Higher Order Thinking Skills - Market Equilibrium | Economics Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Q1: Suppose the government imposes both a price ceiling (below equilibrium) and a price floor (above equilibrium) on the same commodity. Explain the contradictions this would create in the market. Use real-world examples to justify why such a dual policy might fail.
Ans: Contradictions Created by Dual Price Controls:
- If a government imposes both a price ceiling (below equilibrium) and a price floor (above equilibrium) on the same commodity, it creates an inherent contradiction.
- The price ceiling caps the maximum legal price, while the price floor sets a minimum legal price.
- Since the ceiling is set below the equilibrium price and the floor above it, there is no overlapping price range where the market can legally operate.
This results in:
- Market Paralysis: Legally, no transactions can occur because the permissible price range (between the floor and ceiling) does not intersect with the equilibrium price.
- Simultaneous Shortages and Surpluses:
At the price ceiling, quantity demanded exceeds supply (excess demand), creating shortages.
At the price floor, quantity supplied exceeds demand (excess supply), leading to surpluses.
Example from India: Contradictory Price Controls on Wheat
In India, the Minimum Support Price (MSP) system acts as a price floor for crops like wheat and rice to protect farmers. Suppose the government simultaneously imposes a price ceiling on wheat (e.g., under the Essential Commodities Act) to keep consumer prices affordable, setting it below the MSP. This dual policy would create severe contradictions:
Contradictions in the Market
Legal Price Conflict:
- MSP (Floor): ₹2,200 per quintal (guaranteed to farmers).
- Price Ceiling: ₹1,800 per quintal (maximum legal price for consumers).
- Result: No legal market price exists between ₹1,800 and ₹2,200. Farmers cannot sell at the ceiling price (below MSP), and consumers cannot buy at the floor price (too high).
Market Breakdown:
- Farmers: Refuse to sell at the ceiling price (below MSP), leading to hoarding or black-market sales.
- Consumers: Face shortages in regulated markets (e.g., PDS shops) due to low supply at the ceiling price.
- Government: Forced to procure wheat at MSP (₹2,200) but sell it at the ceiling price (₹1,800), incurring massive subsidies.
Black Markets:
- Wheat is sold illegally at prices between ₹1,800 and ₹2,200, bypassing both controls.
Why This Dual Policy Fails
- Farmers’ Distress: MSP guarantees are undermined by ceilings, reducing incentives to produce.
- Fiscal Burden: Subsidizing the gap between MSP and ceiling prices strains government budgets (e.g., India’s food subsidy bill exceeds ₹2 lakh crore annually).
- Consumer Access: Shortages in PDS shops force reliance on expensive private markets.
Q2: Labour markets often face criticism for minimum wage laws causing unemployment. Using the concepts of excess supply and demand, explain why this might happen. Propose alternative policies to ensure fair wages without distorting labor market equilibrium.
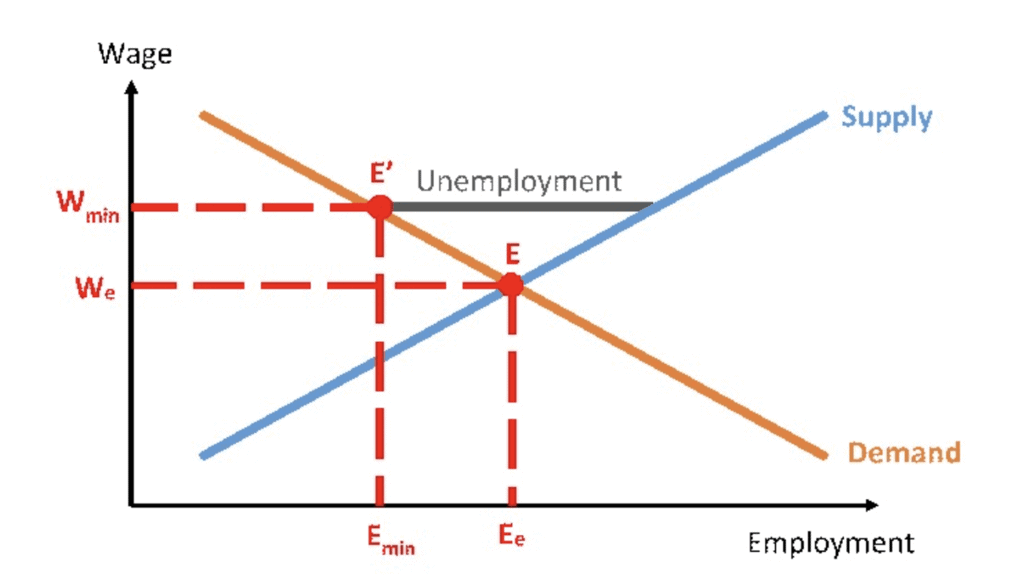
Ans: In a competitive labor market, the equilibrium wage is determined by the intersection of labor demand (from firms) and labor supply (from workers). When a minimum wage is set above the equilibrium wage, it creates a price floor, leading to:
- Excess Supply of Labour: At the higher wage, the quantity of labor supplied exceeds the quantity demanded.This gap represents unemployment (see diagram below).
- Reduced Hiring: Firms hire fewer workers because the cost of labor exceeds the marginal revenue product (MRP) of workers, making some jobs unprofitable.
Alternative Policies to Ensure Fair Wages Without Distorting Equilibrium
To address low wages without causing unemployment, policymakers can use strategies that shift labor demand/supply curves or enhance workers' bargaining power:
Wage Subsidies:
- The government subsidizes a portion of workers’ wages (e.g., paying ₹100/day of a ₹400/day wage).
- Effect: Lowers effective labor cost for firms, increasing demand for workers while ensuring higher take-home pay.
- Example: India’s Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) indirectly subsidizes wages by guaranteeing rural employment at a fixed rate.
Skill Development Programs:
- Invest in vocational training to improve worker productivity (↑ MRP).
- Effect: Shifts labor demand curve rightward, enabling firms to pay higher wages naturally.
- Example: Skill India Mission aims to enhance employability in high-demand sectors like IT and manufacturing.
Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC):
- Provide tax credits to low-income workers, supplementing their earnings without affecting employer costs.
- Effect: Increases workers’ net income without distorting labor market equilibrium.
Sector-Specific Wage Councils:
- Establish industry-specific wage boards (e.g., for textiles, agriculture) to negotiate wages based on productivity and regional conditions.
- Effect: Avoids a one-size-fits-all minimum wage, reducing unemployment in low-productivity sectors.
Strengthen Labor Unions:
- Encourage collective bargaining to negotiate wages aligned with firm profitability.
- Effect: Balances employer-worker power without government-mandated floors.
Q3: Assume coffee and tea are substitutes. If the price of coffee rises due to crop failure:
(i) Analyse the impact on the equilibrium price and quantity of tea.
(ii) How would your answer change if coffee and tea were complements instead?
Ans:
(i) Case 1: Coffee and Tea as Substitutes
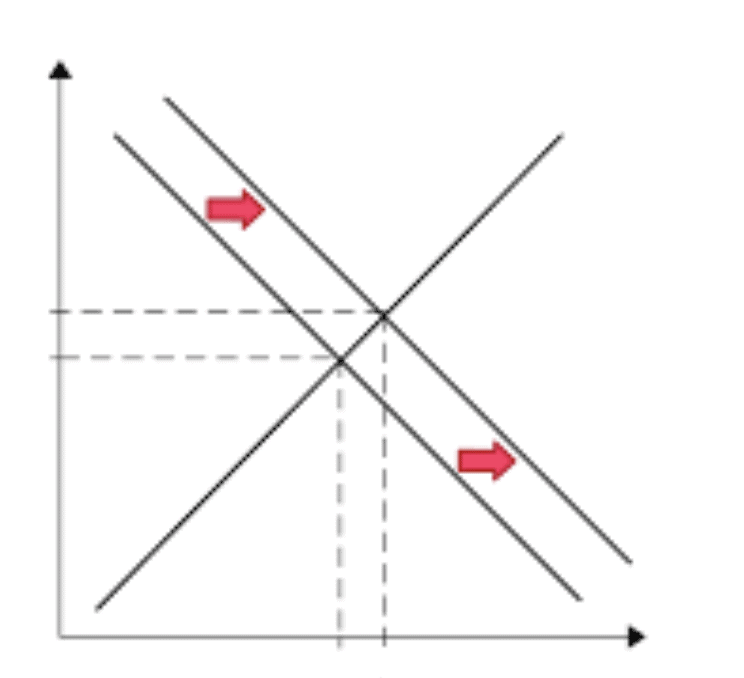
If coffee and tea are substitutes, a rise in coffee prices (due to crop failure) will lead consumers to switch to tea. This increases the demand for tea, shifting its demand curve rightward.
Impact on Tea Market:
- Equilibrium Price: Increases
- Equilibrium Quantity: Increases
Reasoning:
- The substitution effect dominates: Consumers buy more tea as coffee becomes relatively more expensive.
- With no change in tea supply, the increased demand drives up price and quantity.
(ii) Case 2: Coffee and Tea as Complements
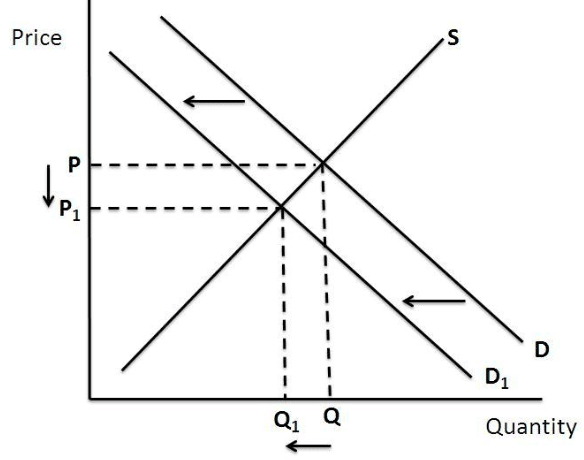
If coffee and tea are complements (e.g., consumed together, like coffee and sugar), a rise in coffee prices reduces coffee consumption, which in turn lowers the demand for tea.
Impact on Tea Market:
- Equilibrium Price: Decreases
- Equilibrium Quantity: Decreases
Reasoning:
- Complementary goods are consumed together. Higher coffee prices reduce coffee purchases, decreasing the need for tea.
- The leftward shift in tea demand reduces equilibrium price and quantity.
Key Difference
- Substitutes: The price and quantity of tea increase due to the substitution effect.
- Complements: The price and quantity of tea decrease due to joint consumption patterns.
|
59 videos|222 docs|43 tests
|
FAQs on Higher Order Thinking Skills - Market Equilibrium - Economics Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What is market equilibrium and why is it important in economics? |  |
| 2. How does a shift in demand or supply affect market equilibrium? |  |
| 3. What factors can cause a shift in supply or demand? |  |
| 4. How do price floors and ceilings relate to market equilibrium? |  |
| 5. Can market equilibrium change over time, and if so, how? |  |
















