Selina Textbook Solutions: Human Evolution | Biology Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
Multiple Choice Type
Q1: Which of the following is not a vestigial organ?
(a) Vermiform appendix
(b) Caecum
(c) Wisdom teeth
(d) Ear pinna
Ans: (b)
The caecum is not considered vestigial as it helps absorb fluid and salts from digested food.
Q2: What selective agent caused the change in the peppered moth?
(a) Lichens
(b) Humans
(c) Birds
(d) Smoke
Ans: (d)
Initially, light-colored moths thrived because they could blend with lichen-covered trees, but industrial pollution darkened the tree bark, making dark-colored moths harder for predators to spot. Smoke from industrialization played a key role in this shift.
Q3: Who was the first scientist to propose a theory of evolution?
(a) Darwin
(b) Lamarck
(c) Mendel
(d) Wallace
Ans: (b)
Lamarck was the first to introduce a theory of evolution.
Q4: What is Lamarck's theory called?
(a) Autogenesis theory
(b) Germplasm theory
(c) Theory of inheritance of acquired characters
(d) Theory of abiogenesis
Ans: (c)
Lamarck's theory suggests that organisms pass traits acquired during their lifetimes to their offspring.
Q5: How did Charles Darwin explain the origin of species?
(a) Mutation
(b) Natural selection
(c) Acquired characters
(d) Hybridization
Ans: (b)
Darwin's theory of evolution emphasized natural selection as the mechanism for species' origins.
Q6: Which of the following was not explained by Darwinism?
(a) Natural selection
(b) Struggle for existence
(c) Use and disuse
(d) Survival of the fittest
Ans: (c)
The concept of "use and disuse" was part of Lamarck's theory, not Darwin's.
Q7: Which of the following human ancestors came just before modern humans?
(a) Cro-magnon
(b) Ramapithecus
(c) Homo habilis
(d) Neanderthal man
Ans: (a)
Cro-magnon preceded modern humans in evolutionary history.
Q8: Who is known as the "Father of Evolution"?
(a) Mendel
(b) Walther Flemming
(c) Darwin
(d) Lamarck
Ans: (c)
Darwin is regarded as the "Father of Evolution" due to his pioneering work on natural selection.
Q9: Which organism was central to the study of industrial melanism?
(a) Polar bear
(b) Butterfly
(c) Peppered moth
(d) Bear
Ans: (c)
The peppered moth illustrated natural selection during the industrial revolution, where dark-colored moths became more prevalent due to pollution.
Q10: Who wrote "The Origin of Species"?
(a) Carl Linnaeus
(b) Darwin
(c) Lamarck
(d) Mendel
Ans: (b)
Charles Darwin wrote the groundbreaking work, "The Origin of Species."
Short Answer Type
Q1: List four postulates of Darwin's theory.
Ans:
- Overproduction: More offspring are produced than can survive.
- Struggle for existence.
- Variation: Individuals show variation within a species.
- Survival of the fittest.
Q2: List the cranial capacities of the following ancestral forms:
(a) Australopithecus
(b) Homo habilis
(c) Homo erectus
(d) Cro-magnon
(e) Homo sapiens sapiens
Ans: (a) Australopithecus → 450 to 600 cm³
(b) Homo habilis → 680 to 735 cm³
(c) Homo erectus → 800 to 1125 cm³
(d) Cro-magnon → 1450 to 1600 cm³
(e) Homo sapiens sapiens → 1450 to 1600 cm³
Q3: State the two principles of Lamarck's theory.
Ans:
- Use and disuse: Organs used extensively become stronger, while unused ones shrink.
- Inheritance of acquired characters: Traits acquired during an organism's life are passed on to offspring.
Q4: Name three vestigial organs in humans.
Ans:
- Wisdom teeth
- Vermiform appendix
- Pinna
Q5: Provide the scientific name of the organism that demonstrates 'natural selection'.
Ans: Biston betularia (Peppered moth)
Q6: Tick the correct options in the following statements:
(a) The fossil history of humans is complete/fragmentary.
(b) The first remarkable human fossil was that of H. habilis/H. africanus.
(c) Evolution is an ever-continuing/promptly ending process.
Ans: (a) Fragmentary
(b) Homo habilis
(c) Ever-continuing
Descriptive Type
Q1: Define the following terms:
(a) Evolution
(b) Vestigial organs
(c) Speciation
(d) Bipedalism
(e) Natural selection
Ans: (a) Evolution: The gradual development of life forms from simpler to more complex organisms over millions of years.
(b) Vestigial organs: Functionless or reduced structures that were once functional in ancestors.
(c) Speciation: The process through which new species arise due to genetic changes.
(d) Bipedalism: The ability to walk on two hind limbs.
(e) Natural selection: A process where organisms with advantageous traits survive and reproduce, passing on those traits.
Q2: Distinguish between:
(a) Australopithecus and Cro-magnon (Chin)
(b) Australopithecus and Modern man (Body hair)
(c) Homo habilis and Homo sapiens sapiens (Posture)
Ans: (a) Australopithecus → No chin; Cro-magnon → Well-developed chin
(b) Australopithecus → Covered with hair; Modern man → Reduced body hair
(c) Homo habilis → Bent knee posture; Homo sapiens sapiens → Fully erect posture
Q3: Differentiate between Lamarck’s Theory and Darwin’s Theory.
Ans:
- Lamarck's Theory: Focuses on inheritance of acquired characteristics and the use/disuse of organs.
- Darwin's Theory: Emphasizes natural selection, where only the fittest individuals with beneficial variations survive and reproduce.
Structured / Application / Skill Type
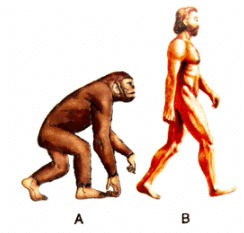
Q1: Given below are two figures (A and B) representing the two stages of evolution of human beings.
Answer the following:
(a) Mention any two contrasting characters between the two stages.
(b) Write all the stages of human evolution in their correct sequence.
(c) State any two characteristic features of stage B.
Ans: Stage A → Australopithecus
Stage B → Homo sapiens sapiens (modern man)
(a) Contrasting characters between Australopithecus and Homo sapiens sapiens :
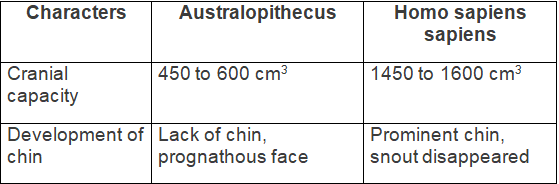
(b) Stages of human evolution in their correct sequence:
Australopithecus → Homo habilis → Homo erectus → Neanderthal man → Cro-Magnon man → Homo sapiens sapiens (modern man)
(c) Characteristic features of stage B (Homo sapiens sapiens):
- Bipedal locomotion with four reversed curves in the spine.
- Thoracic region flattened into a broad chest by flattening of sternum.
Q2: Given below are two figures (A and B) showing a phenomenon that was first observed in Manchester before and after the year 1850.
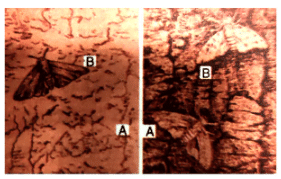
Answer the following.
(a) What name has been given to this phenomenon?
(b) Give the common name and the scientific name of the insect involved in this phenomenon.
(c) Briefly mention why the changes shown in the two figures appeared.
(d) The following phenomenon provides a classical explanation of a scientific theory given by a certain scientist.
(i) Name and explain the said theory.
(ii) Give the name of the scientist who gave this theory.
Ans: (a) Industrial Melanism
(b) Common name — Peppered moth
Scientific name — Biston betularia
(c) Biston betularia, this moth with its light coloured wings dotted with spots blended well with the lichens growing on the houses and tree trunks on which it rested. After the Industrial Revolution, pollution resulted in a decline in the growth of lichens. The tree bark got exposed due to the absence of lichens. As a result, dark-coloured moths now got an advantage of a dark background, were camouflaged and survived, while the light-coloured moths were easily picked by predators. This showed that in a mixed population, those moths which could adapt to the changing environment after the Industrial Revolution survived and increased in number, while the ones which could not adapt were slowly wiped out from the population.
(d) The theory explaining Industrial Melanism and the name of the scientist who gave it is given below:
- Natural selection — During the struggle for existence, only those individuals which have advantageous variations survive while the ones which lack these variations are wiped out. Nature selects only those variations which are suitable for existence. This process is called natural selection.
- Charles Darwin
Q3: Observe the figure given below and answer the questions that follow: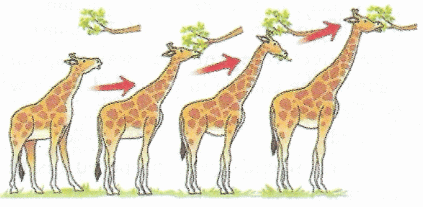 (a) What is the figure depicting ?
(a) What is the figure depicting ?
(b) What was the reason that the giraffe stretched their neck and forelimbs?
(c) What is the name of the theory that is being depicted in the figure?
(d) Who explained the theory?
(e) What is the conclusion of this theory?
Ans: (a) The figure depicts evolution in Giraffe due to extensive use of neck and forelimbs.
(b) The area where giraffe fed on grasses, fell short of its ground level vegetation and therefore they had to stretch their neck and forelimbs to reach leaves of trees.
(c) Lamarck's theory of inheritance of acquired characters
(d) Lamarck
(e) According to this theory, variations are seen in organisms due to less or overuse of organs. These variations are passed on to the offsprings. After many generation these variations become permanent feature of the organism.
|
55 videos|110 docs|21 tests
|
FAQs on Selina Textbook Solutions: Human Evolution - Biology Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What are the major stages of human evolution? |  |
| 2. How does the theory of evolution explain human development? |  |
| 3. What evidence supports the theory of human evolution? |  |
| 4. What role did climate change play in human evolution? |  |
| 5. Why is the study of human evolution important for understanding modern humans? |  |















