Morning Star Textbook Solutions: Manufacturing Industries in India-Agro Based | Geography Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
Choose the correct option
Q1: India is one of the top _______ industrialised countries.
(a) five
(b) seven
(c) eight
(d) ten
Ans: (d)
Q2: The products of agro-based industries mostly consist of _______ .
(a) consumer goods
(b) medicinal goods
(c) beverages
(d) cosmetics
Ans: (a)
Q3: _______ industries are also known as household industries.
(a) Basic
(b) Cottage
(c) Cooperative
(d) Village
Ans: (b)
Q4: Iron and steel industry and petroleum industry are the _______ industries.
(a) Tertiary
(b) Ancillary
(c) Secondary
(d) Basic
Ans: (d)
Q5: _______ are the industries which provide public utility based services.
(a) Basic Industries
(b) Cooperative Industries
(c) Ancillary Industries
(d) Tertiary Industries
Ans: (d)
Q6: Railways, Banking, Post and Telegraph industries are _______ industries.
(a) Basic
(b) Cooperative
(c) Ancillary
(d) Tertiary
Ans: (d)
Q7: _______ is used for producing steam which is used as a source of power for sugar industry.
(a) Molasses
(b) Bagasse
(c) Press mud
(d) Khandsari
Ans: (b)
Q8: _______ are used for the distillation of liquor and to produce some chemicals and synthetic rubber.
(a) Molasses
(b) Bagasse
(c) Press mud
(d) Khandsari
Ans: (a)
Q9: Which of the following is a by-product of sugar industry used for making cardboard, paper and insulation boards?
(a) Molasses
(b) Bagasse
(c) Press mud
(d) All of the above.
Ans: (d)
Q10: Name the by-product of sugar industry used for making wax, carbon paper and shoe polish.
(a) Molasses
(b) Bagasse
(c) Press mud
(d) Khandsari
Ans: (c)
Q11: Which of the following cities account for nearly half of India's cotton mill cloth manufactured?
(a) Jaipur and Kanpur
(b) Ahmedabad and Mumbai
(c) Coimbatore and Chennai
(d) Panipat and Kolkata
Ans: (b)
Q12: The rearing of silkworm for silk production is called _______.
(a) Monoculture
(b) Pisciculture
(c) Sericulture
(d) Apiculture
Ans: (c)
Give the difference between the following
Q1: Micro Enterprise and Medium Enterprise
Ans: 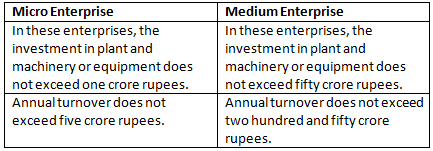
Q2: Heavy and Light industries
Ans: 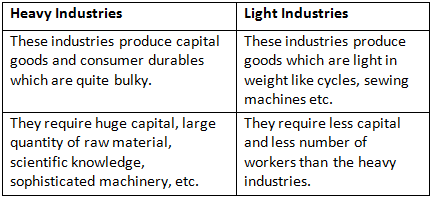
Q3: Basic and Secondary industries
Ans: 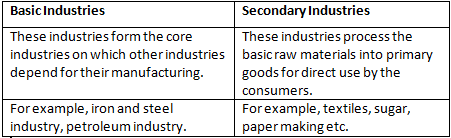
Answer the following questions
Q1(a): What is the difference between Agro-based and Mineral-based industry?
Ans: 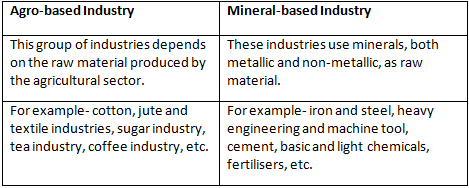
Q1(b): Classify industries on the basis of the nature of products. Give one example of each.
Ans: On the basis of the nature of products, industries can be classified as-
- Heavy industries like ship building industry.
- Light industries like electronic goods industry.
Q1(c): Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i) Sugar mills are located close to sugarcane growing areas.
(ii) Mumbai is known as the 'Cottonopolis of India'.
(iii) The silk industry has a small market.
Ans:
(i) Sugar mills are situated near areas where sugarcane is grown because sugarcane loses weight over time. Its sucrose content decreases, so it is important to process sugarcane within 24 hours after it is harvested.
(ii) Mumbai is referred to as the 'Cottonopolis of India' because it has become a key location for cotton textiles in the country. This is due to various factors such as being close to raw materials, having favorable weather, good transportation and port facilities, a sufficient workforce, enough capital, power, and a large market for cotton textiles.
(iii) The silk industry has a limited market because it competes with artificial silk, which is cheaper and of better quality. Additionally, fluctuations in the prices of raw silk negatively impact both the weavers and the overall silk industry.
Q1(d): (i) Mention two advantages of setting up a small scale industry.
(ii) Give two points of difference between a public sector and a private sector industry.
Ans:
(i) Two advantages of setting up a small scale industry are-
- Less capital is required.
- These industries make use of indigenous raw material.
(ii) The differences are-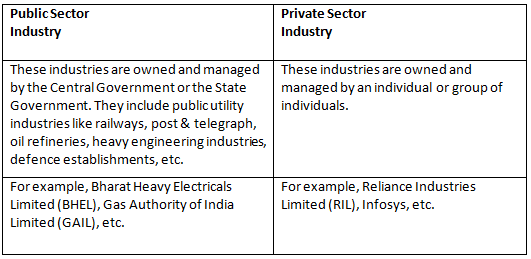
Q2(a): Name two by-products of the sugar industry. Give one use of each.
Ans: Two by-products of the sugar industry are-
- Bagasse, the leftover cane after crushing, is used for producing steam which is used as a source of power for sugar industry.
- Press mud is used for making wax, carbon paper and shoe polish.
Q2(b): Why is the sugar industry highly dispersed in India?
Ans: The sugar industry is highly dispersed in India because sugarcane is cultivated throughout the country. Hence, sugarcane industries are spread in the country near to the sugarcane fields.
Also, the area under sugarcane cultivation is limited due to the pressure of food crops. Thus, the sugar factories are highly dispersed even in areas which have large percentage of land under sugarcane cultivation.
Q2(c): Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i) India produces very little cane-sugar though it is one of the largest producers of sugarcane in the world.
(ii) Higher output of sugar in South India.
(iii) Sericulture flourishes in Karnataka.
Ans:
(i) India produces very little cane sugar, despite being one of the largest producers of sugarcane globally, due to the poor quality of sugarcane grown in the country. Additionally, many people in rural areas prefer using gur and khandasari instead of white sugar. As a result, a significant amount of the sugarcane cultivated is utilized for making gur and khandasari.
(ii) The output of sugar is higher in South India because the yield per hectare is greater in this region. The sucrose content in sugarcane is also higher in southern states compared to northern states. Furthermore, the southern states have modern mills that operate with greater productivity and lower production costs.
(iii) Sericulture thrives in Karnataka as the region has a suitable climate for raising silkworms. Karnataka has set up nurseries, silk farms, and licensed seed distributors to support and promote sericulture.
Q2(d): Give three important reasons which have made Maharashtra the leading producer of sugar in India.
Ans: Three important reasons which have made Maharashtra the leading producer of sugar in India are-
- The maritime climate of Maharashtra is ideal for the cultivation of sugarcane.
- Availability of excellent transport facilities in relation to export markets.
- The sugarcane farms are managed by co-operative societies which have access to better facilities like better seeds, fertilisers, irrigation etc.
Q3(a): Mention any two features of the cotton textile industry in India.
Ans: Two features of the cotton textile industry in India are-
- Cotton textile industry directly or indirectly supports more than nearly 40% of the country's labour force.
- It is the oldest and the largest industry which is found in almost all the states of India.
Q3(b): Why have Mumbai and Ahmedabad emerged as the important cotton manufacturing centres?
Ans: Mumbai and Ahmedabad have emerged as the important cotton manufacturing centres because of the following reasons-
- Climatic conditions — The humid coastal climate favours the textile making without breaking the thread.
- Transport facilities — These states are well connected through rail and road links with cotton growing areas of Maharashtra and Gujarat and also through sea routes with the foreign markets.
- Proximity to raw material — The supply of raw cotton for the mills is supplied by the cotton producing areas of the Deccan Plateau that lie close to these mills.
- Port Facilities — Good port facilities facilitate import of capital goods, chemicals etc. and the export of finished goods.
- Labour — The states have enough labour force from within or nearby states.
- Capital — Both the states have easy access to capital and financial resources.
- Power — Power is supplied in Mumbai by the Tata Hydroelectric system while Ahmedabad gets its power from Ukai and Kakrapara hydroelectric projects.
- Market — There is a huge market for the cotton cloth in these states and in the southern states of the country because of the hot climate which prevails in these areas.
Q3(c): State any three problems faced by the cotton industry in India.
Ans: Three problems faced by the cotton industry in India are-
- Shortage of Raw Material — There is a shortage of raw material, particularly of long staple cotton.
- Shortage of Power — The mills are facing acute shortage of power. This leads to loss of man hours, low productivity and loss in the mills.
- Sick Industrial Units — The industry faces constant threat of sickness and consequent closure. These sick units require heavy financial investments for replacement and modernisation purposes.
Q3(d): What is sericulture? State any two problems faced by the silk industry.
Ans: The rearing of Silkworms for Silk production is known as Sericulture.
Two problems faced by the silk industry are-
- Competition from artificial silk which is cheaper and better in quality.
- The changes in prices of raw silk badly affect both the weavers and the silk industry.
Q4(a): State any two geographical features favourable for setting an industry.
Ans: Two geographical features favourable for setting an industry are-
- Raw materials — The location of the industry is guided by the availability of raw material in a particular area.
- Transport — Good transport facilities are required to carry raw materials to the manufacturing units and finished products to the market.
Q4(b): Name two major silk producing centres in Karnataka and West Bengal.
Ans: Two major silk producing centres in Karnataka are Bengaluru and Mysore.
Two major silk producing centres in West Bengal are Malda and Murshidabad.
Q4(c): Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i) Sugarcane is a weight losing commodity.
(ii) Uttar Pradesh has been relegated to second place in terms of sugar production.
(iii) Ahmedabad is known as the 'Manchester of India'.
Ans:
(i) Sugarcane is a product that loses weight because its sugar content decreases over time. This means it is important to crush sugarcane within 24 hours after it is harvested.
(ii) Uttar Pradesh has dropped to the second position in sugar production due to reasons like old factories, management issues, labor challenges, and a shorter crushing period.
(iii) Ahmedabad is often referred to as the 'Manchester of India' because it stands as the second largest city for cotton manufacturing in India.
Q4(d): (i) Name the state having the largest production of non-mulberry silk.
(ii) Name the type of silk available in these states: Assam and Bihar.
Ans:
(i) Assam is the largest producer of non-mulberry silk in the country.
(ii) Assam provides non-mulberry silk (tasar, eri and muga). Assam is also the only muga producing region of the country. Bihar provides tasar silk.
Thinking Skills
Q1: Ramesh lived in a town far away from the city. He inherited a fortune from his uncle and started an agro-based manufacturing unit in his town. His manufacturing plant had all the modern equipment and produced quality products. Still his unit ran into losses. What could be the reasons for it?
Ans:
- Low Market Demand — There might not be enough interest in Ramesh's products, which could lead to fewer sales and lower income.
- Far from City — Ramesh's manufacturing unit is located a long way from the city, where most of his customers are. This distance might cause him to spend a lot on transportation, contributing to his losses.
- High Competition — There could be many strong competitors in the market, making it hard for Ramesh's business to attract customers and grow.
- High Expenses — If Ramesh's unit has high production costs and other expenses that are not managed well, it could lead to a decrease in profits.
Q2: Your cousin who lives in Lakhimpur Kheri in Uttar Pradesh wants to start a sugar mill. He wants you to advice him on the feasibility of starting a sugar mill in the area, based on the location, availability of resources, transport and market for selling the manufactured products. What would you suggest to your cousin?
Ans:
- Location Advantage — Lakhimpur Kheri is well-known for growing sugarcane, which makes it a great place for a sugar mill because it is close to where the raw materials come from.
- Availability of Resources — There is a plentiful supply of raw materials in the area. It's also important to consider the availability of water, electricity, and skilled workers.
- Transport Infrastructure — Check the current transport system to ensure that sugarcane and finished products can be moved easily to the market.
- Market Potential — Look into the demand for sugar and the level of competition in the industry. Take into account things like pricing, customer preferences, and who the potential buyers are.
- Government Policies and Support — Investigate the government rules, subsidies, and incentives that are available for the sugar industry in Uttar Pradesh.
- Financial Viability — Perform a detailed financial analysis to find out the initial costs to set up the mill, the working capital needed, and the potential for making a profit.
- Risk Assessment — Identify possible risks such as changes in sugarcane prices, shifts in government policies, market instability, and environmental issues like weather conditions that could impact crop yields.
|
33 videos|86 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on Morning Star Textbook Solutions: Manufacturing Industries in India-Agro Based - Geography Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What are agro-based industries in India? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of agro-based industries in India's economy? |  |
| 3. How do agro-based industries contribute to employment generation? |  |
| 4. What are some challenges faced by agro-based industries in India? |  |
| 5. What role does government policy play in the development of agro-based industries in India? |  |
















