Division Chapter Notes | Mental Maths - Class 1 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Division? |

|
| Key Terms in Division |

|
| How to Divide? |

|
| Examples of Division |

|
| Division Using Multiplication Table |

|
| Short Division Method |

|
| Word Problems on Division |

|
What is Division?
Division is the process of splitting a number into equal parts. It is the opposite of multiplication. When we divide, we want to share something equally among different groups or people.
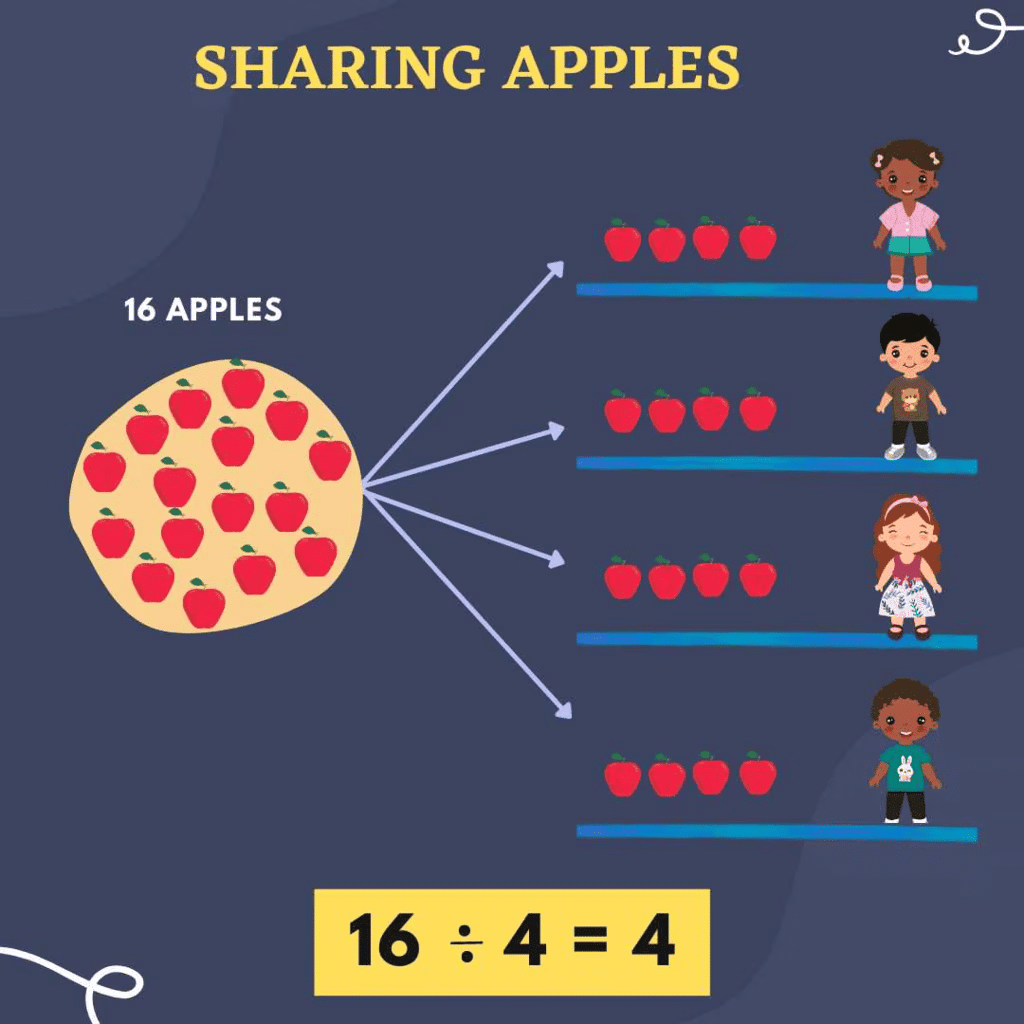 For example:
For example:
- If you have 16 apples and you want to share them equally among 4 friends, how many apples will each friend get?
- 16 ÷ 4 = 4 apples per friend.
So, 16 is divided by 4 and each friend gets 4 apples.
Key Terms in Division
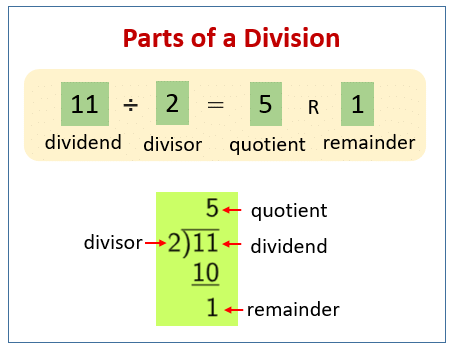
Dividend: The number that you want to divide.
- Example: In 12 ÷ 4 = 3, 12 is the dividend.
Divisor: The number by which you divide.
- Example: In 12 ÷ 4 = 3, 4 is the divisor.
Quotient: The answer to a division problem.
- Example: In 12 ÷ 4 = 3, 3 is the quotient.
Remainder: Sometimes when you divide, there might be something left over. That leftover part is called the remainder.
- Example: If you divide 13 by 4, the answer is 3 with 1 leftover. So, 13 ÷ 4 = 3 remainder 1.
How to Divide?
Here are some simple steps to help you divide:
Step 1: Understand the Division Problem
- Look at the numbers carefully. What is the dividend (the number being divided) and what is the divisor (the number you're dividing by)?
Step 2: Divide the Dividend by the Divisor
- You can either do this by repeated subtraction or by using multiplication tables.
Step 3: Find the Quotient
- The quotient is the number of equal parts after division.
Step 4: Check for Remainder
- Sometimes when you divide, there may be a part left. That part is called the remainder.
Examples of Division
Example 1: Simple Division
- 12 ÷ 3 = 4
- If you have 12 sweets and you want to divide them equally among 3 friends, each friend will get 4 sweets.
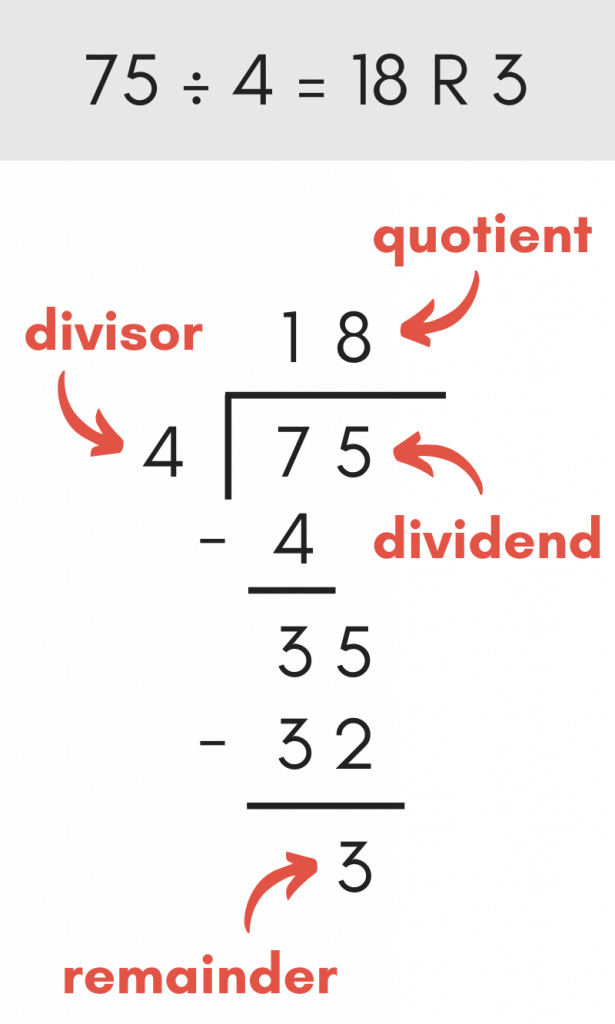
Example 2: Division with Remainder
- 13 ÷ 4 = 3 remainder 1
- If you have 13 chocolates and want to divide them equally among 4 people, each person will get 3 chocolates and there will be 1 chocolate left over.
Division Using Multiplication Table
We can also use multiplication tables to help us divide. For example:
- If you need to divide 20 ÷ 5, you can use the multiplication table of 5.
- 5 × 4 = 20.
- So, 20 ÷ 5 = 4.
Short Division Method
This method is useful for dividing large numbers. Let's look at an example:
Example: 98 ÷ 7
Step 1: Divide the first digit (9) by 7
- 7 goes into 9 one time (since 7 × 1 = 7).
- Write 1 above the 9.
Step 2: Subtract
- 9 - 7 = 2.
Step 3: Bring down the next digit (8)
- Now we have 28.
Step 4: Divide 28 by 7
- 7 goes into 28 four times (since 7 × 4 = 28).
- Write 4 above the 8.
Step 5: Subtract
- 28 - 28 = 0.
Final Answer:
98 ÷ 7 = 14.
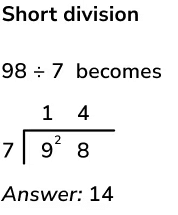
Word Problems on Division
Problem 1:
- Mary has 24 marbles. She wants to divide them equally between her 6 friends. How many marbles will each friend get?
- Solution: 24 ÷ 6 = 4 marbles per friend.
Problem 2:
- There are 15 biscuits in a box. If 3 children want to share the biscuits equally, how many biscuits will each child get?
- Solution: 15 ÷ 3 = 5 biscuits per child.
Division Facts to Remember:
Any number divided by 1 is the number itself.
- Example: 10 ÷ 1 = 10.
Any number divided by itself is 1.
- Example: 8 ÷ 8 = 1.
When dividing by 0, the answer is undefined.
- Example: 10 ÷ 0 does not have an answer because you cannot divide by zero.
|
39 videos|158 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on Division Chapter Notes - Mental Maths - Class 1
| 1. What is division and why is it important in mathematics? |  |
| 2. How do you perform division using a multiplication table? |  |
| 3. What is the short division method, and how is it used? |  |
| 4. Can you provide an example of a word problem that involves division? |  |
| 5. What are some common challenges students face when learning division? |  |





















