Class 6 Science: Sample Paper Solutions- 5 | Sample Papers For Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Section - A |

|
| Section - B |

|
| Section - C |

|
| Section - D |

|
Time: 3 hrs
Total Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- This question paper consists of 34 questions in total and all questions are compulsory.
- Questions 1-7 are multiple-choice questions and carry 1 mark each. Write the correct answer in your answer sheet.
- Questions 8-17 are very short answer questions and carry 2 marks each.
- Questions 18-28 are short answer questions and carry 3 marks each.
- Questions 29-34 are long answer questions and carry 5 marks each.
Section - A
Q1. Which of these is NOT a stage in a mosquito’s life cycle? (1 Mark)
(a) Egg
(b) Larva
(c) Froglet
(d) Adult
Ans: (c)
The froglet is a stage in the life cycle of a frog, not a mosquito. A mosquito's life cycle includes egg, larva, pupa, and adult stages.
Q2. What process cools water in an earthen pot? (1 Mark)
(a) Condensation
(b) Evaporation
(c) Freezing
(d) Melting
Ans: (b)
Evaporation of water from the surface of the earthen pot cools the water inside. As water evaporates, it takes away heat from the water, lowering its temperature.
Q3. Which star is the brightest in the night sky? (1 Mark)
(a) Pole Star
(b) Sirius
(c) Sun
(d) Venus
Ans: (b)
Sirius, located in the constellation Canis Major, is the brightest star visible in the night sky due to its proximity and intrinsic brightness.
Q4. Which method separates oil from water? (1 Mark)
(a) Filtration
(b) Decantation
(c) Sieving
(d) Magnetic separation
Ans: (b)
In decantation, the oil, which is less dense than water, floats on the surface. It can be poured off, separating it from the water beneath.
Q5. What motion does a merry-go-round show? (1 Mark)
(a) Linear
(b) Circular
(c) Oscillatory
(d) Random
Ans: (b)
A merry-go-round moves in a circular path, revolving around a central point, which is a perfect example of circular motion.
Q6. Which of the following substances are commonly separated using the churning method? (1 Mark)
(a) Oil from water
(b) Sand from water
(c) Cream from milk
(d) Oxygen from air
Ans: (c)
The churning method is used to separate cream from milk. By churning milk, the fat globules combine to form cream, which can then be separated. This method is commonly used in dairy processing to produce butter or cream.
Q7. Which living process involves producing young ones? (1 Mark)
(a) Respiration
(b) Reproduction
(c) Excretion
(d) Growth
Ans: (b)
Reproduction is the biological process by which organisms produce offspring, ensuring the continuation of their species, such as cats having kittens.
Section - B
Q8. Write the names of movements performed by the following animals and the organs that they use to move from one place to another. (2 Marks)
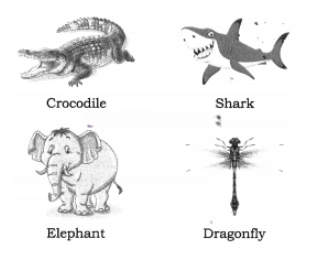
Ans:
- A crocodile crawls with its four short legs.
- A shark swims with its fins.
- An elephant runs and walks with its four legs.
- A dragonfly flies with its wings.
Q9. Name the vitamin found in these food items. (2 Marks)
(i) Papaya, Carrot, Fish oil, Milk
(ii) Orange, Guava, Lemon, Tomato, Chilli
(iii) Fishes, Butter, Egg, Milk, Liver
(iv) Legumes, Nuts, Whole grains, Milk products
Ans:
(i) Vitamin ‘A’
(ii) Vitamin ‘C’
(iii) Vitamin D’
(iv) Vitamin B1
Q10. Write short note on forglet. (2 Marks)
Ans: When the tadpole reaches the forglet stage, it is almost a full adult. At this point, the tadpole’s gills have disappeared, and its lungs have enlarged. This means it is ready to leave the water and live on land. Once its tail disappears, it will become an adult frog.
Q11. A given bar magnet was broken into pieces as shown in the figure. Where will be its North and South pole? (2 Marks)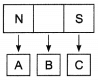
Ans: If you cut a bar magnet into pieces then the end labelled as North remains north and the other end formed will be south. Similarly, the end that was pointing south will be south pole and its opposite end will be the new north pole.
Q12. Name the device used to measure the following: (2 Marks)
(a) Size of your shoulder
(b) Size of your wrist
(c) Your height
(d) Your weight
(e) Cloth for curtain
(f) Circumference of round table
Ans:
(a) Measuring tape
(b) Measuring tape
(c) Measuring tape.
(d) Weighing balance
(e) Metre scale or measuring tape
(f) A long thread or measuring tape
Q13. What is the role of flowers in a plant’s life cycle? (2 marks)
Ans:
- Flowers are the reproductive organs of plants.
- They produce seeds after pollination, which is essential for the production of new plants.
- Once pollination occurs, the flower's ovary develops into a fruit that contains seeds, thus completing the plant's life cycle. This process can be observed in the bean plant, where after pollination, the flower produces a pod containing seeds.
Q14. How does a strainer improve tea-making? (2 marks)
Ans:
- A strainer is used to filter out tea leaves when pouring the brewed tea, ensuring that only the liquid passes through.
- This provides a clearer tea with no solid leaves left, offering a smoother drinking experience compared to decantation, which only partially separates the tea leaves from the liquid.
Q15. Why are asteroids irregular in shape? (2 marks)
Ans:
Asteroids are remnants from the early formation of the Solar System, often made of rock and metal.
Unlike planets, which have been shaped by gravity into spheres, asteroids are too small and lack enough gravity to pull themselves into a round shape. This is why they are irregular in shape, as seen in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
Q16. How do climbers show movement in plants? (2 marks)
Ans:
Climbers are plants that move and grow in search of support, like vines or creepers.
They use specialized structures such as tendrils or twining stems to wind around objects like fences or trees for support. This movement helps them reach sunlight, an essential factor for their growth, as observed in plant characteristics.
Q17. Name two uses of rocks in daily life. (2 marks)
Ans:
Granite is commonly used in building materials for its strength, such as countertops and flooring.
Slate is often used for roofing due to its durability and ability to withstand weathering.
Both are essential for construction and architecture,
Section - C
Q18. How does sedimentation help in water purification? (3 marks)
Ans:
- Sedimentation is the process where heavier particles such as mud, sand, and other debris settle down at the bottom of water when it is allowed to stand still.
- This happens because gravity pulls down the solid particles, leaving the upper water relatively clearer.
- This process is important in water purification because it removes larger contaminants, making it easier for further purification steps, like filtration and disinfection, to be effective in providing cleaner water.
Q19. Why is the Moon’s surface covered with craters? (3 marks)
Ans:
- The Moon does not have an atmosphere like Earth, which means it cannot burn up meteoroids or asteroids before they hit the surface.
- These space objects collide with the Moon at high speeds, creating craters on its surface.
- The craters remain preserved because there is no wind, rain, or life to erode them, unlike on Earth, where weathering and erosion would gradually wear down such features. As a result, the Moon’s surface still shows crater impacts from billions of years ago.
Q20. How does a measuring tape assist in sports? (3 marks)
Ans:
- A measuring tape is essential in sports for marking precise distances, ensuring fairness and accuracy in measurements.
- It helps determine the correct dimensions of sports fields (e.g., a Kabaddi court) and race tracks, ensuring that all participants compete in a standard, measured area.
- The flexibility of the tape allows it to measure curved paths or irregular shapes, which makes it especially useful in marking lines and measuring distances accurately during sports events.
Q21. What are the benefits of using wind energy? (3 marks)
Ans:
- Wind energy is a renewable energy source that generates electricity by harnessing the power of wind.
- It produces no pollution, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels, which contribute to air pollution and global warming.
- Wind energy is also sustainable, as wind is an abundant natural resource. The windmills used to capture wind energy can generate electricity without depleting the environment, making it a sustainable source of power for the future.
Q22. How does freezing change water’s properties? (3 marks)
Ans:
- When water freezes, it undergoes a physical change from a liquid to a solid at 0°C.
- During freezing, the water molecules lose their energy, slow down, and form a rigid structure, making water less fluid and giving it a fixed shape as ice.
- This change in state from liquid to solid causes water to expand as ice, which is why ice floats on water. Unlike liquid water, ice does not flow, and its molecules are tightly packed, making it solid and hard.
Q23. Why is threshing followed by winnowing in farming? (3 marks)
Ans:
- Threshing is the process that separates the grains from the stalks and husk by beating or combing.
- After threshing, the grains are mixed with lighter husk or chaff. To separate the husk from the grains, winnowing is used.
- Winnowing involves tossing the mixture into the air, allowing the wind to blow away the lighter husk, while the heavier grains fall back to the ground. This helps in cleaning the grains and preparing them for storage.
Q24. How do mosquitoes breed in stagnant water? (3 marks)
Ans:
- Female mosquitoes lay their eggs in stagnant water, such as puddles, ponds, or containers with standing water.
- The eggs hatch into larvae, which live in water, feeding on microorganisms.
- As they grow, the larvae turn into pupae, which are non-feeding but eventually transform into adult mosquitoes, continuing the life cycle. This is why stagnant water becomes a breeding ground for mosquitoes, as it provides the necessary environment for their development.
Q25. What is the role of forests in soil conservation? (3 marks)
Ans:
Forests play a critical role in soil conservation by preventing soil erosion. The roots of trees and plants hold the soil together, preventing it from being washed away by rain or wind.
The canopy of the trees also slows down rainfall, reducing its impact on the ground and allowing water to seep into the soil rather than running off.
Additionally, when leaves and branches decay, they contribute to the formation of humus, enriching the soil with nutrients that support plant growth, creating a sustainable and healthy ecosystem.
Q26. How does the Sun affect plant growth after germination? (3 marks)
Ans:
After germination, plants require sunlight for photosynthesis, the process by which they produce food.
Sunlight provides the energy that plants need to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
The shoots of the plant grow upward towards the sunlight, while the roots grow downward in search of water and nutrients, helping the plant develop fully and grow stronger.
Q27. Why is a kilometre used for large distances? (3 marks)
Ans:
A kilometre (km) is a metric unit of distance that is practical for measuring larger distances. One kilometre equals 1000 meters, which is more suitable for distances like from one city to another or the length of roads, rather than using smaller units like centimetres or millimetres.
For example, measuring the distance between two cities in metres would result in very large numbers, while kilometres are more manageable and easier to understand for large-scale measurements.
Q28. How do clouds form from water vapour? (3 marks)
Ans:
- Clouds form when water vapour rises into the atmosphere, cools down, and condenses into tiny droplets.
- As the air rises, it cools and the water vapour turns into liquid droplets or ice crystals that cluster together. These droplets are too small to fall as rain at first, but they form clouds when they combine.
- Clouds are made up of these tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air, and as they become heavier, they fall as precipitation (rain, snow, etc.), completing the water cycle.
Section - D
Q29. Discuss the formation of a comet’s tail and the behaviour of comets as they approach and move away from the Sun. (5 marks)
Ans:
- A comet is a small celestial object made up of ice, dust, and rocky material.
- When a comet gets close to the Sun, the heat causes the frozen materials to evaporate, creating a glowing tail that extends away from the Sun.
- This tail is formed by the solar wind and radiation pressure.
- As comets approach the Sun, they become more visible due to the formation of this tail. However, when they move away from the Sun, they cool down, and the tail starts to disappear, making the comet look dim or even invisible.
- Some comets have orbits that bring them close to the Sun periodically, while others may escape the Solar System or break apart due to gravitational forces or collisions.
Q30.
(i)After rain water puddles appear in the playground. After some time these disappear. Where does the water go?
(ii) After washing the utensils, water remains on the surface of utensils. After sometime it dries. Where does the water disappear?
(iii) Do you heat the pan to observe evaporation?
(iv) Give three examples of evaporation.
(v) Where does hand sanitizer disappear as you rub it in your hands.
(vi) Explain how surface area affects the rate of evaporation. (5 marks)
Ans: (i) Water gets absorbed by the soil on the playground. It also evaporates.
(ii) Water from the surface of utensils evaporates with time.
(iii) No. Evaporation takes place at room temperature also.
(iv) Drying of wet clothes, Drying of mopped floor and Drying of sweat from our body.
(v) It disappears due to evaporation because on rubbing hands heat is produced.
(vi) A larger surface area speeds up evaporation because more water is exposed to air, allowing more molecules to escape into the vapour phase.
Q31. Explain the difference between renewable and nonrenewable natural resources with examples. (5 marks)
Ans: Renewable resources are natural resources that can be replenished or restored through natural processes within a relatively short period of time.
Examples include:
- Air: Continuously refreshed through natural processes like photosynthesis and the water cycle.
- Water: Renewed through the water cycle, although it may néed conservation to prevent depletion.
- Forests: Can regenerate through natural growth and seed dispersal, though this process can be slow.
Non-renewable resources are those that take millions of years to form and are found in limited quantities. They cannot be replenished within a human lifespan once exhausted.
Examples include:
- Coal: Formed over millions of years from ancient plant material, used primarily for electricity generation.
- Petroleum: This includes oil and natural gas, which are formed from ancient marine organisms and are used for fuel and various other products.
- Minerals and Rocks: These resources are extracted for construction and manufacturing but cannot be replenished quickly.
Q32. (a) What is linear motion?
(b) Give two examples from daily life.
(c) How does it differ from circular motion? (5 marks)
Ans: (a) Linear motion is the movement of an object in a straight line. This motion can occur in one direction or along a path where the object maintains a constant direction without turning.
(b) Examples of linear motion:
A bus moving straight along a road. The bus travels in a straight line without changing its direction.
A stone falling from a height. The stone moves directly downward due to gravity.
(c) Difference between linear and circular motion:
Linear motion occurs when an object moves along a straight path without changing its direction, like a car driving on a straight road.
Circular motion occurs when an object moves along a curved path, completing a full circle around a central point, like a fan’s blades rotating.
The key difference is that linear motion is along a straight line, while circular motion involves rotation or movement along a curve.
Q33. (a) What are minerals?
(b) Explain two examples and their uses.
(c) Suggest two ways to conserve them. (5 marks)
Ans: (a) Minerals are naturally occurring inorganic substances found in the Earth’s crust. They are formed through various geological processes and are important for many human activities and industrial processes.
(b) Two examples of minerals and their uses:
Copper: Copper is a good conductor of electricity and is widely used in making electrical wires and circuit boards. It is also used in making coins and jewelry.
Aluminium: Aluminium is a lightweight metal commonly used in the aerospace industry for building aircraft and spacecraft. It is also used in packaging, like aluminium foil, due to its non-corrosive properties.
(c) Ways to conserve minerals:
Recycling: Recycling metals like copper, aluminium, and other minerals helps to reduce the demand for new minerals, as these materials can be reused multiple times.
Use of substitutes: Using alternative materials like plastics or synthetic materials in place of metals for certain applications can reduce the consumption of minerals, helping in their conservation.
Q34. List various types of nutrients and write the functions of each. (5 marks)
Ans: The various types of nutrients are:
- Carbohydrates: They are mainly energy-providing nutrients.
- Fats: They provide energy for the body. They give much more energy than carbohydrates if consumed in same amount.
- Proteins: They are called body-building foods. Proteins help in the formation and repairing of body parts. Skin, hair, muscles, enzymes are made up of proteins.
- Vitamins: Vitamins help in protecting our body against diseases. They also protect eyes, bones, teeth and gums.
- Minerals: Minerals are essential for proper growth of body and to maintain good health.
FAQs on Class 6 Science: Sample Paper Solutions- 5 - Sample Papers For Class 6
| 1. What are the main topics covered in Class 6 Science? |  |
| 2. How can I prepare effectively for the Class 6 Science exam? |  |
| 3. What types of questions can I expect in the Class 6 Science exam? |  |
| 4. Are there any important diagrams I should study for the Class 6 Science exam? |  |
| 5. What resources can I use to supplement my Class 6 Science studies? |  |