Morning Star Textbook Solutions: Waste Management-I | Geography Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
Choose the correct option
Q1: Any material that is discarded after it has served its purpose and is no longer useful is called _______.
(a) compost
(b) waste
(c) manure
(d) pathogen
Ans: (b) waste
Q2: Any material that is rendered useless during or left over in a manufacturing process is called _______.
(a) industrial waste
(b) domestic waste
(c) commercial waste
(d) mining waste
Ans: (a) industrial waste
Q3: Which of the following is NOT a toxic substance present in e-waste?
(a) Cadmium
(b) Lead
(c) Mercury
(d) Methane
Ans: (d) Methane
Q4: The process of depletion of oxygen from water bodies occurring either naturally or due to human activities is called _______.
(a) Biomagnification
(b) Oxygenation
(c) Eutrophication
(d) Acid rain
Ans: (c) Eutrophication
Q5: The increase in the number of phytoplankton and algae reduces the penetration of _______, light and heat into the water body.
(a) small fish
(b) nitrogen
(c) oxygen
(d) carbon dioxide
Ans: (c) oxygen
Q6: Domestic waste being organic in nature undergoes _______and creates conditions favorable for the growth of pathogens.
(a) fermentation
(b) nitrification
(c) magnification
(d) oxygenation
Ans: (a) fermentation
Q7: _______is a harmful toxin that affects the development of a child's brain.
(a) Zinc
(b) Lead
(c) Mercury
(d) Cadmium
Ans: (b) Lead
Q8: _______is a chemical that is said to cause cancer.
(a) Arsenic
(b) Calcium
(c) Cadmium
(d) Lead
Ans: (a) Arsenic
Q9: The increase in the concentration of various toxic substances along the food chain is called _______.
(a) Bio-accumulation
(b) Demagnification
(c) Biomagnification
(d) Eutrophication
Ans: (c) Biomagnification
Q10: The phenomenon of concentrated toxic deposition at the higher trophic level is known as _______.
(a) Biodegradation
(b) Bio-accumulation
(c) Eutrophication
(d) Biodegradation
Ans: (b) Bio-accumulation
Q11: The accumulation of toxins will be higher in which of the following?
(a) Water
(b) Algae
(c) Small fish
(d) Big fish
Ans: (d) Big fish
Q12: Waste accumulation is a breeding ground for _______like flies, mosquitoes, rodents and pet animals.
(a) hectors
(b) vectors
(c) spreaders
(d) carriers
Ans: (b) vectors
Q13: Which of the following diseases are NOT spread by houseflies?
(a) Typhoid
(b) Diarrhea
(c) Cholera
(d) Amoebiosis
Ans: (d) Amoebiosis
Q14: The warming of the atmosphere due to the increased concentration of Greenhouse Gases is known as _______.
(a) Global Warming
(b) Climate change
(c) Radiation
(d) Acid rain
Ans: (a) Global Warming
Q15: Hepatitis, diarrhea and corona are _______diseases.
(a) bacterial
(b) viral
(c) fungal
(d) None of the above
Ans: (b) viral
Answer the following questions
Q1(a): What is waste? Name two sources of waste.
Ans: Waste refers to any material that is discarded after it has served its purpose and is no longer useful.
Two sources of waste include:
- Domestic waste, such as food scraps and bits of paper.
- Industrial waste, including materials like paints, sand, and fly ash.
Q1(b): How is the 'use and throw' concept responsible for the increase in waste generation?
Ans: The 'use and throw' concept implies using products only once and then disposing of them. For instance, when we buy a pen and throw it away once the ink is finished, rather than purchasing a refill. If many people adopt this behavior, it leads to a significant increase in waste volume. Thus, this concept contributes to greater waste generation.
Q1(c): What is acid rain? State its impact on the environment.
Ans: Acid rain refers to rainwater that contains excessive acids. This occurs when burning fossil fuels like coal and petroleum releases sulfur and nitrogen, which react with oxygen to form sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide. These gases then combine with water vapor to create acids that fall as rain.
Impacts of acid rain on the environment include:
- Increasing soil acidity, which harms forests and crops.
- Corroding buildings, monuments, and infrastructure.
- Contaminating air and water, posing health risks.
- Adversely affecting aquatic life.
- Harming plant growth, leading to leaf damage.
Q1(d): What is meant by ozone layer depletion? How is it harmful?
Ans: Ozone layer depletion refers to the thinning of the ozone layer in the upper atmosphere, primarily caused by chlorine and bromine compounds that destroy ozone molecules.
This is harmful as the ozone layer protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet rays. When depleted, these rays can reach the surface, leading to:
- Skin cancer and cataracts in humans.
- Genetic disorders affecting heredity.
- Disruptions in marine ecosystems.
- Damage to complex chemical substances.
Q2(a) What is E-waste? Why is it increasing at a fast rate?
Ans: E-waste, or electronic waste, encompasses discarded electronic devices that are no longer useful due to obsolescence, replacement, or damage.
The rapid advancement of information technology leads to the production of new electronics at a high rate, resulting in an increase in obsolete devices. E-waste is one of the fastest-growing waste types, making up over 5% of all municipal solid waste.
Q2(b): Explain briefly how industrial waste reaches human beings and affects their health.
Ans: Industries producing chemicals and other materials generate various waste products. Smoke from factories contains harmful particles that pollute the air. For instance, burning sulfur in coal releases sulfur dioxide, which can lead to acid rain and health hazards.
Additionally, industrial waste can contaminate water bodies through direct discharge or leaching, making the water unsafe for consumption and causing health issues in humans and animals.
Q2(c): Name two toxic particulate materials. State the effect of each on human health.
Ans:
- Lead: It can affect the blood system, cause behavioral disorders, and potentially lead to death.
- Nickel: It is associated with respiratory issues and lung cancer.
Q2(d): Give two differences between toxic and non-toxic waste.
Ans: 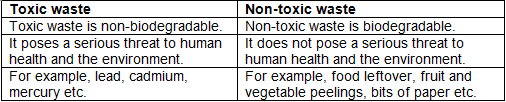
Q3(a): Explain how eutrophication affects aquatic life.
Ans: Eutrophication is the depletion of oxygen in water bodies caused by excess nutrients, either from natural sources or human activities.
Under normal conditions, phytoplankton and algae utilize carbon dioxide and nutrients for food, which supports aquatic life. However, an overabundance of nutrients leads to excessive algae growth, which reduces oxygen levels in the water and can cause the death of aquatic organisms.
Q3(b): What harm is done by dumping waste near water bodies?
Ans: Dumping waste near water sources leads to contamination of the water, resulting in toxic accumulation. This can cause various waterborne diseases such as typhoid and cholera if the contaminated water is consumed without treatment.
Q3(c): Give a reason for each of the following:
(i) Marine animals and turtles are found dead in many coastal areas.
(ii) Radioactive waste is more harmful than other waste.
(iii) Uncontrolled burning of waste causes air pollution.
Ans:
(i) Marine animals and turtles die due to ingesting plastic debris that pollutes the ocean, leading to blockages in their digestive systems.
(ii) Radioactive waste is extremely harmful as it releases radiation that can cause long-term environmental harm and health issues for centuries.
(iii) Uncontrolled burning of waste emits smoke and toxic pollutants into the air, contributing to air pollution and respiratory health problems.
Q3(d): What is biomagnification? What can be its effects on humans?
Ans: Biomagnification refers to the increasing concentration of toxic substances in organisms at successively higher levels of the food chain.
For instance, small amounts of toxins in water can accumulate in algae, which are then consumed by fish, leading to higher concentrations of toxins in the fish. When humans consume these fish, they can suffer from various health issues due to the accumulated toxins.
Q4(a): Name two diseases which occur because of waste accumulation on land.
Ans: Two diseases caused by waste accumulation on land include:
- Malaria
- Dengue
Q4(b): Name two common diseases caused as a result of gaseous pollution.
Ans: Two common diseases caused by gaseous pollution include:
- Bronchitis
- Lung cancer
Q4(c): Name three water-borne diseases.
Ans: Three water-borne diseases are:
- Typhoid
- Cholera
- Hepatitis
Q4(d): Explain briefly the need for management of waste.
Ans: Waste management is crucial as waste remains in the environment and can cause harm. Rapid population growth has exacerbated waste issues, leading to pollution of air, soil, and water. Improper waste management results in environmental degradation. Thus, effective waste management is essential to mitigate these issues and protect ecosystems.
Q5(a) Why is the handling of solid wastes a major problem?
Ans: Handling solid waste poses challenges as many disposal methods harm the environment. Open dumps can leak toxins into soil and water, while burning waste releases harmful pollutants into the air, leading to health hazards. Additionally, scavengers and animals can spread waste over large areas, increasing the risk of disease.
Q5(b): Name the gas produced by the decomposition of accumulated waste. Why is this gas harmful?
Ans: Methane is a gas produced from the decomposition of accumulated waste. It is highly flammable and can lead to explosions if not managed properly.
Q5(c): Give a reason for each of the following:
(i) 'Use and throw' concept generates more waste.
(ii) Run off from fields leads to death in adjacent water bodies.
(iii) Birds feeding on agricultural waste are at the brink of extinction.
Ans:
(i) The 'use and throw' concept increases waste generation because it encourages single-use products, leading to more disposals and less recycling.
(ii) Runoff from fields often contains fertilizers and pesticides, which contaminate nearby water bodies, harming aquatic life and disrupting ecosystems.
(iii) Birds that feed on agricultural waste are declining because such waste can lead to thinner egg shells and increased mortality rates among young birds.
Q5(d): What is Global Warming? Name any two Greenhouse Gases?
Ans: Global warming refers to the increase in the Earth's average temperature due to elevated levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Two greenhouse gases include:
- Carbon dioxide
- Methane
Thinking Skills
Q1: According to a World Bank Report, global waste will increase by 70 per cent by 2050 unless urgent action is taken. Suggest five measures to reduce accumulation of waste.
Ans: Five measures to reduce accumulation of waste are:
- Implement comprehensive waste reduction and recycling programs to encourage waste separation and divert waste from landfills.
- Adopt extended producer responsibility (EPR) policies to hold manufacturers accountable for product lifecycle and promote sustainable design and disposal practices.
- Transition to a circular economy model that emphasizes reusing, repurposing, and refurbishing products, reducing waste generation.
- Conduct education and awareness campaigns to inform the public about responsible consumption, waste segregation and recycling techniques.
- Promote composting and organic waste management to divert organic waste from landfills and produce nutrient-rich compost for agricultural purposes.
- These measures can help reduce waste accumulation, conserve resources and mitigate the environmental impact of waste generation.
Q2: Waste accumulation is the most visible form of pollution, which creates global environmental challenges. State any three such challenges and their probable remedies.
Ans: Three global environmental challenges and their probable remedies are as follows:
Land and soil pollution
- Both open dumps and landfills may contain toxins that seep into the soil and cause soil pollution. Scavengers and stray animals invade the open garbage dumps and spread the waste over a large area, thereby, spreading germs and diseases as well as destroying the beauty of the place.
Remedy
- Implement strict waste management practices, including proper landfill design, lining, and leachate collection systems.
- Promote waste reduction, recycling, and composting to minimize the amount of waste sent to landfills.
Air pollution
- Improper waste incineration and open burning release harmful pollutants into the air, contributing to air pollution and respiratory health issues. As accumulated waste decomposes, it produces a large quantity of methane gas. This is highly inflammable, and can cause an explosion if not managed properly.
Remedy
- Promote waste-to-energy technologies that use proper incineration methods and emissions control systems.
- Encourage the adoption of cleaner energy sources and waste management strategies that prioritize recycling and composting over incineration.
Water pollution
- Water pollution occurs when people discharge large amount of waste into water bodies, and the natural cleansing process in the water bodies cannot function properly. The process of eutrophication takes place due to introduction of nutrients and chemicals through discharge of domestic sewage, industrial effluents and fertilizers from agricultural fields. This causes death of most of the aquatic organisms, draining water of all its oxygen.
Remedy
- Implement effective waste management systems, including proper waste collection, recycling, and awareness campaigns to discourage littering.
- Encourage the use of reusable and sustainable materials to reduce plastic waste.
|
33 videos|148 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on Morning Star Textbook Solutions: Waste Management-I - Geography Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What are the main environmental impacts of waste accumulation? |  |
| 2. How does waste accumulation affect human health? |  |
| 3. What are the strategies to manage waste accumulation effectively? |  |
| 4. Why is recycling important in reducing waste accumulation? |  |
| 5. What role do individuals play in combating waste accumulation? |  |
















