Morning Star Textbook Solutions: Water Resources | Geography Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
Choose the Correct Option
Q1: What is an aquifer?
(a) An underground well that readily gives out water on digging the land.
(b) An underground pond that was once a source of water and is now buried under rocks.
(c) An underground stream saturated with water that is transmitted readily on to the surface.
(d) None of the above.
Ans: (c) An underground stream saturated with water that is transmitted readily on to the surface.
Q2: Which of the following measures are not used to conserve water?
(a) Rainwater harvesting
(b) Using bottled drinking water only
(c) Water recycling
(d) Preventing water pollution
Ans: (b) Using bottled drinking water only
Q3: Which of the following is not a secondary source of water?
(a) Rivers
(b) Groundwater
(c) Lakes and ponds
(d) Rain
Ans: (d) Rain
Q4: Sprinkler irrigation is also known as ._______.
(a) Seepage irrigation
(b) Overhead irrigation
(c) Protected irrigation
(d) Nozzle irrigation
Ans: (b) Overhead irrigation
Q5: Tanks form the main source of irrigation in _______.
(a) Punjab and Haryana
(b) the Deccan Plateau
(c) Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat
(d) All of the above.
Ans: (b) the Deccan Plateau
Q6: ._______is not a conventional means of irrigation.
(a) Furrow irrigation
(b) Wells
(c) Tanks
(d) Inundation canals
Ans: (a) Furrow irrigation
Q7: The most advanced and efficient method of irrigation is _______.
(a) Tank irrigation.
(b) Drip irrigation.
(c) Canal irrigation.
(d) Well irrigation.
Ans: (b) Drip irrigation
Q8: Most of the canals in India belong to which category?
(a) Perennial canals
(b) Inundation canals
(c) Navigation canals
(d) None of the above.
Ans: (a) Perennial canals
Q9: Which of the following least irrigated state of India is solely dependent on canals?
(a) Assam
(b) Mizoram
(c) Tripura
(d) Arunachal Pradesh
Ans: (b) Mizoram
Q10: Which of the following is the most advanced and efficient method of irrigation?
(a) Furrow irrigation
(b) Spray irrigation
(c) Drip irrigation
(d) Sprinkler irrigation
Ans: (c) Drip irrigation
Answer the Following Questions
Q1(a): What do you understand by the term 'water resource'?
Ans: The term 'water resource' refers to the complete range of natural waters available on Earth that can be utilized by living beings.
Q1(b): Give two points of difference between 'surface water' and 'ground water'.
Ans: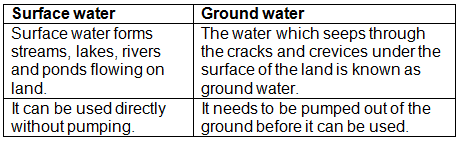
Q1(c): Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i) Need to adopt different means of irrigation.
(ii) Need for conserving water.
(iii) Man is responsible for water crisis in India.
Ans:
(i) Different means of irrigation are necessary due to variations in rainfall, crop needs, soil characteristics, and the desire to maximize agricultural output.
(ii) Water conservation is crucial due to groundwater depletion, deforestation leading to droughts, high water usage in irrigation, population growth causing scarcity, and pollution affecting water quality.
(iii) Human activities such as population growth, industrialization, and agricultural demands have increased the water demand, resulting in declining groundwater levels.
Q1(d): (i) What is meant by rainwater harvesting?
(ii) Mention any two rainwater harvesting systems practiced in India.
Ans:
(i) Rainwater harvesting involves capturing and storing rainwater to recharge groundwater locally.
(ii) Two rainwater harvesting systems in India are:
- Khatri in western Himalayas
- Johads in central India
Q2(a): What is meant by the term irrigation?
Ans: Irrigation refers to the artificial watering of agricultural plants using methods such as wells, tanks, tube wells, and canals.
Q2(b): What is meant by the term 'water scarcity'? What has caused this scarcity in India?
Ans: Water scarcity refers to insufficient available water resources to meet the demands of a specific area. Causes in India include population growth, over-exploitation, and unequal water distribution among social groups.
Q2(c): Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i) Inundation canals are being converted to perennial canals.
(ii) Tank irrigation is preferred over other means of irrigation in Peninsular India.
(iii) Groundwater reserves are depleting at a fast rate.
Ans:
(i) Inundation canals receive water only during floods, while perennial canals provide year-round access to water, making them more reliable for irrigation.
(ii) Tank irrigation is favored in Peninsular India due to reliance on rain-fed rivers, which can dry up, making tanks essential for water storage during dry periods.
(iii) Groundwater levels are declining due to increased demand from population growth, agriculture, and industrialization.
Q2(d): (i) What is meant by traditional or conventional methods of irrigation?
(ii) Name any two conventional methods of irrigation.
Ans:
(i) Traditional irrigation involves supplying water to crops using natural sources like ponds or rivers through gravity-driven channels.
(ii) Two conventional methods of irrigation are wells and tanks.
Q3(a): State any two drawbacks of conventional methods of irrigation.
Ans: Two drawbacks include:
- Inefficient water use leading to wastage.
- Waterlogging in low-lying fields due to excessive irrigation.
Q3(b): Give two advantages and two disadvantages of well irrigation.
Ans: Advantages:
- Low-cost well construction accessible to poor farmers.
- Pumps can extract water from deep underground.
Disadvantages:
- Groundwater distribution is uneven, affecting well availability.
- Over-extraction can deplete traditional wells.
Q3(c): Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i) Well irrigation is confined mainly to the alluvial plains.
(ii) In Tamil Nadu, nearly one-third of the net irrigated area is under canal irrigation.
(iii) Drip irrigation reduces loss of water through evaporation.
Ans:
(i) Alluvial plains have soft soil suitable for well digging, resulting in high crop yields.
(ii) Tamil Nadu relies on canal irrigation due to seasonal rainfall, necessitating irrigation during dry spells.
(iii) Drip irrigation minimizes evaporation by delivering water directly to the plant roots through perforated pipes.
Q3(d): (i) Name any two states where well irrigation is practiced.
(ii) Give one advantage and one disadvantage of tubewell irrigation.
Ans:
(i) States with well irrigation include Punjab and Uttar Pradesh.
(ii) Advantage: Tubewells provide clean water. Disadvantage: Tubewells are ineffective if groundwater is brackish.
Q4(a): Name the two types of canals. Name two states where perennial canals are widely used.
Ans: Two types of canals are-
- Inundation canals
- Perennial canals
Q4(b): How are the fields irrigated using the Persian wheel method?
Ans: The Persian wheel method uses a vertical wheel with buckets that are turned by animals. As the wheel rotates, the buckets fill with water and empty into a trough to irrigate fields.
Q4(c): Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i) Canals make the soil infertile.
(ii) Tubewell irrigation is quite expensive.
(iii) Excessive accumulation of salts makes the soils unsuitable for cultivation.
Ans: (i) Canals can raise the water table, causing salts to surface and degrade soil quality.
(ii) Tubewell irrigation is costly due to the need for continuous electricity supply.
(iii) High salt concentrations in soil hinder water movement to plant roots, leading to wilting and crop failure.
Q4(d): (i) Name two states in which tubewells are extensively used.
(ii) State why tubewell irrigation is important in Punjab.
Ans:
(i) States with extensive tubewell use include Punjab and Haryana.
(ii) Tubewell irrigation is crucial in Punjab for efficient year-round irrigation of large agricultural areas.
Q5(a): What is meant by rainwater harvesting?
Ans: Rainwater harvesting is the technique of capturing and storing rainwater to enhance groundwater recharge.
Q5(b): State any two methods of rainwater harvesting.
Ans: Two methods of rainwater harvesting include:
Q5(c): Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i) Many farmers in India still use wells.
(ii) There is very little recharge of groundwater.
(iii) The traditional wells dry up.
Ans:
(i) Farmers prefer wells due to low construction costs and the ability to use oxen for water retrieval.
(ii) Groundwater recharge is minimal as only a small portion of rainfall seeps into the ground.
(iii) Traditional wells are drying up due to excessive groundwater extraction and declining water tables.
Q5(d): (i) What is watershed management?
(ii) How is it beneficial for farmers in the long run?
Ans:
(i) Watershed management involves effectively managing both surface and groundwater resources to prevent runoff and enhance water storage.
(ii) It benefits farmers by conserving soil and water, essential for crop cultivation, thereby maximizing yield and income.
Q6(a): What is 'drip irrigation'? How is it useful?
Ans: Drip irrigation is an efficient irrigation method that delivers water directly to plant roots through perforated pipes, significantly reducing evaporation and conserving water.
Q6(b): Explain briefly the need to conserve water.
Ans: The need for water conservation arises from various factors, including population growth, industrial demands, and pollution, all of which stress existing water resources.
Q6(c): Give a geographical reason for each of the following:
(i) Modern means of irrigation are gaining popularity.
(ii) Sprinkler irrigation helps in conserving water.
(iii) Spray irrigation is quite expensive.
Ans:
(i) Modern irrigation reduces water loss, conserves resources, prevents soil erosion, and is efficient in low rainfall areas.
(ii) Sprinkler irrigation directly targets plants, minimizing seepage and evaporation losses.
(iii) Spray irrigation is costly due to the complex machinery required for operation.
Q6(d): What is meant by furrow irrigation? What is its advantage?
Ans: Furrow irrigation is a flood irrigation method where water flows through narrow channels between crop rows, allowing targeted watering. Its advantage is lower initial equipment costs and reduced pumping expenses.
Thinking Skills
Q1: Nature has endowed India with plentiful water resources. Despite this, acute shortage of water is noticed in some states. What could be the reasons for this shortage?
Ans:
- India is recognized as a country rich in rivers, featuring 12 major rivers and 46 medium rivers. Many of these rivers are perennial, while others are seasonal.
- The average annual rainfall in India is 1,170 mm, which is higher than the global average of 800 mm. However, some states face a serious water shortage for several reasons:
- Uneven distribution — The water resources in the country are not evenly spread out. The monsoon rains also fall unevenly, leading to situations where some states suffer from floods while others experience droughts at the same time.
- Population growth — With one of the largest populations in the world, India's need for water is increasing rapidly due to urbanization, industrial development, and agricultural needs. India has about 17% of the world's population but only 4% of the world's freshwater resources.
- Poor water management — The inefficient handling of water resources, lack of proper infrastructure, and inadequate governance are also factors that contribute to the water scarcity in some states.
- Pollution — The contamination of water bodies such as rivers, lakes, and groundwater is diminishing the availability of clean water for household, agricultural, and industrial use.
Q2: In your city, critical shortage of water has been reported due to the sharp fall in the groundwater level. What steps you will take to check this scarcity of water?
Ans: To address the issue of water scarcity, it is essential to implement swift actions that involve creating suitable policies and laws along with adopting effective methods for water conservation.
One effective method for conservation is rainwater harvesting. This technique involves capturing and storing rainwater to enhance the recharge of groundwater in local underground reservoirs.
There are several types of recharge structures that can help ensure that rainwater seeps into the ground instead of flowing away on the surface. Some of these structures include:
- Borewells and Dugwells — These are used to elevate the underground water table.
- Recharge Pit — These are dug into the ground and are lined with bricks or stones that have openings at regular intervals.
- Percolation Pits — These are holes drilled into the ground, typically about 30 cm in diameter and extending to a depth of 3 to 10 meters.
- Recharge Trenches — These are trenches dug into the ground, which are then filled with porous materials like pebbles, boulders, or broken bricks to collect surface runoff.
- Permeable Surfaces — For instance, a grassy area can hold a significant amount of rainwater, allowing only 10-15 percent of it to run off.
- Porous Tiles — These can be utilized on walkways and footpaths to aid in water retention.
Q3: A number of water saving technologies have been developed in recent decades. Which one would you prefer to use in your area and why?
Ans:
- I want to use rainwater harvesting to save water because my area gets enough rain during the monsoon season.
- In my neighborhood, there are large parks with grass and trees in every block.
- The trees and grass help reduce water runoff.
- People in my area can work together to collect rainwater from their rooftops.
- They can also use the parks to build different recharge structures such as:
- Borewells
- Recharge pits
- Percolation pits
- Recharge trenches
- Porous tiles on the pavement
Q4: If you are given a choice between using traditional or modern methods of irrigation, which method you would prefer to use in your area and why?
Ans:
- I prefer using drip irrigation because it is a modern and effective way to water plants.
- This method is the most advanced and efficient way to irrigate crops.
- The system uses perforated pipes that are placed between rows of plants or buried along their roots, delivering water directly to the crops. This significantly reduces the amount of evaporation.
- It helps in conserving water used for irrigation.
- It allows farmers to create a personalized irrigation schedule that is most helpful for each type of crop.
|
33 videos|86 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on Morning Star Textbook Solutions: Water Resources - Geography Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What are the main sources of water resources discussed in Class 10 Geography? |  |
| 2. How do human activities impact water resources? |  |
| 3. What are the methods of conserving water resources mentioned in the textbook? |  |
| 4. Why is it important to manage water resources sustainably? |  |
| 5. What role do rivers play in the water cycle according to the Class 10 Geography syllabus? |  |





















