Morning Star Textbook Solutions: Transport | Geography Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
Choose the correct option
Q1: India has the _______ largest road network in the world.
(a) second
(b) third
(c) fourth
(d) sixth
Ans: (a)
Q2: _______ are the backbone of road infrastructure in India.
(a) Border Roads
(b) Expressways
(c) National Highways
(d) State Highways
Ans: (c)
Q3: Which of the following is the longest National Highway in India?
(a) NH 77
(b) NH 7
(c) NH 5
(d) NH 2
Ans: (b)
Q4: What percentage of road traffic is handled by the National Highways?
(a) 10 per cent
(b) 20 per cent
(c) 35 per cent
(d) 40 per cent
Ans: (d)
Q5: Which of the following is an important difference between a Highway and an Expressway?
(a) Presence of multiple roads on an Expressway.
(b) Controlled access through absence of multiple roads on an Expressway.
(c) Presence of large number of intersections on an Expressway.
(d) All of the above.
Ans: (b)
Q6: The North South corridor connects _______.
(a) Porbandar to Silchar
(b) Mumbai to Odisha
(c) Srinagar to Kanyakumari
(d) Lucknow to Ghazipur
Ans: (c)
Q7: The two terminal points of East-West corridor are _______.
(a) Porbandar and Silchar
(b) Mumbai and Dispur
(c) Ahmedabad and Imphal
(d) Surat and Gangtok
Ans: (a)
Q8: Which mode of transport allows farmers to move their perishable products quickly to the markets?
(a) Railways
(b) Airways
(c) Roadways
(d) Waterways
Ans: (c)
Q9: The railways are divided into _______ which are the basic operating units.
(a) 20 routes
(b) 18 circles
(c) 20 zones
(d) 18 zones
Ans: (d)
Q10: The railway track system is based on which of the following?
(a) Width of the track
(b) Length of the track
(c) Route of the track
(d) Load of the track
Ans: (a)
Q11: Which of the tracks is called the India gauge?
(a) Narrow Gauge
(b) Metre Gauge
(c) Broad Gauge
(d) All of the above
Ans: (c)
Q12: The distance between rails in a metre gauge is _______.
(a) 1.67 m
(b) 1 m
(c) 0.762 m
(d) 2 m
Ans: (b)
Q13: Suburban trains that handle commuter traffic in cities are mostly _______.
(a) Diesel Multiple Units (DMUs)
(b) Coal Multiple Units (CMUs)
(c) Electric Multiple Units (EMUs)
(d) Solar Panel Units (SPUs)
Ans: (c)
Q14: The rivers of Peninsular India are not ideal for inland waterways because they are marked by number of _______.
(a) Estuaries
(b) Waterfalls
(c) Stones and silt on the river beds
(d) Tributaries
Ans: (b)
Q15: Which of the following is an advantage of airways?
(a) Ease of crossing difficult terrain
(b) Dependency on weather conditions
(c) Carriage of low tonnage
(d) Fuel used is petroleum
Ans: (a)
Q16: Inland waterways are _______ and _______.
(a) Expensive; inaccessible
(b) Cheap; environment friendly
(c) Cheap; carry low tonnage
(d) Cheap; easily cross barriers.
Ans: (b)
Ans: the following questions
Q1(a): Name the types of roads used in India. Which agency is responsible for maintenance of each category separately?
Ans: The types of roads used in India are as follows-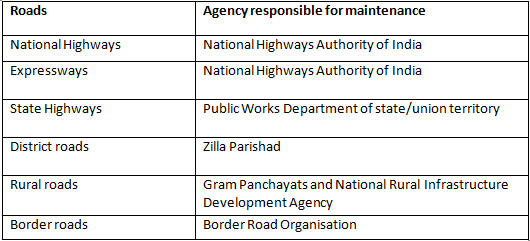
Q1(b): Name the two major projects developed by NHAI.
Ans: Two major projects developed by NHAI are-
- Golden Quadrilateral
- North-South and East-West Corridors
Q1(c): Transport is the backbone of a country's economy. Give reasons to support your Answer.
Ans: Transport is the backbone of a country's economy because of the following reasons-
- Transportation helps in the better utilisation of the resources of the backward areas by linking them with the more advanced areas.
- It aids in the process of industrialisation and urbanisation.
- It removes scarcity of goods during any crisis.
- It helps in minimising the effects of natural disasters.
- It brings in homogeneity and National integration in thought and culture through easy movement of people and bringing them in contact with each other.
Q1(d): Why is road transport in India considered more useful than rail transport? Give reasons to support your Answer.
Ans: Road transport in India is considered more useful than rail transport because of the following reasons-
- Roads make every village and hamlet reachable.
- Construction cost of roads is much lower than that of the railway line.
- Roads can be constructed even in the areas of difficult terrain and where railway lines do not exist.
- Roads offer door to door service and thereby, reduce the cost of loading and unloading.
- The movement of goods is safer through road transport as the chances of pilferage are lesser than in the railways.
- Road transport provides link between railway stations and ports and their hinterlands.
Q2(a): What is an expressway? Name one expressway.
Ans: Expressways are highways planned for high-speed traffic, having few intersections, limited points of access or exit and a divider between lanes for traffic moving in opposite directions. They usually have six to eight lanes.
An example is Yamuna Expressway that connects Greater Noida with Agra.
Q2(b): Give two points of difference between highways and expressways.
Ans: 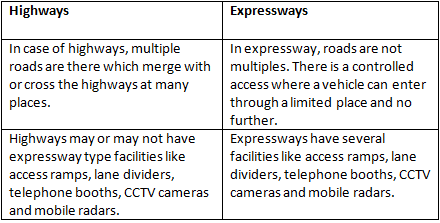
Q2(c): Give two advantages and one disadvantage of railways.
Ans: Two advantages of railways are-
- Railways transport raw materials to the production units and finished goods to the markets.
- Railways help in reducing sufferings during natural calamities.
One disadvantage of railways is that rail transport lacks flexibility of routes. Train tracks cannot be laid in every region of the country like in the hilly areas and the remote forested areas.
Q2(d): Mention any three problems being faced by the Indian Railways.
Ans: Three problems being faced by the Indian Railways are-
- Indian Railways have to play a double role of revenue earning as well as fulfilling the social obligations. This is because the Railways are seen as a commercial organisation on one hand and it is treated as a social organisation on the other hand.
- Railway lines are difficult to construct in the hilly and mountainous parts of India.
- Obsolete trains, tracks and equipment make railway unsafe.
Q3(a): What are National Highways?
Ans: The main roads which are constructed and maintained by the Central Government are known as National Highways. These are main highways running through the length and breadth of the country and are the backbone of road infrastructure.
National Highways in India are designated as NH followed by the State highway numbers.
Q3(b): What is the Golden Quadrilateral Project?
Ans: The Golden Quadrilateral is the largest express highway project in India. It connects India's four largest metropolies: Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata and Chennai and thus, forms a quadrilateral of sorts. Bengaluru, Pune, Ahmedabad and Surat are also served by this network.
Q3(c): Give three economic benefits of the Golden Quadrilateral Project.
Ans: Three economic benefits of the Golden Quadrilateral Project are-
- This highway interconnects many major cities and ports. It provides an impetus to truck transport throughout India.
- It enables the industrial growth of all small towns through which it passes.
- It provides vast opportunities for transport of agricultural produce from hinterland to major cities and ports for export.
Q3(d): Give three points to explain the role of roads in the economic development of the country.
Ans: The role of roads in the economic development of the country can be understood from the following points-
- Roads offer door to door service and thereby, reduce the cost of loading and unloading. Roads also help farmers to move their perishable products quickly to the markets.
- National highways and expressways link various important cities and reduce the time of travel and distance between mega cities.
- Construction cost of roads is much lower than that of the railway lines and roads connect the fields of raw material to industries and markets.
Q4(a): What is the significance of an efficient transport system?
Ans: The significance of an efficient transport system is as follows-
- It brings in homogeneity and National integration in thought and culture through easy movement of people and bringing them in contact with one another.
Q4(b): Name the types of gauges of railways used in India.
Ans: The types of gauges of railways used in India are-
- Broad gauge
- Metre gauge
- Narrow gauge
Q4(c): Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i) Railways bind the economic and cultural life of the country.
(ii) Railways are not common in North-East India.
(iii) North India is better suited for railways and roadways.
Ans:
(i) Railways constitute the principal mode of transportation for freight and passengers. It binds the economic life of the country as Indian railways carry a huge variety of goods ranging from mineral ores, fertilizers, petro-chemicals, agricultural produce, iron and steel. Ports and major urban areas have their own freight lines. Thus, railways help in accelerating the development of industry and agriculture, consequently improving the economic conditions in the country.
Further, the railways bind the cultural life of the country as it brings people together from the farthest corners of the country for conducting business, sightseeing, pilgrimage, education etc.
(ii) The north-eastern part of the country is marked with the presence of big rivers, dissected relief, dense forests, frequent floods, landslides and international frontiers, etc. Since it is difficult to lay railway lines in hilly terrains or remote forested areas, railways are not common in North-East India.
(iii) North India is better suited for railways and roadways because north India has level land with a gradual slope due to the presence of northern plains and it is easier to build roads and lay railway tracks when the land is level and devoid of hilly terrain or remote forested areas.
Q4(d): How is the Indian rail network one of the largest and busiest networks in the world?
Ans: The Indian rail network is one of the largest and busiest networks in the world, transporting over 18 million passengers and more than 2 million tonnes of freight daily. It is the world's largest employer, with more than 1.4 million employees. The railways traverse the length and breadth of the country, covering 7,137 stations over a total route length of more than 66,030 kilometres.
Q5(a): Name the regulatory body looking after air transport in India. State any two of its functions.
Ans: The Airports Authority of India is looking after air transport in India.
Two of its functions are-
- It provides aeronautical communication services in the country.
- It is responsible for creating, upgrading, maintaining and managing civil aviation infrastructure.
Q5(b): Discuss the contribution of Air India in the air transport of India.
Ans: Air India provides international service for both passengers and cargo. It is the 16th largest airline in Asia, serving 50 domestic destinations and 39 international routes and serving over 100 cities.
Q5(c): List two advantages and one disadvantage of air transport in India.
Ans:
Two advantages of air transport in India are-
- It is the fastest and comfortable mode of transport. It connects the far flung and remote areas of the country.
- The speed and ease with which aeroplanes can cross mountain barriers, sandy deserts, large expanses of water or forests make the air transport indispensible.
- One disadvantage of air transport in India is that it is costly.
Q5(d): Give two advantages and one disadvantage of helicopter services over aeroplane services.
Ans: Two advantages of helicopter services over aeroplane services are-
- Helicopters can hover, land and take off in a vertical position due to its small size. Aeroplanes cannot do that.
- Helicopter service provides site-seeing for the tourists and offer a wide variety of services including flying ambulances to hold patients, assistance in loading water to fight giant fires.
- One disadvantage of helicopter services over aeroplane services is that the noise and vibration might cause nausea, pain and motor dysfunction in the passengers. The comfort level is less as compared to an aeroplane.
Q6(a): Explain why India has an extensive network of waterways.
Ans: India has an extensive network of water ways because it has a long indented coastline. India also have a good network of inland waterways as it has numerous rivers, canals, backwaters and creeks. The river Ganga and Brahmaputra are perennial rivers and hence are also used for inland navigation.
Q6(b): Explain the role of oceanic waterways in the transport sector of India's economy.
Ans: Oceanic waterways constitute an important role in the transport sector of India's economy as ocean routes handle 95% of India's foreign trade by volume and about 70% by value. Besides international trade, these routes are also used for transportation between the islands and the rest of the country.
Q6(c): Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i) The Ganga is navigable from its mouth right upto Allahabad.
(ii) The Peninsular rivers are not ideal for inland water transport.
(iii) Mumbai is a harbour and a port.
Ans:
(i) The Ganga is navigable from its mouth right upto Allahabad because of the following reasons-
- Ganga is a perennial river fed by monsoon rains in the rainy season and melting of snow on the lofty mountains during dry season.
- It is joined by Yamuna, Son, Ramaganga, Gomti, Ghagra, Gandak and Kosi which increase the depth of water in Ganga, which is more than 10 metres up to Allahabad.
- The slope of the Ganga is gradual and the river bed is free from stones and silt.
(ii) The Peninsular rivers are not ideal for inland water transport because of the following reasons-
- These rivers are seasonal as they are rain-fed.
- These rivers are comparatively shorter than the rivers of northern India.
- These rivers are marked by a number of waterfalls.
(iii) When natural harbours have all the facilities of ports they serve as ports. Mumbai is a harbour as it is surrounded by land on most sides but has an entrance point to the Arabian sea. It is also a port as it has facilities for loading and unloading of cargo ships as well as buildings and warehouses for storing goods and well built transport system.
Q6(d): Give two advantages and one disadvantage of water transport.
Ans: Two advantages of water transport are-
- Inland water transport mode is environment friendly and cost effective mode of transport.
- It is most suitable for carrying heavy and bulky material.
- One disadvantage of water transport is that it depends on weather conditions.
Q7(a): What are the two prerequisites of waterways to be navigable?
Ans: The two prerequisites of waterways to be navigable are-
- Regular flow of water
- Appropriate depth in which the craft can sail easily.
Q7(b): Give two points of difference between Inland Waterways and Oceanic Waterways.
Ans:
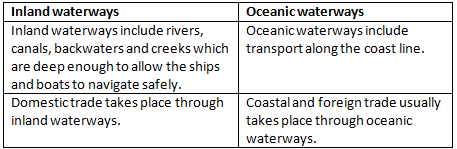
Q7(c): Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i) Nearly 70 percent of Indians do not use air transport.
(ii) A well-developed transport network is important for industrial progress.
(iii) Airways are quite useful during natural calamity.
Ans:
(i) Nearly 70 percent of Indians do not use air transport because air transport is very costly as compared to roadways and railways, depends on weather conditions and it has high freight rates.
(ii) A well-developed transport network is important for industrial progress because it helps in connecting one part of the country with the other. It facilitates movement of raw material, fuel, machinery etc., to the points of production and finished goods to the points of marking and consumption. Thus, a well developed transport network is essential for industrialisation and urbanisation.
(iii) Airways are quite useful during natural calamity because it can be used to air-lift people from the affected areas and to air-drop food, medicines and other necessary things to calamity affected people.
Q7(d): (i) Give two points of difference between a Port and a Harbour.
(ii) On which river and between which two places does the National Waterway No.2 lie?
Ans:
(i) Two points of difference between a port and a harbour are-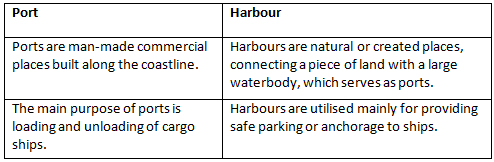
(ii) National Waterway No. 2 lies on Brahmaputra river and connects the North-East region with Kolkata and Haldia ports through Bangladesh and Sunderbans waterways.
Thinking Skills
Q1: In India, latest technologies and improved management techniques are being used to establish a highly developed network of roads. This has led to a rapid increase in the number of vehicles on the road, which in turn lead to a sharp increase in pollution levels, especially in cities. Do you think we should halt the process of making new roads, bridges and tunnels to check the increase in vehicular pollution? Give reasons to support your answer.
Ans:
The issue of increasing vehicular pollution is indeed a significant concern in many cities of India. While it's important to address this problem, completely halting the construction of new roads, bridges, and tunnels may not be the most practical solution because of the following reasons:
- Economic growth and development rely on well-connected infrastructure, making it necessary to construct new roads, bridges, and tunnels.
- Effective traffic management measures like improved public transportation and congestion charges can alleviate pollution without halting infrastructure projects.
- Implementing stricter environmental regulations and vehicle emission standards can reduce pollution levels without stopping infrastructure development.
- Sustainable urban planning and design, such as pedestrian-friendly areas and dedicated cycling lanes, can promote alternative modes of transportation.
- Incorporating green infrastructure elements alongside road networks can improve air quality and mitigate pollution. Balancing economic growth and environmental sustainability requires a comprehensive approach.
Q2: Instead of developing road transport, India should focus more on the development of Metro rail. Do you agree with this statement? Give reasons to support your view.
Ans:
While it's essential to consider a balanced transportation approach, focusing more on the development of Metro rail in India can offer several advantages:
- Efficient and sustainable — Metro rail systems consume less energy, produce fewer emissions, and can transport a large number of passengers at once.
- Reduced congestion — Metro rail networks can lead to smoother traffic flow, reduced travel time, and improved overall efficiency of the transportation system.
- Improved connectivity — Metro rail systems can enhance connectivity within cities and regions.
- Safety and reliability — Metro rail networks are designed with safety measures, reducing the risk of accidents compared to road transport.
- Space utilization — Metro rail systems require less physical space compared to road networks.
|
33 videos|86 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on Morning Star Textbook Solutions: Transport - Geography Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What are the key concepts covered in the Transport Class 10 syllabus? |  |
| 2. How can students effectively study for the Transport exam in Class 10? |  |
| 3. What types of questions are commonly asked in the Transport Class 10 exam? |  |
| 4. What role does technology play in modern transportation systems? |  |
| 5. How does transportation contribute to economic development? |  |





















