Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Notes > Physics Class 9 ICSE > Revision Notes: Upthrust In Fluids, Archimedes` Principle And Floatation
Revision Notes: Upthrust In Fluids, Archimedes` Principle And Floatation | Physics Class 9 ICSE PDF Download
Buoyancy and Upthrust
- The weight of the object exerts a force on the liquid. The liquid also exerts a certain amount of force on the object in the upward direction. This force is called the buoyant force.
- The tendency of a liquid to exert an upward force on any object immersed in it is called buoyancy.
- The upward force exerted by a liquid is also called upthrust.
Condition for a Body to Sink or Float
- A body immersed in water experiences two forces—its weight in the downward direction and the upthrust due to water in the upward direction.
- When FB > W or FB = W, the body will float. When FB > W, the body will float with a part submerged for which the upthrust is equal to the weight. When FB = W, the body will float with its body completely submerged.
- When FB < W, the body will sink. It will go down with acceleration equal to difference in both forces divided by its mass.
a = (W - FB)/M
Characteristic Properties of Upthrust
- Larger the volume of the body submerged in fluid, greater is the upthrust.
- More the density of fluid, greater is the upthrust.
- The upthrust acts on the body in the upward direction at the centre of gravity of the displaced fluid which is called the centre of buoyancy.
Reason for Upthrust
- The liquid kept in a vessel exerts uniform pressure in all directions.
- The pressure at a point in a liquid is the same in all directions.
- It increases with increase in depth.
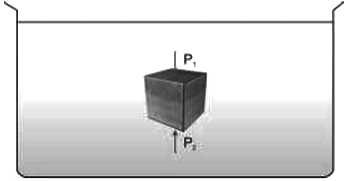
- The pressure P2 on the lower face is more than the pressure P1 on the upper face. This creates a pressure difference between the two faces of the block.
- Thus, there is a net upward force generated on the block.
Upthrust = F =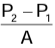
Archimedes’ principle
- Archimedes’ principle: When an object is immersed wholly or partially in a fluid, it experiences an upthrust which is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by it.
Buoyant force acting on an object = Weight of fluid displaced by that object - Gases however exert a very negligible buoyant force on the objects placed in them.
Experimental Verification of Archimedes’ Principle
- We can verify Archimedes’ principle with the help of the following two experiments.
Experiment 1
- In this experiment, a solid cylinder A and a hollow cylinder B of the same volume are used.
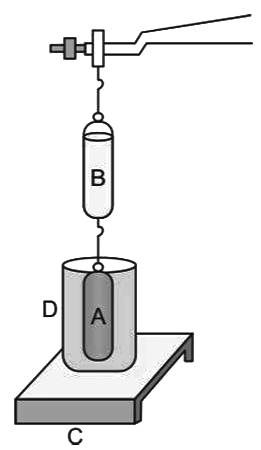
- The solid cylinder A is immersed in water contained in a beaker D. We observe that the solid cylinder loses some weight, that is, the left arm rises.
- Water is poured in the hollow cylinder B till it is completely filled. The beam is balanced.
- Thus, we can conclude that buoyant force acting on the solid cylinder A is equal to the weight of water filled in cylinder B.
- Because A and B have the same volume, the weight of water in cylinder B is equal to the weight of water displaced by A.
- Thus, the buoyant force acting on cylinder A is equal to the weight of water displaced by it.
Experiment 2
- In this experiment, a solid is suspended by a thin thread from the hook of a spring balance. The balance will show a reading.
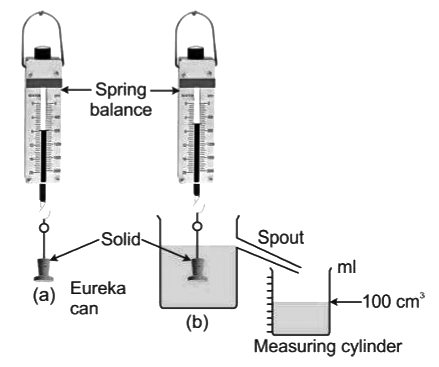
- A can called eureka can filled with water up to the spout is taken. A measuring cylinder is kept near the spout of the can.
- The solid is gently immersed in the can. This leads to spilling of water from the spout which gets collected in the measuring cylinder.
- Note the weight of the solid and the volume of water collected in the cylinder.
- Water has density 1 g cm−3. Thus, the volume of water collected in the cylinder is equal to the mass (or weight) of water displaced by the solid.
Density
- Density of a substance is defined as mass per unit volume.
- It is a scalar quantity and is represented by the Greek letter ρ.
ρ = M/V - Its SI unit is kg m−3, and its CGS unit is g cm−3.
- Most substances expand on heating and contract on cooling.
- Thus, the density of a substance increases with decrease in temperature and decreases with increase in temperature.
Relative Density
- The relative density of a substance is the ratio of its density to that of water at 4°C.
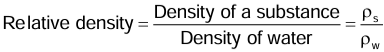
- It is also given as the ratio of the mass of the substance to the mass of equal volume of water at 4°C.

- It has no units because it is a ratio of similar quantities.
- In the SI system, the density of water is 1000 kg m−3. Thus, we have
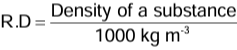
∴ Density in kg m-3 = 1000 R.D - Now, the density of water in the CGS system is 1 g cm−3 . Thus, we have
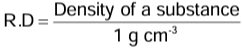
∴ Density in g cm-3 = R.D
Relative Density of a Solid by Archimedes’ Principle
Relative density = (Mass of a certain volume of substance/Mass of same volume of water)- According to the Archimedes’ principle, the mass of water of volume equal to that of the body is found by finding the mass of water displaced by the body when it is completely immersed in water. Thus, we have

- If W1 is the weight of the body in air and W2 is the weight of the body in water, then
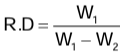
Determination of RD of a Solid Denser than Water and Insoluble in it
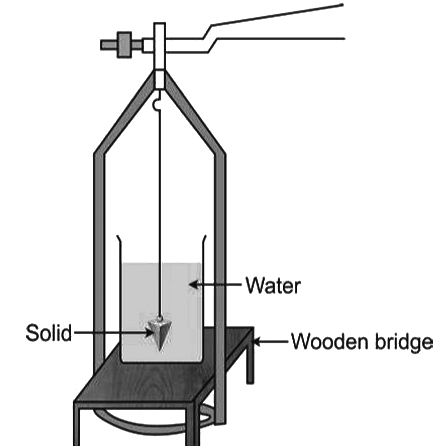
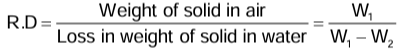
Determination of RD of a Solid Denser than Water and Soluble in it
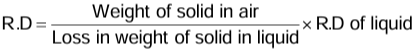
Relative Density of a Liquid by Archimedes’ Principle
Relative density = (Weight of a given volume of liquid)/(Weight of the same volume of water)- According to the Archimedes’ principle, a solid immersed in water displaces the liquid or water equal to its own volume.
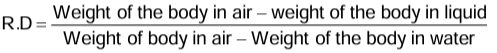
- If W1 is the weight of the body in air, W2 is the weight of the body in liquid and W3 is the weight of the body in water, then
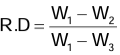
Floatation
- A body immersed in liquid experiences two forces:
- Its weight in the downward direction through its centre of gravity G.
- The upthrust due to the liquid in the upward direction through the centre of gravity of the displaced liquid. This centre is called the centre of buoyancy B.
- Case I: When W > FB, i.e. the weight of the body is greater than the weight of the displaced liquid, the body will sink.
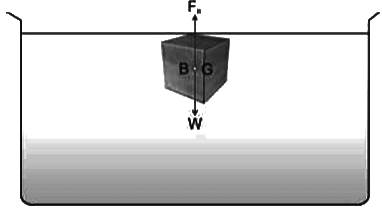
- Case II: When W = FB, i.e. the weight of the body is equal to the weight of the displaced liquid, the body will float with its body submerged just below the surface of the liquid.
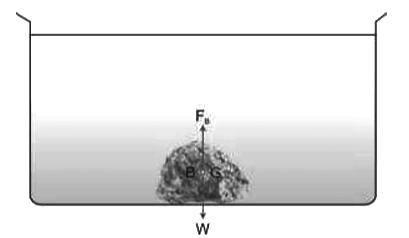
- Case III: When W < FB, i.e. the weight of the body is less than the weight of the liquid displaced, the body will float partially above the surface of the liquid.
- Principle of floatation: The weight of a floating body is equal to the weight of the liquid displaced by its submerged part.
Relation between Volume of the submerged part of a floating body, the Densities of the Liquid and the Body

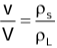
Applications
- Floatation of Iron Ship
(i) An iron nail sinks in water while a ship floats.
(ii) A ship begins to submerge more as it sails from sea water to river water.
(iii) An unloaded ship is filled with sand at its bottom. - Floatation of Man
(i) A swimmer fills his lungs with air and keeps his nose and mouth just above the water surface. Thus, the weight of water displaced by the swimmer is nearly equal to his own weight. Thus, he can swim with less effort.
(ii) A man can swim easily in sea water than in fresh water. - Floatation of Submarines
- Floatation of iceberg
An iceberg floats in water with 1/12th part of its total volume above the surface of water. - Floatation of fish
- Rising of balloons
The document Revision Notes: Upthrust In Fluids, Archimedes` Principle And Floatation | Physics Class 9 ICSE is a part of the Class 9 Course Physics Class 9 ICSE.
All you need of Class 9 at this link: Class 9
|
9 videos|74 docs|10 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Upthrust In Fluids, Archimedes` Principle And Floatation - Physics Class 9 ICSE
| 1. What is Archimedes' Principle and how does it relate to upthrust in fluids? |  |
Ans.Archimedes' Principle states that when a body is partially or fully immersed in a fluid, it experiences an upward force, known as upthrust or buoyant force, that is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the body. This principle explains why objects float or sink in a fluid based on their density relative to the fluid.
| 2. What conditions must be met for a body to float or sink in a fluid? |  |
Ans.For a body to float, the buoyant force acting on it must be equal to its weight. This occurs when the density of the body is less than or equal to the density of the fluid. Conversely, a body will sink if its weight is greater than the buoyant force, which happens when the body’s density is greater than that of the fluid.
| 3. How can we experimentally verify Archimedes' Principle? |  |
Ans.Archimedes' Principle can be experimentally verified by measuring the weight of a solid object in air and then measuring its weight when submerged in water. The difference in weight corresponds to the weight of the water displaced by the object, confirming the principle.
| 4. What is relative density and how is it determined for solids that are denser than water? |  |
Ans.Relative density (RD) is the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of a reference substance, typically water. For solids denser than water, the RD can be determined by weighing the solid in air and then weighing it again while submerged in water. The RD is calculated using the formula: RD = Weight in air / (Weight in air - Weight in water).
| 5. How does the volume of the submerged part of a floating body relate to the densities of the liquid and the body? |  |
Ans.The volume of the submerged part of a floating body is directly proportional to the density of the body and inversely proportional to the density of the liquid. This relationship can be expressed mathematically: \( V_{sub} = \frac{W_{body}}{\rho_{liquid}} \), where \( V_{sub} \) is the volume submerged, \( W_{body} \) is the weight of the body, and \( \rho_{liquid} \) is the density of the liquid.
Related Searches
















