Important Questions: India, That is Bharat | Social Studies for Class 6 PDF Download
Very Short Answer Questions
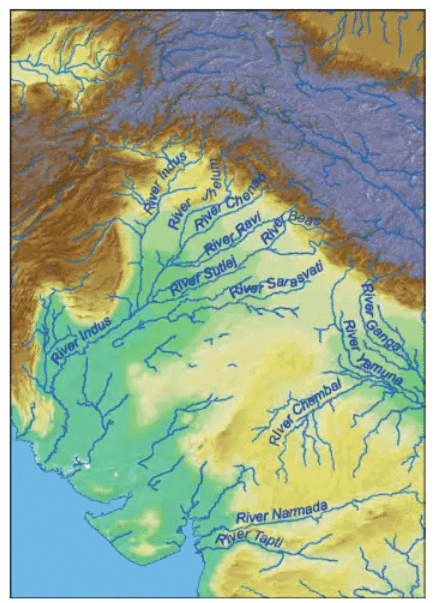
Q1: What is the meaning of 'Sapta Sindhava' as mentioned in the Rig Veda?
Ans: 'Land of the seven rivers.'
Q2: Which ancient text mentions the name 'Käshmira'?
Ans: The Mahabharata.
Q3: Which river is referred to as 'Sindhu' in ancient texts?
Ans: The Indus River.
Q4: What does the term 'Bhäratavarsha' refer to?
Ans: It refers to the entire Indian Subcontinent, meaning 'the country of the Bharatas.'
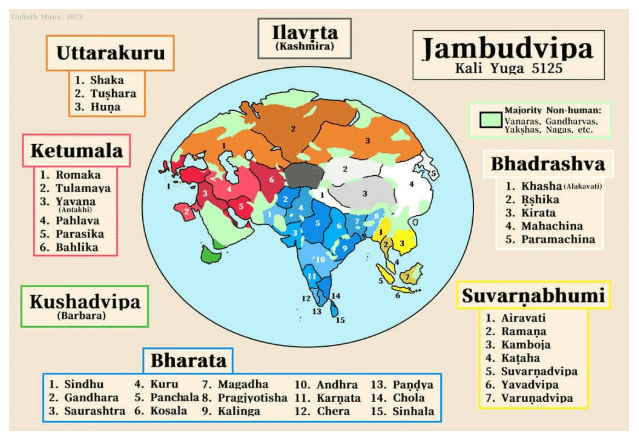
Q5: What regions did 'Jambudvipa' include during Ashoka's time?
Ans: India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, and parts of Afghanistan
Q6: What did the Persians call the region around the Indus River?
Ans: The Persians called it 'Hind,' 'Hidu,' or 'Hindu.'
Q7: In what century did the Persian emperor gain control over the region around the Indus River?
Ans: The 6th century BCE.
Q8: Who were the first foreigners to mention India?
Ans: The Persians were the first foreigners to mention India.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q9-Q12 How Foreigners named India: Greeks
Q9: What name did the ancient Greeks use to refer to the region that is now India?
Ans: The ancient Greeks called the region 'Indoi' or 'Indike.'
Q10: Why did the Greeks drop the letter 'h' from the name 'Hindu'?
Ans: The Greeks dropped the letter 'h' because there was no 'h' sound in their language.
Q11: What does the term 'Indike' refer to in ancient Greek sources?
Ans: 'Indike' refers to the lands and people of India as described by the Greeks in their writings.
Q12: How did the Greek language affect the names they used for other regions?
Ans: The Greek language influenced names by changing them to fit their sounds, like removing letters that didn't exist in Greek.
Q13-16 How Foreigners named India: Chinese
Q13: Who was Xuanzang?
Ans: Xuanzang was a Chinese scholar who travelled from China to India in the 7th century CE. He went on a long journey that lasted 17 years to learn more about Buddhism and to collect important texts.
Q14: Why did Xuanzang travel to India?
Ans: Xuanzang travelled to India to meet scholars and learn about Buddhism. He wanted to find texts that would help him understand and spread Buddhist teachings when he returned to China.
Q15: What did Xuanzang do after he returned to China?
Ans: After returning to China, Xuanzang translated the Buddhist texts he collected from Sanskrit into Chinese. This helped many people in China learn about Buddhism.
Q16: How long did Xuanzang's journey to India take?
Ans: Xuanzang's journey to India took 17 years. During this time, he visited many places and learned from different teachers about Buddhism.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q17: Explain how ancient Indians named their land with examples from history.
Ans:
- Ancient Indians gave their land many names over time. Early on, the Rig Veda called the northwest ‘Sapta Sindhava,’ meaning ‘land of seven rivers,’ tied to the Indus River, or Sindhu.
- Later, the Mahābhārata named the whole Subcontinent‘Bhāratavarṣha,’ after the Bharata people, and ‘Jambudvīpa,’ meaning ‘island of the jamun tree.’
- Emperor Aśhoka, around 250 BCE, used ‘Jambudvīpa’ in inscriptions to describe India, including today’s Bangladesh and Pakistan.
- The Viṣhṇu Purāna defined ‘Bhārata’ as the land north of the ocean and south of the snowy Himalayas.
- A Tamil poem from 2,000 years ago echoed this, praising a king ruling from Cape Kumari to the northern mountains.
- These names show how Indians saw their land’s geography and unity long ago.
Q18: Describe how foreigners named India and why their names changed over time.
Ans:
- Foreigners named India based on the Indus River, or Sindhu, with names evolving across cultures.
- Persians, in the 6th century BCE, called it ‘Hind’ or ‘Hindu’ after conquering the Indus region, a geographic label then.
- Greeks, learning from Persians, dropped the ‘h’—their language lacked it—calling it ‘Indoi’ or ‘Indike.’
- Chinese travellers like Xuanzang, in the 7th century CE, used ‘Yintu’ or ‘Yindu,’ tweaking ‘Sindhu’ to ‘Indu.’
- They also said ‘Tianzhu,’ meaning ‘heavenly master,’ honouring India as Buddha’s land.
- The Persians later used ‘Hindustān,’ as seen in an inscription 1,800 years ago, which was adopted by the invaders.
- These shifts occurred as each group adapted ‘Sindhu’ to their own tongue, reflecting trade, travel, and respect for India’s rivers and its fame over centuries.
|
46 videos|327 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Important Questions: India, That is Bharat - Social Studies for Class 6
| 1. What are the main themes discussed in "India, That is Bharat"? |  |
| 2. How does the article describe the geographical features of India? |  |
| 3. In what ways does "India, That is Bharat" highlight the cultural diversity of the country? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the title "India, That is Bharat"? |  |
| 5. How does the article address the challenges faced by India today? |  |

















