Introduction - Basic of Control System and Transfer Function - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
Control systems are essential for managing the behavior of dynamic processes in engineering and technology. They regulate systems by comparing desired inputs with actual outputs and making adjustments accordingly. The transfer function is a key tool in this field, describing the relationship between input and output in the Laplace domain. Applicable to Linear Time-Invariant (LTI) systems, it simplifies analysis and design. This framework underpins applications from robotics to industrial automation.
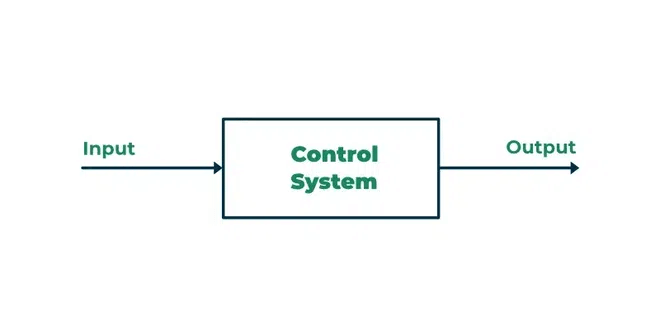
Fundamentals of Control Systems
Control systems manage the behavior of physical processes to achieve specific goals. They involve a controller that processes the error between the input (command) and output (response).
- Definition: A system designed to regulate processes like speed, temperature, or position.
- Types:
- Open-loop: No feedback (e.g., a timer).
- Closed-loop: Uses feedback (e.g., thermostat).
- Components: Input, output, controller, and process.
- Purpose: Ensures accuracy, stability, and efficiency.
Role of Feedback in Control Systems
Feedback allows a system to monitor its output and adjust the input, enhancing performance. It is the backbone of closed-loop systems.
Feedback Types:
- Negative: Reduces error, stabilizes system (e.g., cruise control).
- Positive: Amplifies output, may cause instability.
- Process: Output is compared to input; error drives corrections.
- Benefits: Improves accuracy, handles disturbances.
- Challenge: Requires careful design to avoid oscillations.
Applications and Tools in Control Systems
Control systems and transfer functions are applied across industries, from stabilizing aircraft to optimizing manufacturing processes. The transfer function enables block diagram representations, visually depicting system components and their interactions. Tools like Laplace transforms and frequency analysis help engineers assess stability, design controllers, and meet performance criteria. Techniques such as pole placement and root locus leverage transfer functions to tune system responses. Together, these concepts and tools form the foundation for precision engineering and automation.
FAQs on Introduction - Basic of Control System and Transfer Function - Electrical Engineering (EE)
| 1. What is a control system and how does it work? |  |
| 2. What is a transfer function in control systems? |  |
| 3. How do you derive the transfer function of a control system? |  |
| 4. What are the different types of control systems? |  |
| 5. Why is the stability of a control system important? |  |


















