZERO)
(b) Correct algorithm is
Accept_1to100_Algo
INPUT Number
IF (0< Number) AND (Number <= 100)
ACCEPT
Else
REJECT
|
33 docs|11 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction to Problem Solving NCERT Solutions - Computer Science for Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is the importance of problem-solving skills in academics? |  |
| 2. How can students improve their problem-solving abilities? |  |
| 3. What are some common problem-solving strategies? |  |
| 4. How does problem-solving relate to real-life situations? |  |
| 5. Can problem-solving skills be developed over time? |  |
















