NCERT Based Activity: Exploring Magnets | Science for Class 6 PDF Download
Activity 4.1: Let us explore (Magnetic and Non-Magnetic Materials)
Task:
- Collect objects made of different materials.
- Predict which objects will stick to a magnet.
- Test the objects with a magnet and record observations.
 Identifying the materials attracted by a magnet
Identifying the materials attracted by a magnet
Record your observations in Table 4.1.
Ans: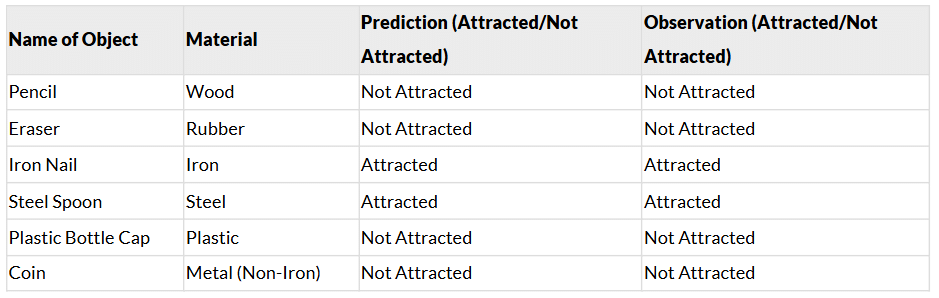
Conclusion:
- Objects made of iron, steel, nickel, and cobalt are magnetic.
- Objects made of wood, plastic, rubber, and non-iron metals are non-magnetic.
Was your prediction correct for all objects? Which materials stuck to the magnet? What conclusion can you draw? Through this activity, we found out that some of the objects were attracted to the magnet and stuck to it, while others were not.
The materials which are attracted towards a magnet are called magnetic materials. The metal iron is a magnetic material. Nickel and cobalt are other metals that are also magnetic. Some of their combinations with other metals are also attracted towards magnets.
The materials which are not attracted towards a magnet are called non-magnetic materials.
Q: Which materials listed in Table 4.1 were found to be non-magnetic?
Ans: Pencil (Wood)Eraser (Rubber)Plastic Bottle Cap (Plastic)Coin (Metal, Non-Iron)
Conclusion:
- Magnetic materials: Iron, Steel
- Non-magnetic materials: Wood, Rubber, Plastic, Non-Iron metal (Coin)
Activity 4.2: Let us investigate (Poles of a Magnet)
Task:
- Spread iron filings on paper.
- Place a bar magnet over them and tap the paper.
- Observe the distribution of iron filings.
 Iron filling stick to the bar magne
Iron filling stick to the bar magne
Ans:
Observations:
- Most iron filings stick to the ends (poles) of the magnet.
- Few or no filings stick to the middle of the magnet.
Conclusion:
- A magnet has two poles – North and South.
- Poles have the strongest magnetic force.
- No single North or South pole can exist alone.
Activity 4.3: Let us experiment (Finding Directions Using a Magnet)
Task:
- Suspend a bar magnet freely using a thread.
- Let it settle in a fixed direction.
- Rotate the magnet and let it settle again.
- Observe the final position.
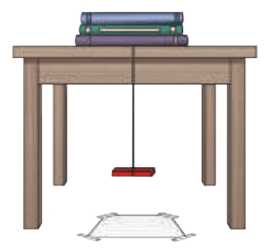 A freely suspended Bar Magnet
A freely suspended Bar Magnet
Ans:
Observations:
- The magnet always aligns along the North-South direction.
- Even after rotating, it returns to the same direction.
Conclusion:
- A freely suspended magnet always points North-South because Earth acts like a giant magnet.
- This property is used in magnetic compasses to find directions.
Activity 4.4: Let us construct (Making a Simple Magnetic Compass)
Task:
- Magnetize a sewing needle using a bar magnet.
- Pass it through a cork and float it in water.
- Observe the direction in which the needle settles.
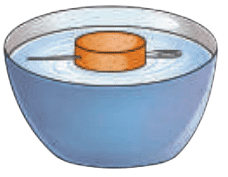 A compass needle in a bowl of water
A compass needle in a bowl of water
Ans:
Observations:
- The needle always aligns in the North-South direction.
- When rotated, it realigns in the same direction.
Conclusion:
- This homemade compass works because the needle is now a magnet.
- It behaves like a magnetic compass used by sailors in olden times.
Activity 4.5: Let us experiment (Attraction and Repulsion Between Magnets)
Task:
- Take two bar magnets marked with North and South poles.
- Bring different poles of the magnets close to each other and observe.
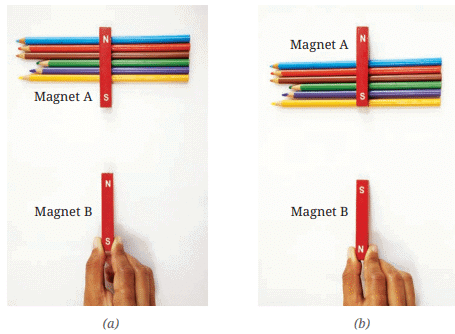 Interaction between two bar magnets
Interaction between two bar magnets
Ans: 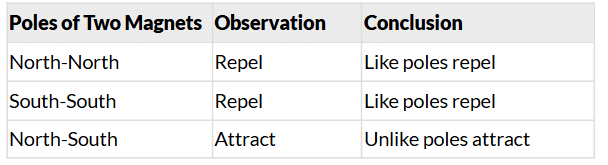
Conclusion:
- Like poles repel each other.
- Unlike poles attract each other.
- This is a unique property of magnets that helps identify them.
Activity 4.6: Let us experiment (Effect of a Magnet on a Compass Needle)
Task:
- Place a magnetic compass on a flat surface.
- Bring a bar magnet near the compass and observe the needle’s movement.
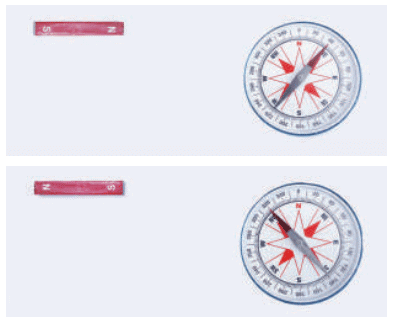 A compass needle and a magnet
A compass needle and a magnet
Ans:
Observations:
- When the North pole of the bar magnet is brought near the North pole of the compass needle, it moves away.
- When the South pole of the bar magnet is brought near the North pole of the compass needle, it moves closer.
Conclusion:
- The compass needle itself is a small magnet.
- Like poles repel, and unlike poles attract, affecting the movement of the needle.
Activity 4.7: Let us investigate (Effect of Magnetic Force Through Materials)
Task:
- Repeat the first or second part of Activity 4.6.
- Without disturbing the bar magnet and magnetic compass, place a piece of wood between them, perpendicular to the table as shown in Fig. 4.10. Observe the compass needle carefully
- Is there any effect on the deflection of compass needle due to the piece of wood? Record your observation in Table 4.2.
- Repeat the process by replacing the piece of wood by a cardboard sheet, thin plastic sheet, and a thin glass sheet.
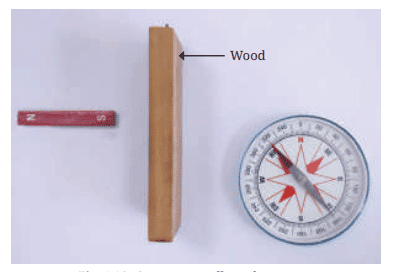 Compass needle and a magnet with a piece of wood in between
Compass needle and a magnet with a piece of wood in between
Ans: 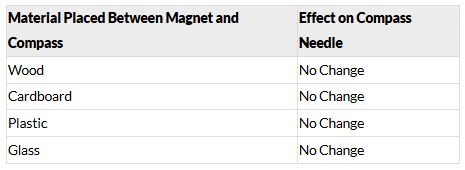
In this experiment, the goal is to observe the effect of different materials placed between a bar magnet and a compass needle, and how they affect the deflection of the compass needle. Here's a step-by-step guide and what to look for:
Procedure:
Set up the magnet and compass:
- Place the bar magnet and the magnetic compass on the table as shown in Fig. 4.10.
- Observe the deflection of the compass needle.
Repeat with different materials:
- Start by placing a piece of wood between the magnet and the compass, perpendicular to both as shown in the image.
- Observe any changes in the deflection of the compass needle.
- Record your observations in Table 4.2.
Testing other materials:
- Repeat the experiment by replacing the piece of wood with:
- Cardboard sheet
- Thin plastic sheet
- Thin glass sheet
- Observe and record the effect of each material on the compass needle's deflection.
- Repeat the experiment by replacing the piece of wood with:
Expected Observations:
- Wood: Being a non-magnetic material, the piece of wood should have no significant effect on the deflection of the compass needle. The needle will likely still point in the same direction, indicating that the wood does not interfere with the magnetic field.
- Cardboard: Similarly, a cardboard sheet, being non-magnetic, should have a minimal or no effect on the needle’s deflection.
- Plastic Sheet: A thin plastic sheet is also a non-magnetic material, and it should not significantly affect the needle.
- Glass Sheet: The thin glass sheet, like the plastic and wood, is non-magnetic, so it should not change the needle's deflection.
Conclusion:
The materials tested (wood, cardboard, plastic, and glass) are non-magnetic and should not significantly alter the deflection of the compass needle. The compass needle will continue to align with Earth's magnetic field, unaffected by these non-magnetic materials. However, if a magnetic material (like iron) were placed between the magnet and the compass, it might affect the needle's deflection by interfering with the magnetic field.
Final Summary of Learning from the Chapter
- Magnets attract iron, nickel, and cobalt but not plastic, wood, or glass.
- Every magnet has two poles – North and South.
- A freely suspended magnet always aligns in the North-South direction.
- Like poles repel, unlike poles attract.
- Magnetic force can act through non-magnetic materials.
- Magnets have various uses in daily life, from navigation to toys.
|
68 videos|260 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Based Activity: Exploring Magnets - Science for Class 6
| 1. What are the poles of a magnet, and how do they behave? |  |
| 2. How can a magnet be used to find directions? |  |
| 3. What is the purpose of making a simple magnetic compass? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between attraction and repulsion between magnets? |  |
| 5. Can a magnet's force affect a compass needle through materials? |  |
















