Morning Star Textbook Solutions: Location, Extent, Physical features of India-Map Study | Geography Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
Answer the following questions
Q1(a): Give two differences between the Eastern Coastal Plains and the Western Coastal Plains.
Ans: 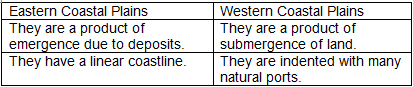
Q1(b): What kind of mountains are the Himalayas? By what name are the offshoots of the Eastern Himalayas known?
Ans: The Himalayas are classified as active fold mountains. The offshoots of the Eastern Himalayas include the Darjeeling Himalaya, Sikkim Himalaya, Bhutan Himalaya, and Arunachal Himalaya.
Q1(c): Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i) The rivers of south India are less suitable for irrigation than the rivers of north India.
(ii) The Peninsular Plateau of India is considered to be a part of Gondwanaland hundreds of millions of years ago.
(iii) The Narmada and Tapi do not form deltas.
Ans:
(i) The rivers of South India are less suitable for irrigation than those in North India because Northern rivers are perennial, fed by snow, while Southern rivers are seasonal and rain-fed.
(ii) The Peninsular Plateau is viewed as part of Gondwanaland due to the similarity in rock types, ages, and sequences found in both regions, resulting from tectonic movements.
(iii) The Narmada and Tapi rivers do not create deltas as they flow over hard rocks and lack the ability to form distributaries before reaching the Arabian Sea.
Q1(d): State how the Northern Plains were formed.
Ans: The Northern Plains were formed by the alluvial deposits brought by three major rivers: the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra, along with their tributaries. Over millions of years, alluvium was deposited at the foothills of the Himalayas, resulting in the fertile Northern Plains.
Q2(a): Give two differences between the Plains of North India and the Coastal Plains.
Ans:
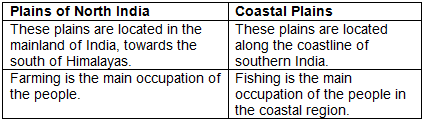
Q2(b): Name two rivers of the Peninsular Plateau that flow towards the Arabian Sea. Name two rivers that flow into the Bay of Bengal.
Ans: Rivers in the Peninsular Plateau that flow towards the Arabian Sea include Narmada and Tapi. Meanwhile, rivers flowing into the Bay of Bengal include Mahanadi and Godavari.
Q2(c): Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i) Less land is available for agriculture on the West Coast than on the East Coast.
(ii) Access through the Western Ghats is difficult.
(iii) The Peninsular Plateau of India is rich in mineral resources.
Ans:
(i) The West Coast has less land available for agriculture due to its narrower coastal plains, while the Eastern Coastal Plains are wider and fertile due to river deltas.
(ii) The Western Ghats present accessibility challenges because of their high elevation, ranging from 900 to 1600 meters, and their continuous nature, allowing crossings only through specific passes.
(iii) The Peninsular Plateau is mineral-rich as it consists of basaltic lava and lava sheets, which are abundant in minerals.
Q2(d): (i) Name the four parts of the Peninsular Plateau of India.
(ii) Name the landforms that form the boundaries of the Peninsular Plateau.
Ans:
(i) The four parts of the Peninsular Plateau of India are:
- The Central Plateaus
- The Eastern Plateaus
- The Kathiawar and Kutch
- The Deccan Plateau
(ii) The boundaries of the Peninsular Plateau are formed by:
- The Aravali range in the northwest
- The Bundelkhand plateau in the extreme north
- The Western Ghats in the west
- The Eastern Ghats in the east
Q3(a): Give two differences between Eastern Ghats and Western Ghats.
Ans: 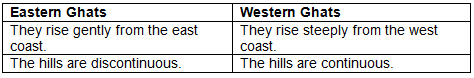
Q3(b): Name the source of the river Ganga. Where does this river enter the plains?
Ans: The source of the river Ganga is the Gangotri glacier in the Himalayas, and it enters the plains at Haridwar, Uttarakhand.
Q3(c): Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i) The Northern Plains of India are one of the most densely populated regions of the world.
(ii) The Deccan Plateau is an example of a dissected plateau.
(iii) The rivers of South India are easier to tap for power than the rivers of north India.
Ans:
(i) The Northern Plains are densely populated due to their fertile soil, abundant rivers, and favorable climate that support agriculture.
(ii) The Deccan Plateau is termed a dissected plateau as it features several seasonal rivers that have eroded the landscape, creating valleys.
(iii) South Indian rivers are more efficient for power generation because they have significant waterfalls and less silt due to their flow over igneous rocks.
Q3(d): (i) Name any two left bank tributaries of the Ganga.
(ii) Is Ganga a perennial river? Give reason.
Ans:
(i) Two left bank tributaries of the Ganga are Gomti and Ghaghra.
(ii) Yes, the Ganga is a perennial river as it flows continuously throughout the year, receiving water from rain, melting ice in summer, and snow in winter.
Q4(a): Give two differences between rivers of Northern India and the rivers of Southern (Peninsular) India.
Ans: 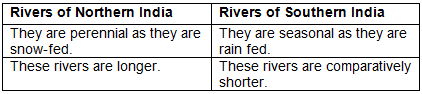
Q4(b): Name the only significant river of the Rajasthan Plains. Name the largest river island in the world.
Ans: The only significant river in the Rajasthan Plains is the Luni. The largest river island in the world is Majuli.
Q4(c): Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i) Most of the rivers in South India flow into the Bay of Bengal.
(ii) The Rann of Kutch is not cultivated.
(iii) The Rajasthan Plains are an area of inland drainage.
Ans:
(i) Most South Indian rivers flow into the Bay of Bengal due to the gentle eastward slope of the Peninsular Plateau, facilitating their flow from higher to lower elevations.
(ii) The Rann of Kutch is not cultivated as it is a marshy area with saline water that is not suitable for agriculture.
(iii) The Rajasthan Plains represent inland drainage as the rivers lack sufficient water to reach the sea, often drying up or disappearing into the sand.
Q4(d): (i) How is cultivation carried out in the Rajasthan Plains?
(ii) Name the fertile tracts of these plains.
Ans:
(i) Agriculture is practiced in small patches, utilizing water from seasonal streams that flow from the Aravali range during the rainy season.
(ii) The fertile tracts in these plains are known as Rohi.
|
33 videos|148 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on Morning Star Textbook Solutions: Location, Extent, Physical features of India-Map Study - Geography Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What is the geographical location of India in relation to other countries? |  |
| 2. What are the major physical features of India? |  |
| 3. How does the extent of India affect its climate? |  |
| 4. What role do rivers play in the geography of India? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the Himalayas in India's geography? |  |
















