Selina Textbook Solutions: Chemical Coordination in Plants | Biology Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
Multiple Choice Type
Q1: The only phytohormone which is a gas at ordinary temperature:
(a) Ethane
(b) Ethyl alcohol
(c) Ethylene
(d) Ethyne
Ans: (c)
Ethylene is the only plant hormone that is gaseous at room temperature.
Q2: The hormone which promotes the ripening of fruits is:
(a) Auxins
(b) Gibberellins
(c) Cytokinins
(d) Ethylene
Ans: (d)
Ethylene facilitates the natural and artificial ripening of fruits.
Q3: A growth inhibiting hormone in plants:
(a) Gibberellins
(b) Indole-3 acetic acid
(c) Abscisic Acid
(d) Cytokinins
Ans: (c)
Abscisic Acid acts as a growth inhibitor by reducing the plant’s metabolic processes.
Q4: The hormone which stimulates cell division:
(a) Auxins
(b) Cytokinins
(c) Gibberellins
(d) Abscisic acid
Ans: (b)
Cytokinins promote cell division and encourage plant growth. They are abundant in germinating seeds and developing fruits.
Q5: Development of fruits without fertilization is called:
(a) Parthenogenesis
(b) Parthenon
(c) Parthenocarpy
(d) Dormancy
Ans: (c)
The term for fruit development without fertilization is Parthenocarpy, and it can be triggered by auxins.
Q6: The response by parts of the plant towards stimulus is called as:
(a) Nastic movement
(b) Tropism
(c) Tactic movement
(d) Senescence
Ans: (b)
Tropism refers to the growth movements of plant parts in response to unidirectional external stimuli.
Q7: Apical dominance is influenced by :
(a) Gibberellins
(b) Ethylene
(c) Cytokinins
(d) Auxins
Ans: (d)
Apical dominance, where the growth of lateral buds is inhibited by the apical bud, is controlled by auxins in the apex of the plant.
Q8: The growth movement of plant parts which occurs due to touch stimulus is called:
(a) Heliotropism
(b) Chemotropism
(c) Hydrotropism
(d) Thigmotropism
Ans: (d)
Thigmotropism refers to the growth movement of plant parts triggered by touch, such as the coiling of tendrils.
Q9: The instrument which can be used to demonstrate geotropism is:
(a) Manometer
(b) Thermostat
(c) Clinostat
(d) Barometer
Ans: (c)
Geotropism can be studied using a Clinostat, which consists of two setups with planted pots—one stationary and one rotating.
Q10: The hormone which accelerates senescence (ageing) and abscission of leaves is :
(a) IAA
(b) GA3
(c) ABA
(d) GA1
Ans: (c)
Abscisic Acid (ABA) speeds up the aging (senescence) of leaves and promotes their abscission. It is a growth inhibitor.
Short Answer Type
Q1: Match the items in column A with those of column B.
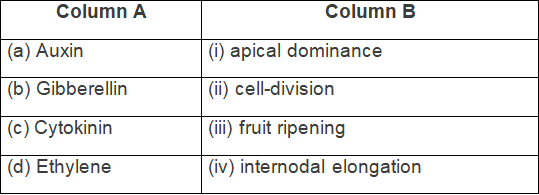
Ans: 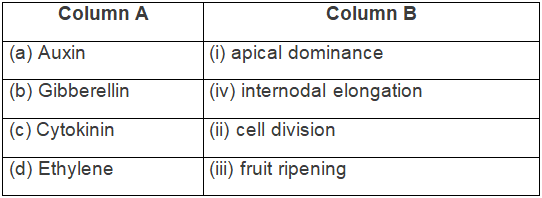
Q2: Complete the following sentences:
(a) Growth of root towards water is ____ .
(b) ____ hormone inhibits apical dominance.
(c) ____ and ____ induce chemotropism of angiosperms and gymnosperms.
(d) ____ of sweet peas exhibit thigmotropism.
(e) ____ is also called as "stress hormone".
Ans: (a) Growth of root towards water is hydrotropism .
(b) Cytokinins hormone inhibits apical dominance.
(c) Sugars and peptones induce chemotropism of angiosperms and gymnosperms.
(d) Tendrils of sweet peas exhibit thigmotropism.
(e) Abscisic acid is also called as "stress hormone".
Q3: How is movement in plants different from that in animals?
Ans: Differences between movement in plants and movement in animals are as follows —
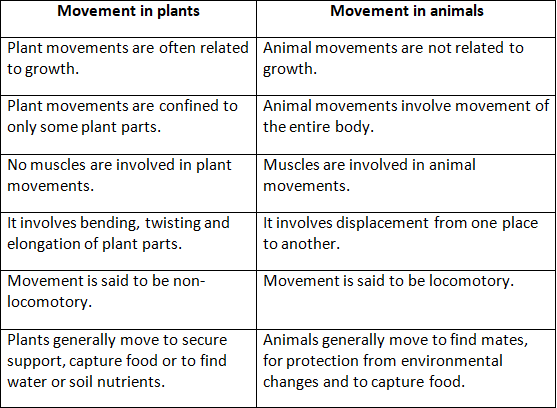
Q4: Name the stimulus which causes the following movements in plants: phototropism, thigmotropism, hydrotropism and geotropism.
Ans:
- Phototropism → Light
- Thigmotropism → Touch
- Hydrotropism → Water
- Geotropism → Gravity
Q5: Name the following.
(a) A hormone that stimulates growth by cell division.
(b) A growth-retarding hormone in plants.
(c) The main auxin found in most plants.
Ans: (a) Cytokinin
(b) Abscisic acid
(c) Indole 3-acetic acid (IAA)
Descriptive Type
Q1: Define the following terms:
(a) Phytohormones
(b) Tropism
(c) Clinostat
(d) Apical dominance
(e) Parthenocarpy
(f) Abscission
(g) Heliotropism
Ans: (a) Phytohormones – Phytohormones, also known as plant hormones, are naturally occurring small organic compounds in plants.
(b) Tropism – Tropism refers to the directional growth or movement of a plant in response to a stimulus, where the response is more intense from one direction.
(c) Clinostat – A clinostat is a mechanical device that rotates slowly to demonstrate the plant’s response to gravity (geotropism).
(d) Apical dominance – Apical dominance is the process where the growth of lateral buds is inhibited by the apical bud.
(e) Parthenocarpy – Parthenocarpy is the formation of fruit without fertilization.
(f) Abscission – Abscission is the process where parts of a plant, such as leaves, flowers, buds, or fruits, are shed.
(g) Heliotropism – Heliotropism is the phenomenon where young flower heads track the sun’s movement across the sky from east to west.
Q2: List five plant growth hormones and mention one important role of each.
Ans:
- Auxins — Auxins promote the growth of stem, roots and fruits by cell elongation.
- Gibberellins — Gibberellins promote the growth of internodes by cell elongation.
- Cytokinins — Cytokinins stimulate cell division.
- Ethylene — Ethylene helps in ripening of fruits.
- Abscisic acid — Abscisic acid induces dormancy of buds and seeds.
Q3: Differentiate between:
(a) Thigmotropism and geotropism
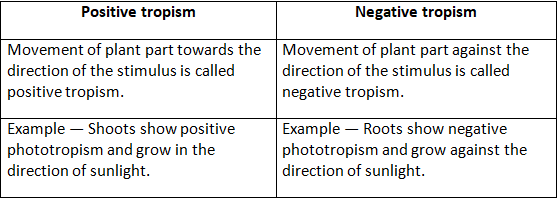
(b) Positive and negative tropism
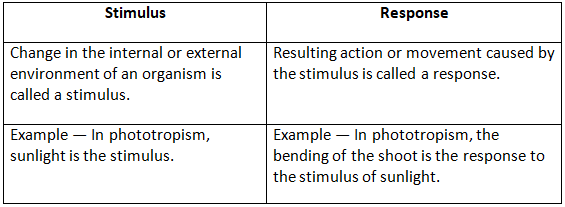
(c) Stimulus and response
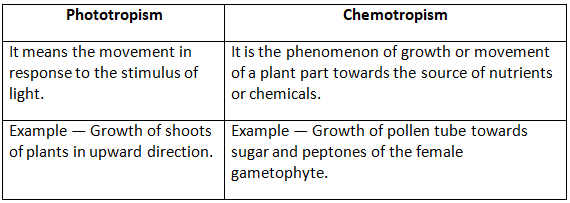
(d) Phototropism and chemotropism
Ans: (a) Difference between thigmotropism and geotropism
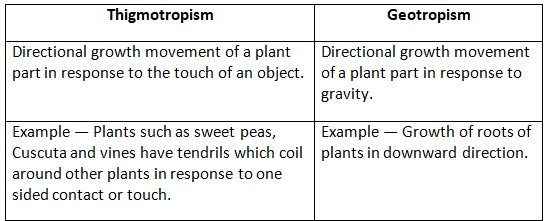
(b) Difference between positive and negative tropism
(c) Difference between stimulus and response
(d) Difference between phototropism and chemotropism
Structured / Application / Skill Type
Q1: The tea plants are never allowed to grow lengthwise. This is done by cutting their apical buds, a process known as pruning. In this way, tea plants get a dense growth and easy yield. Answer the following questions:
(a) Name the scientific phenomenon that is being overcome by pruning.
(b) What plant hormone is responsible for the scientific phenomenon mentioned in (a).
(c) Name one plant hormone which inhibits the said phenomenon.
Ans: (a) Apical dominance
(b) Auxins
(c) Cytokinins
Q2: The figure given below shows the stages of ripening in a banana. Answer the questions that follow:
(a) Name the plant hormone responsible for the above changes.
(b) Mention two characteristic features of this hormone.
Ans: (a) The plant hormone that causes the mentioned changes is Ethylene. It is unique as the only hormone that exists as a gas at normal temperatures. It is produced within fruits and stays in the same fruit.
(b) Key characteristics of ethylene include:
- It is produced in flowers, germinating seeds, and ripening fruits. It stimulates root growth and root hair development, and also triggers and accelerates fruit ripening.
Q3: The diagram given alongside shows a type of tropism. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
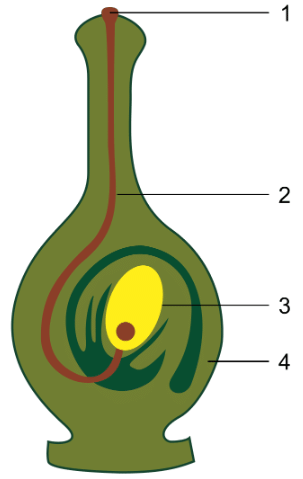
(a) Name and define the type of tropism shown in the diagram.
(b) Label the guidelines (1) to (4).
(c) Name two effective stimulants that help in the growth of part (2).
(d) Name two groups of plants where part (2) grows towards gametophyte with the help of the stimulants mentioned in (c).
Ans: (a) The type of tropism shown in the diagram is Chemotropism. It is the phenomenon of growth of plant organs in response to chemicals.
(b) Guidelines (1) to (4) are labelled below:
1 → Pollen grain
2 → Pollen tube
3 → Ovule
4 → Ovary
(c) Sugars and peptones.
(d) Gymnosperms and angiosperms.
Q4: Study the diagrams given below and answer the following questions.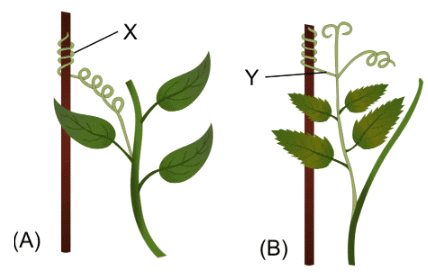
(a) Name the structures shown as X and Y in the figures (A) and (B), respectively.
(b) Write the functions performed by the structures X and Y.
(c) Name the phenomenon depicted and define it.
(d) How do the structures X and Y differ from each other?
(e) Give examples of the plants which show the said phenomenon.
Ans: (a) X → Stem tendrils, Y → Leaf tendrils.
(b) Stem tendrils (X) and leaf tendrils (Y) enable the plant to climb up a support.
(c) Thigmotropism is the phenomenon depicted. It is the growth movement of plant parts in response to touch stimulus.
(d) Stem tendrils (X) arise from the stem while leaf tendrils (Y) arise from the leaf of the plant.
(e) Sweet Pea, Vines and Cuscuta.
Q5: Given below are the figures showing some kinds of tropic movements in plants. Study the same and answer the following questions: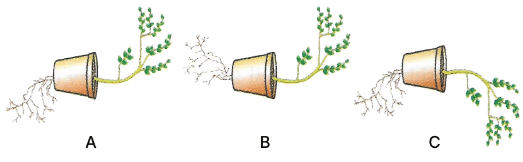
(a) Which one of these figures is correct? Give reason in support of your answer.
(b) Name the kind of movements shown by the root system and the shoot system. Define each.
(c) What are the two stimuli which affect root system and shoot system? Name them.
(d) Which of the following stimuli affect the growth of root strongly?
- Gravity
- Water
(e) Draw a neat and labelled diagram of the longitudinal section of a pistil showing chemotropism in an angiospermic plant.
Ans: (a) Figure A is correct as it shows roots growing towards gravity and shoot growing away from gravity.
(b) Root shows positive geotropism and shoot shows negative geotropism.
Positive geotropism is defined as movement of plant towards earth's gravity. For example, roots show positive geotropism.
Negative geotropism is defined as movement of plant away from gravity. For example, shoot shows negative geotropism.
(c) Root system — Gravity
Shoot system — Light
(d) Gravity
(e) Below diagram shows chemotropism in a pistil: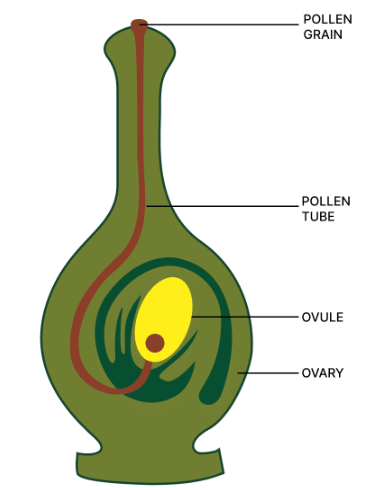
Q6: The box given below contains twelve words. Out of these, ten can be arranged in five suitable matching pairs. Make these five pairs in the form of a table.
Auxin, Abscisic acid, Fruit ripening, Cytokinins, Closure of stomata, Parthenocarpy, Ethylene, Gibberellins, Tropism, Stem elongation, Cuscuta, Cell division
Ans:
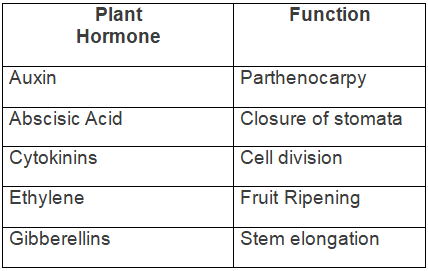
Q7: The figure given below depicts a kind of tropic movement in plants. Study the same and answer the following questions.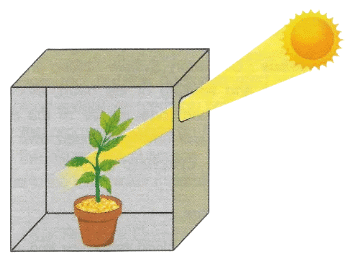
(a) What kind of a movement is shown in figure. Define it.
(b) How does this movement differ from geotropism?
(c) Name the stimulus responsible for thigmotropism. Give one example of a plant showing thigmotropism.
(d) Name one stimulus which gives a positive response for the roots but negative response for the shoot.
(e) Draw a neat and labelled diagram of the part of plant showing leaf tendril. Name the plant.
Ans: (a) Phototropism.
It is defined as the movement in response to the stimulus of light.
(b) Stimulus for phototropism is light whereas for geotropism it is gravity.
(c) Touch is the stimulus for thigmotropism.
Example — The tendrils of sweet pea plant start coiling around the support in response to touch.
(d) Gravity
(e) Sweet pea plant shows thigmotropism. The labelled diagram showing leaf tendril is given below: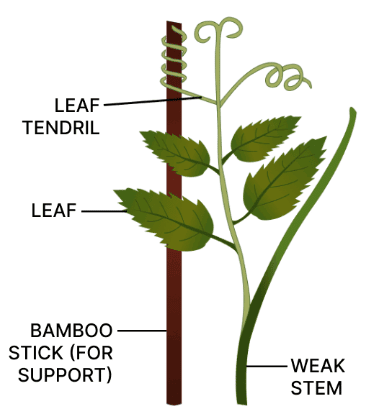
|
55 videos|189 docs|21 tests
|
FAQs on Selina Textbook Solutions: Chemical Coordination in Plants - Biology Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What is chemical coordination in plants? |  |
| 2. What are the main types of plant hormones? |  |
| 3. How do auxins affect plant growth? |  |
| 4. What role do gibberellins play in plants? |  |
| 5. How do plants respond to environmental stress through chemical coordination? |  |





















