Selina Textbook Solutions: Sense Organs | Biology Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
Q1: State the functions of the following: Q2: Write in proper sequence the names of all the parts of the human eye through which the light rays coming from an object pass before they form an image on the retina. Q3: Name the following : Q4: Give the reason for the following: These adjustments take a little time during which the person feels blinded. Q1: Categorise the following parts under Q2: State the functions of the following :- (ii) Cochlea (iii) Auditory nerve (i) Human ear is concerned with hearing only. Q4: Given below is a diagrammatic representation of a part of the human ear. Ans: (i) The parts numbered 1-6 are: Ans: (d) Q2: The vitamin required for the synthesis of rhodopsin is : Q3: An aperture that controls the passage of light into the eye is: Q4: Tears have an antiseptic property due to the presence of: Q5: Which of the following is responsible for the adjustment of the size of pupil ? Q6: The median canal of cochlea is filled with : Q7: The thin, transparent extension of sclerotic layer found in front of the lens is: Q8: The part of the inner ear which is responsible for hearing is : Q9: The spiral organ possessing sensory cells for hearing is: Q10: Which of the following structures equalises the air pressure on either side of the tympanum ?Progress Check 1
(i) Eyelids
(ii) Eyelashes
(iii) Tears
(iv) Iris
(v) Ciliary muscles
Ans: (i) Eyelids — Protects the outer surface of the eyes and can shut out light.
(ii) Eyelashes — Prevent falling of large particles into the eye.
(iii) Tears — serve as lubricant, washes away dust particles.
(iv) Iris — regulates the amount of light that can enter the eye.
(v) Ciliary muscles — It changes the shape of the lens during accommodation reflex.
Ans: Conjunctiva → cornea → aqueous humour → lens → vitreous humour → retina
(i) Place of best vision in the retina of the eye
(ii) Place of no vision in the retina of the eye
(iii) Kind of retinal cells sensitive to dim light
(iv) The circular opening enclosed by iris
(v) The fibres which collectively hold the lens in position
(vi) Capacity of the eye to focus at different distances
(vii) The kind of lens required to correct near sightedness
(viii) The layer of the wall of the eye-ball that corresponds to the black lining of the box of a camera
Ans: (i) Yellow spot
(ii) Blind spot
(iii) Rod cells
(iv) Pupil
(v) Suspensory ligaments
(vi) Accommodation
(vii) Concave
(viii) Choroid
(i) Medicines dropped in the eye flow down into the nose.
(ii) A person from bright sunlight outside enters a poorly lit room and feels blinded for a short while.
Ans: (i) Nasolacrimal duct connects the eyes with the nasal cavity. Medicines dropped in the eye, sometimes flow down through this duct and come into the nose.
(ii) When a person enters a poorly lit room after being exposed to bright sunlight outside, they may feel blinded for a short while due to dark adaptation. The following changes take place in dark adaptation:Progress Check 2
(i) external (ii) middle (iii) internal ear.
Ear drum, hammer, pinna, cochlea, anvil, stirrup, eustachian tube, tympanum, oval window, semi-circular canals.
Ans:
(i) Semi-circular canals
(ii) Cochlea
(iii) Auditory nerve
Ans: (i) Semi-circular canals
Q3: Mention if the following statements are true (T) or false (F) :
(ii) Pinna concentrates and directs sound waves towards tympanum.
Ans: (i) False
Corrected Statement — Human ear is concerned with hearing and balancing.
(ii) True
(i) Name the parts numbered 1-6.
(ii) Which parts of the ear shown here are complete.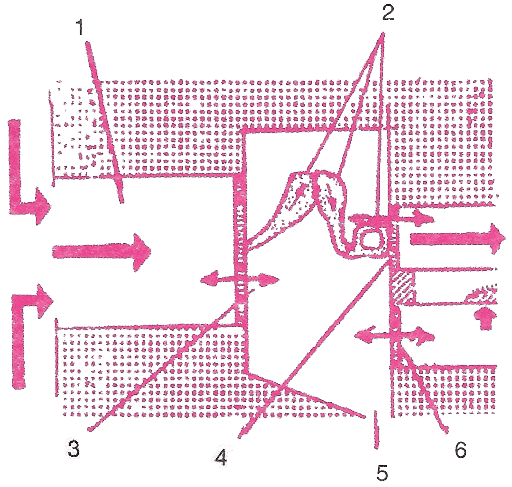
1 → Ear canal
2 → Ear ossicles
3 → Ear drum
4 → Oval wind
5 → Opening of Eustachian tube
6 → Round Window
(ii) Middle EarMultiple Choice Type
Q1: The layer in the eye where sensory cells (rods and cones) are located:
(b) Cornea
(c) Choroid
(d) Retina
The retina contains sensory cells that capture light, forming an image.
(a) Vitamin A
(b) Vitamin B
(c) Vitamin C
(d) Vitamin D
Ans: (a)
Vitamin A (retinol) is required to produce rhodopsin.
(a) Blind spot
(b) Pupil
(c) Yellow spot
(d) Iris
Ans: (b)
The pupil adjusts its size to regulate the amount of light entering the eye.
(a) Lysosome
(b) Aqueous humour
(c) Lysozyme
(d) Vitreous humour
Ans: (c)
Lysozyme in tears helps prevent infection by acting as an antiseptic.
(a) Iris
(b) Sclera
(c) Lens
(d) Choroid
Ans: (a)
The iris, with its radial and circular muscles, controls pupil size.
(a) Perilymph
(b) Lymph
(c) Endolymph
(d) Tissue fluid
Ans: (c)
The central canal of the cochlea contains endolymph.
(a) Cornea
(b) Cochlea
(c) Conjunctiva
(d) Choroid
Ans: (a)
The cornea is the thin, clear extension of the sclera that bulges in front of the lens.
(a) Semicircular canal
(b) Utriculus
(c) Cochlea
(d) Sacculus
Ans: (c)
The cochlea, which houses the organ of Corti, is responsible for hearing.
(a) Ampulla
(b) Semicircular Canal
(c) Vestibule
(d) Organ of Corti
Ans: (d)
The organ of Corti, located in the cochlea’s middle canal, contains sensory cells for hearing.
(a) Auditory tube
(b) Eustachian tube
(c) Vestibular canal
(d) Tympanic canal
Ans: (b)
The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear with the throat and helps equalize air pressure on either side of the eardrum.Very Short Answer Type
Q1 Name the following:
(a) The photosensitive pigment present in the rods of the retina.
(b) The part which equalizes the air pressure in the middle and external ear.
(c) The ear ossicle attached to the tympanum.
(d) The tube which connects the cavity of the middle ear with the throat.
(e) The part of the eye responsible for its shape.
(f) The nerves which transmit impulse from ear to the brain.
(g) The photoreceptors found in the retina of the eye.
(h) The eye defect caused due to shortening of the eye ball from front to back.
Ans: (a) Rhodopsin
(b) Eustachian tube
(c) Hammer
(d) Eustachian tube
(e) Sclerotic layer or Sclera
(f) Auditory nerves
(g) Rods and cones
(h) Hypermetropia
Q2: Note the relationship between the first two words and suggest the suitable word/words for the fourth place.
(a) Cones : Iodopsin :: Rods: ............... .
(b) Eyes : Photoreceptors :: Ears : ............... .
(c) Ears : Auditory nerve :: Eyes : ............... .
(d) Ear pinna : Auricle :: Inner ear : ............... .
(e) Semi-circular canal : Ampulla :: Cochlea : ............... .
Ans: (a) Cones : Iodopsin :: Rods: Rhodopsin.
(b) Eyes : Photoreceptors :: Ears : Phonoreceptors.
(c) Ears : Auditory nerve :: Eyes : Optical nerve.
(d) Ear pinna : Auricle :: Inner ear : Membranous labyrinth.
(e) Semi-circular canal : Ampulla :: Cochlea : Basilar membrane.
Q3: Match the terms in column I with those in column II and write down the matching pairs.
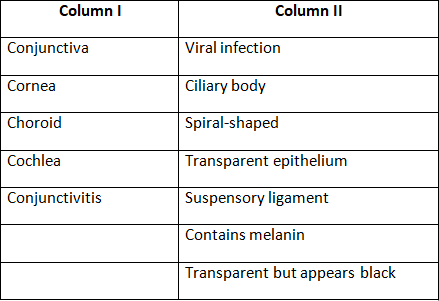
Ans: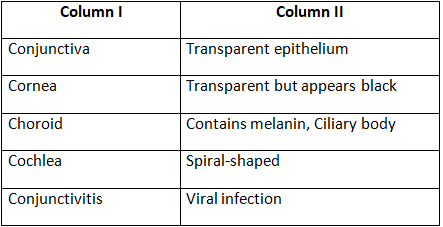
Short Answer Type
Q1: State whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F). If false, correct them by changing any one single word in each.
(a) Deafness is caused due to rupturing of the pinna.
(b) Semicircular canals are concerned with static (positional) balance.
Ans: (a) False
Corrected statement — Deafness is caused due to rupturing of the eardrum.
(b) False
Corrected statement — Semicircular canals are concerned with dynamic balance.
Q2: Where are the following located? State their main functions:
(a) Yellow spot
(b) Lacrimal gland
(c) Organ of Corti
(d) Eustachian canal
(e) Incus
Ans: (a) Yellow spot: The yellow spot is located at the back of the eye, nearly at the center on the horizontal axis of the eyeball. It is the area responsible for the sharpest vision and is involved in color vision.
(b) Lacrimal glands: The lacrimal glands are situated at the upper outer portion of the eye orbit. They secrete tears, which act as a lubricant, antiseptic, and help wash away dust particles from the eyes.
(c) Organ of Corti: The Organ of Corti is located in the middle cochlear canal of the ear. It plays a crucial role in hearing.
(d) Eustachian canal: The Eustachian canal connects the middle ear to the throat. It helps in equalizing the air pressure on both sides of the tympanic membrane.
(e) Incus: The incus is located in the middle ear. It aids in transmitting sound vibrations from the external ear to the inner ear.
Q3: Given below are two sets (a) and (b) of five parts in each. Rewrite them in correct sequence.
(a) Cochlea, tympanum, auditory canal, ear ossicles, oval window
(b) Conjunctiva, retina, cornea, optic nerve, lens.
Ans: (a) Auditory canal, tympanum, ear ossicles, oval window, cochlea
(b) Conjunctiva, cornea, lens, retina, optic nerve.
Q4: Write the main functional activity of each of the following structures.
(a) Cochlea
(b) Semicircular canal
(c) Iris
(d) Choroid
(e) Ciliary body and suspensory ligament
Ans: (a) Cochlea — Hearing.
(b) Semicircular canal — Dynamic Equilibrium.
(c) Iris — Regulates the size of pupil controlling the amount of light entering the eyes.
(d) Choroid — Provides nourishment to the eye and prevents light rays from reflecting and scattering inside the eye.
(e) Ciliary body and suspensory ligament — Accommodation of eye.
Q5: Complete the following table by filling in the blank spaces.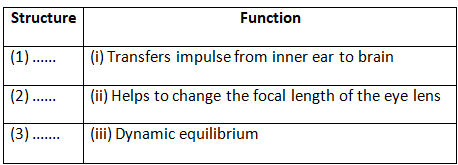
Ans: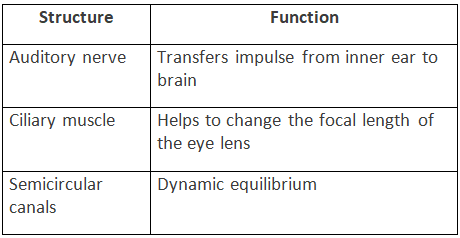
Q6: Name the following:
(a) Two pigments of the sensory cells.
(b) Two types of adaptations.
(c) Two kinds of accommodations.
(d) Three layers of the eyeball.
Ans: (a) Rhodopsin or visual purple and iodopsin or visual violet.
(b) Dark adaptation and light adaptation.
(c) Distant vision accommodation and near vision accommodation.
(d) Sclera, choroid and retina.
Q7: Name the eye defects caused due to each of the following: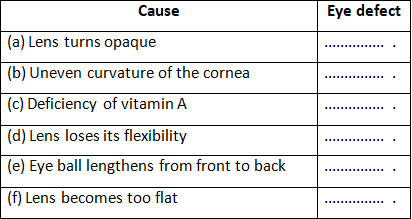
Ans: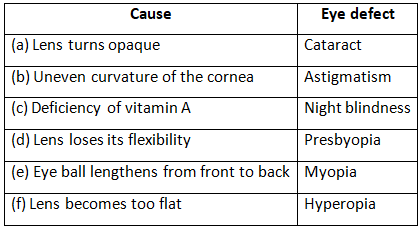
Descriptive Type
Q1: Define the following terms:
(a) Conjunctiva
(b) Lysozyme
(c) Adaptation
(d) Power of accommodation
(e) Ear ossicles
Ans: (a) Conjunctiva — A delicate membrane that covers the front surface of the eye and is continuous with the inner lining of the eyelids.
(b) Lysozyme — An enzyme found in tears that possesses antibacterial properties.
(c) Adaptation — The process by which the eye adjusts to varying light conditions, enabling clear vision in both bright and low-light environments.
(d) Power of accommodation — The eye’s ability to change the shape of the lens to focus on both near and distant objects by altering its thickness and focal length.
(e) Ear ossicles — The three small bones in the middle ear, namely the malleus, incus, and stapes, collectively known as the ear ossicles.
Q2: Differentiate between members of each of the following pairs with reference to what is asked in brackets.
(a) Myopia and hyperopia (type of lens used for correction)
(b) Rods and cones (sensitivity)
(c) Aqueous humour and vitreous humour (location)
(d) Near and distant accommodation (shape of lens)
(e) Dark and light adaptation (pigments which will be regenerated)
(f) Night blindness and colour blindness (sensory cells which cannot function properly)
Ans: (a) Difference between myopia and hyperopia (type of lens used for correction) —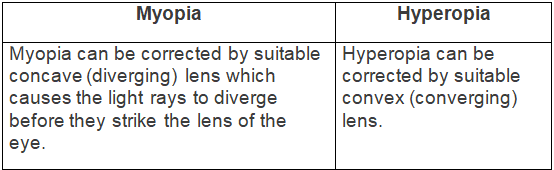 (b) Difference between rods and cones (sensitivity) —
(b) Difference between rods and cones (sensitivity) —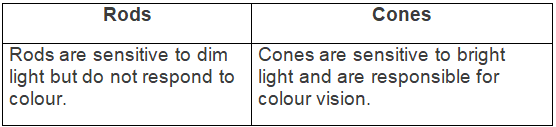 (c) Difference between aqueous humour and vitreous humour (location) —
(c) Difference between aqueous humour and vitreous humour (location) —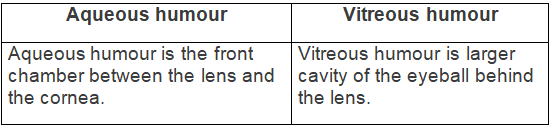 (d) Difference between near and distant accommodation (shape of lens) —
(d) Difference between near and distant accommodation (shape of lens) —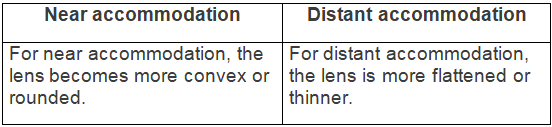 (e) Difference between dark and light adaptation (pigments which will be regenerated) —
(e) Difference between dark and light adaptation (pigments which will be regenerated) — (f) Difference between night blindness and colour blindness (sensory cells which cannot function properly) —
(f) Difference between night blindness and colour blindness (sensory cells which cannot function properly) —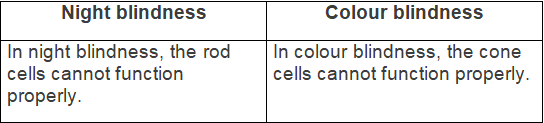 Q3: Give reason:
Q3: Give reason:
(a) Sometimes medicines dropped into the eyes come into the nose and even throat.
(b) Three small bones of ear ossicles are advantageous as compared to one single bone for hearing.
(c) Blind spot is considered as 'area of no vision'.
Ans: (a) Nasolacrimal duct connects the eyes with the nasal cavity. Medicines dropped in the eye, sometimes flow down through this duct and come into the nose and even throat.
(b) Three small bones of ear ossicles transmit the vibrations received by the tympanum and amplify them. If these were replaced by a single bone, the vibrations received by the tympanum would not be amplified. Hence, three small bones of ear ossicles are advantageous as compared to one single bone for hearing.
(c) There are no sensory cells in the blind spot and therefore, this is considered as 'area of no vision' and image striking it cannot be perceived.
Q4: Mention the characteristics of the image that falls on the retina of the eye.
Ans: The image formed on the retina is inverted and real.
Q5: Describe the mechanism of focusing the image of a distant object in your eye when you raise your head after reading a book.
Ans: Light rays from the object enter the eyes through the transparent structures.
For distant vision, the lens is more flattened or thinner.
For near vision, the lens becomes more convex or rounded.
While reading a book, the lens is more convex or rounded due to contraction of ciliary muscles because the book is usually read from a short distance. When we raise our head and look at a distant object, the ciliary muscles relax to build the tension on the suspensory ligament so that they can stretch the lens. This change in the curvature of the lens makes us focus on distant object.
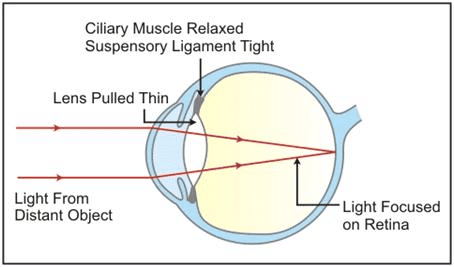
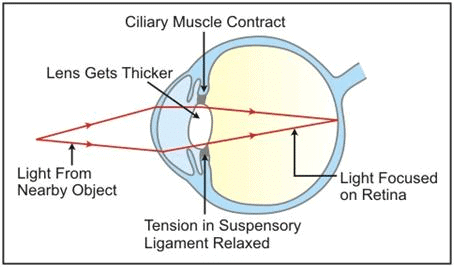
Q6: By closing the eyes and gently pressing them with your palms, you may see some specs of brilliant light. How do you get this sensation while there is no light entering your eyes?
Ans: The sensation of light can persist briefly after we look at a bright light source and then close our eyes. This aftereffect lasts for about one-tenth of a second. So, when you close your eyes and gently press them with your palms, you may see these brief specks of light due to this residual effect.
Q7: Name the three ear ossicles. How do they contribute in the mechanism of hearing?
Ans: The three ear ossicles are the Malleus (hammer), Incus (anvil), and Stapes (stirrup). The stapes, the last ossicle, vibrates and transmits these vibrations to the oval window. The other two ossicles, the malleus and incus, help amplify the vibrations from the stapes through their lever-like motion.
Structured / Application / Skill Type
Q1: The figures (A) and (B) given below are showing some kind of adjustment. Study the figures and answer the questions that follow.
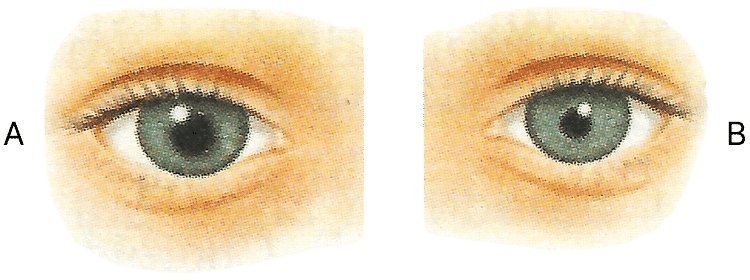
(a) Identify the kinds of adjustments done in the figure (A) and (B).
(b) Distinguish between the adjustments of figures (A) and (B) on the basis of :
(i) The size of pupil.
(ii) The pigment which gets regenerated.
(iii) Cells of the retina.
Ans: (a) Kinds of adjustments done in the figure:
(A) → dilated pupil due to dim light.
(B) → Constricted pupil due to bright light.
(b)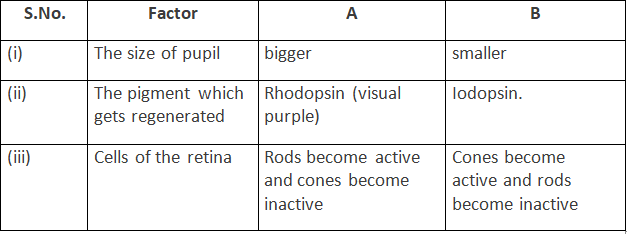
Q2: With reference to human eye and ear answer the questions that follow :
(a) Name the parts of the eye associated with:
(i) Regulation of the size of pupil.
(ii) Regulation of the shape of lens.
(iii) Keeping the lens moist and protecting it from physical shock.
(iv) The layer providing nourishment to the eye.
(b) Name the part of the ear associated with :
(i) Static balance.
(ii) Dynamic balance.
(iii) Hearing.
(iv) Amplification of vibrations.
Ans: (a) (i) Regulation of the size of pupil — Iris.
(ii) Regulation of the shape of lens — Ciliary muscles.
(iii) Keeping the lens moist and protecting it from physical shock — Aqueous Humour.
(iv) The layer providing nourishment to the eye — Choroid layer.
(b) (i) Static balance — Vestibule.
(ii) Dynamic balance — Ampulla.
(iii) Hearing — Organ of Corti.
(iv) Amplification of vibrations — Ear ossicles (Malleus, incus and stapes).
Q3: The figure given below refers to the vertical section of the eye of a mammal. Study the figure carefully and answer the following questions.
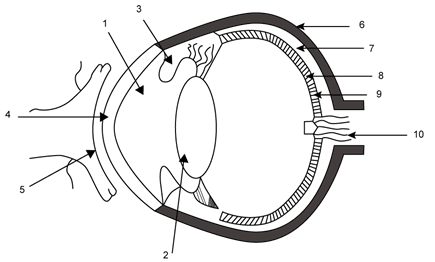
(b) Write one important role of parts shown as 3 and 7.
(c) Write one structural difference between the parts shown as 9 and 10.
(d) Mention one functional difference between the parts shown as 6 and 8.
Ans: (a) The guidelines are labelled below:
1 → Aqueous chamber 2 → Lens 3 → Iris 4 → Cornea 5 → Conjunctiva 6 → Sclera 7 → Choroid 8 → Retina 9 → Yellow spot 10 → Optic nerve (Blind spot)
Part 7 (Choroid) — It is the middle layer of the eyeball, richly supplied with blood vessels and provides nourishment to the eye.
(c) Part 9 (yellow spot) contains sensory cells especially the cone cells while part 10 (blind sport) contains no sensory cells.
(d) Part 6 (sclera) gives shape to the eyeball and part 8 (retina) acts as screen to form image of an object.
Q4: Given below is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye? Study the same and answer the questions that follow: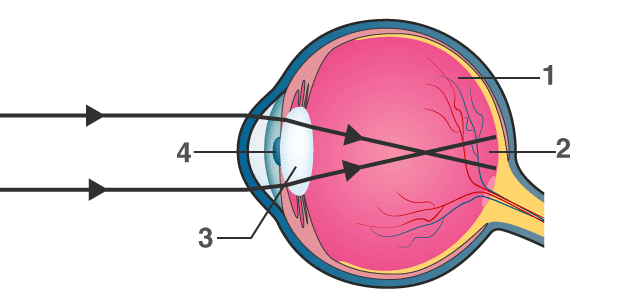 (a) Name the defect shown in the diagram.
(a) Name the defect shown in the diagram.
(b) Give two possible reasons for this defect.
(c) Name the parts labelled 1 to 4.
(d) Name the type of lens used to correct this eye defect.
(e) Draw a labelled diagram to show how the above mentioned defect is rectified using the lens named above.
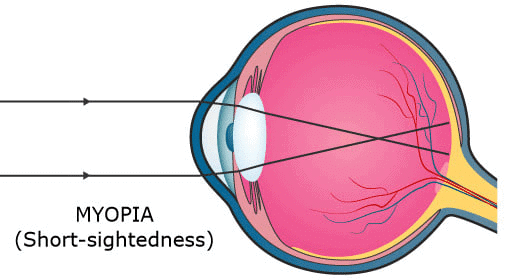
Ans: (a) Myopia
(b) The two possible reasons for myopia are either the eye ball is lengthened from front to back or the lens is too curved.
(c) Parts labelled 1 to 4 are:
- 1 → vitreous humour
- 2 → blind spot
- 3 → lens
- 4 → pupil
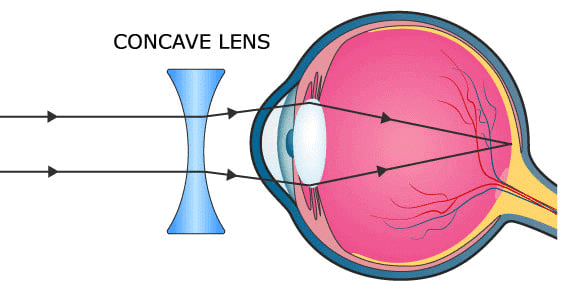
(d) Concave lens
(e) The below diagrams show the condition of Myopia and how it is corrected using a Concave Lens:
Q5: (a) Draw a neat and well labelled diagram of the membranous labyrinth found in the inner ear.
(b) Based on the diagram drawn above in (a), give a suitable term for each of the following descriptions:
(i) The structure responsible for hearing.
(ii) The sensory cells that help in hearing.
(iii) The membrane-covered opening that connects the middle ear to inner ear.
(iv) The nerves that carry impulses from the ear to the brain.
(v) The tube which equalises the air pressure on either side of the ear drum.
Ans: (a) Below labelled diagram shows the membranous labyrinth found in the inner ear:
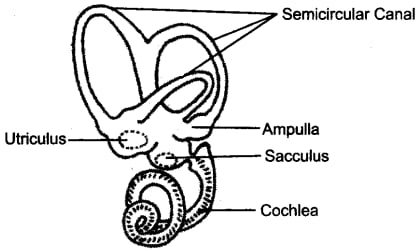
(b) (i) Cochlea
(ii) Organ of corti
(iii) Oval window
(iv) Auditory nerve
(v) Eustachian tube
Q6: Given below is a diagram of a part of the human ear. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
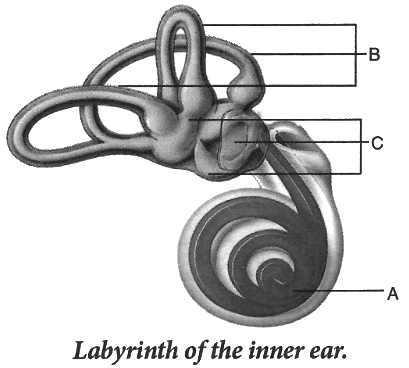 (i) Give the collective biological term for Malleus, Incus and Stapes.
(i) Give the collective biological term for Malleus, Incus and Stapes.
(ii) Name the parts labelled A, B and C in the diagram.
(iii) State the functions of the parts labelled 'A' and 'B'.
(iv) Name the audio receptor region present in the part labelled 'A'.
Ans: (i) Ear ossicles
(ii) The labelled parts are:
- A → Cochlea
- B → Semicircular canals
- C → Ear ossicles
(iv) Organ of Corti
Ans: Below is the labelled diagram of the inner ear:
Utriculus and Sacculus collectively termed as vestibule are responsible for maintaining static balance in human beings.
Q8: Have a look at the posture of this girl who is reading a book and answer the questions which follow:
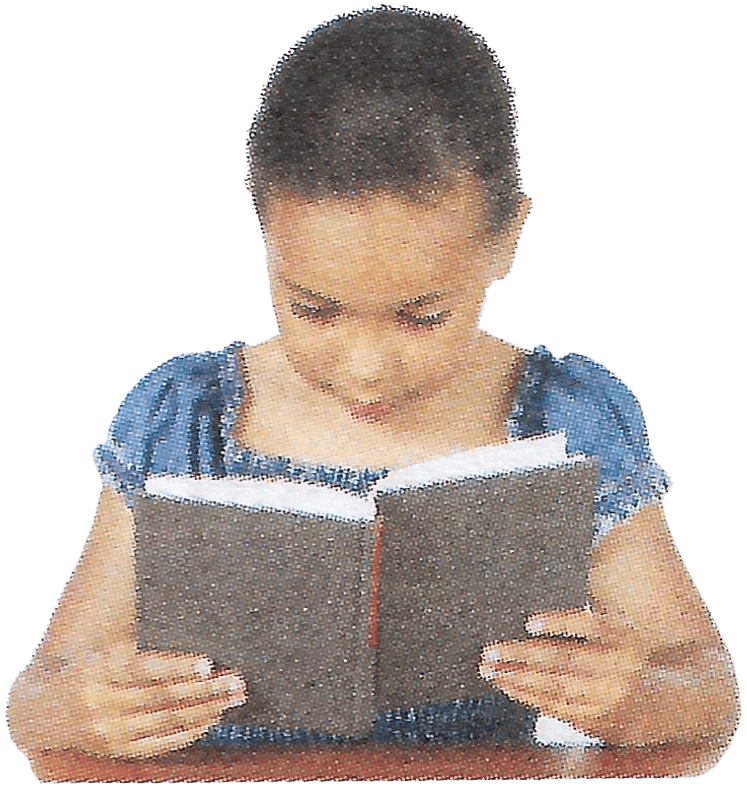 (a) Name the problem she is facing.
(a) Name the problem she is facing.
(b) What are the two conditions shown in sections A and B of the eye as applicable to her?
(c) What kind of reading glasses does she need ?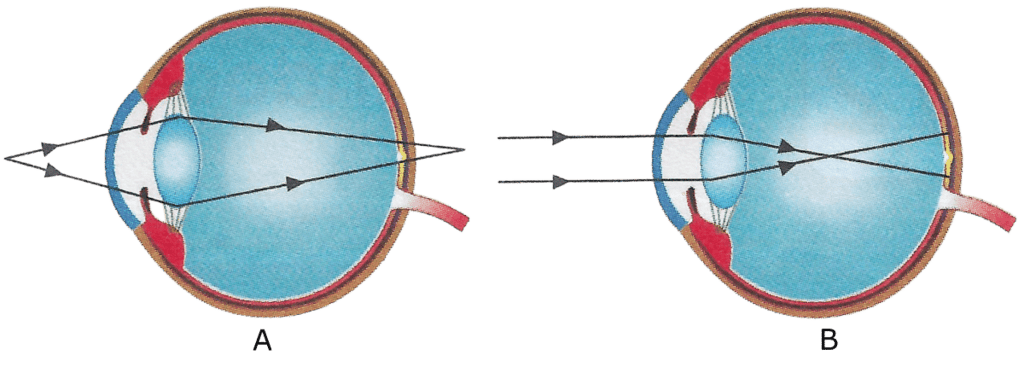 Ans: (a) Myopia
Ans: (a) Myopia
(b) The condition shown in section A is Hyperopia as the image is formed behind the retina. The condition shown in section B is Myopia as the image is formed in front of the retina.
(c) She needs reading glasses with concave lens.
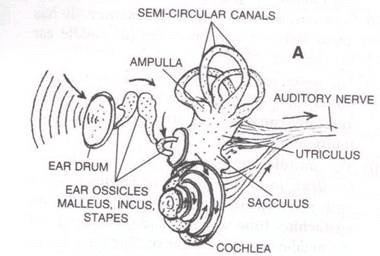
Q9: The figure given below shows the principal parts of a human ear. Study the diagram and answer the following questions.
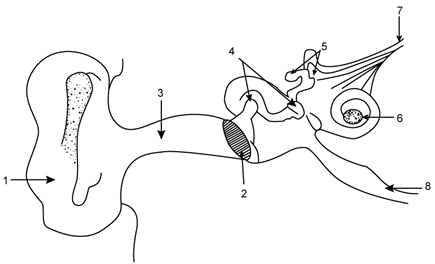
(b) State the role of parts 6, 7 and 8.
(c) Why is it harmful to use a sharp object to remove ear wax? Mention the number and name of the part involved.
Ans: (a) The labelled parts are:
- → External ear (pinna)
- → Ear drum (tympanum)
- → Auditory canal
- → Malleus
- → Semicircular canals
- → Cochlea
- → Auditory nerve
- → Eustachian tube
Part 7 (Auditory nerve) — It transmits impulse of hearing to the brain.
Part 8 (Eustachian tube) — It equalizes air pressure on both the sides of the tympanum.
(c) It is harmful to use a sharp object to remove ear wax as it can rupture the ear drum.
The part involved is part 2 — Ear drum (tympanum).
|
55 videos|110 docs|21 tests
|
FAQs on Selina Textbook Solutions: Sense Organs - Biology Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What are the main sense organs in the human body? |  |
| 2. How do the sense organs function? |  |
| 3. Why are sense organs important for survival? |  |
| 4. What are some common disorders related to sense organs? |  |
| 5. How can we take care of our sense organs? |  |















