Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Notes > Biology Class 9 ICSE > Revision Notes: Flower
Revision Notes: Flower | Biology Class 9 ICSE PDF Download
The Flower
Introduction:
- A flower is a specialized part of a plant where the leaves are modified to create floral structures.
- Flowers are essential for plant reproduction and come in various forms, some complete with all parts, while others may be missing certain whorls.
Complete and Incomplete Flowers:
- A complete flower has all four whorls: calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynoecium. Examples include hibiscus, rose, and sunflower.
- An incomplete flower lacks one or more floral whorls. Examples include rue anemone, American elm, and black walnut.
Essential and Non-Essential Whorls:
- Essential whorls are directly involved in reproduction, such as the stamen and carpel.
- Non-essential whorls help protect or attract pollinators to the reproductive parts, like the calyx and corolla.
Modified Floral Structures:
- In plants like wheat and grasses, petals and sepals are undifferentiated and together form the perianth.
- Some plants have petaloid sepals, where sepals are brightly colored like petals, creating a petaloid perianth. An example is orchids.
- In certain plants, sepaloid petals are green petals, and the perianth is called a sepaloid perianth. Examples include Viscum and mistletoe.
- Bracts are modified leaves that can be green or colored like petals, found in plants like hibiscus and bougainvillea.
- Nectaries are groups of cells that secrete nectar, located at the base of the pistil or on the petals. An example is nasturtium.
Types of Flowers:
- Bisexual flowers contain both male and female reproductive structures, such as hibiscus.
- Unisexual flowers have either male or female reproductive structures.
- Male or staminate flowers have only the androecium, while female or pistillate flowers have only the gynoecium. Examples include eastern cottonwood (male) and date palm (female).
- Neuter flowers lack both male and female reproductive organs, like ray florets of sunflower.
Plant Types:
- Monoecious plants have male and female flowers on the same plant, such as pumpkin, maize, and cucumber.
- Dioecious plants have male and female flowers on separate plants, like palm and papaya.
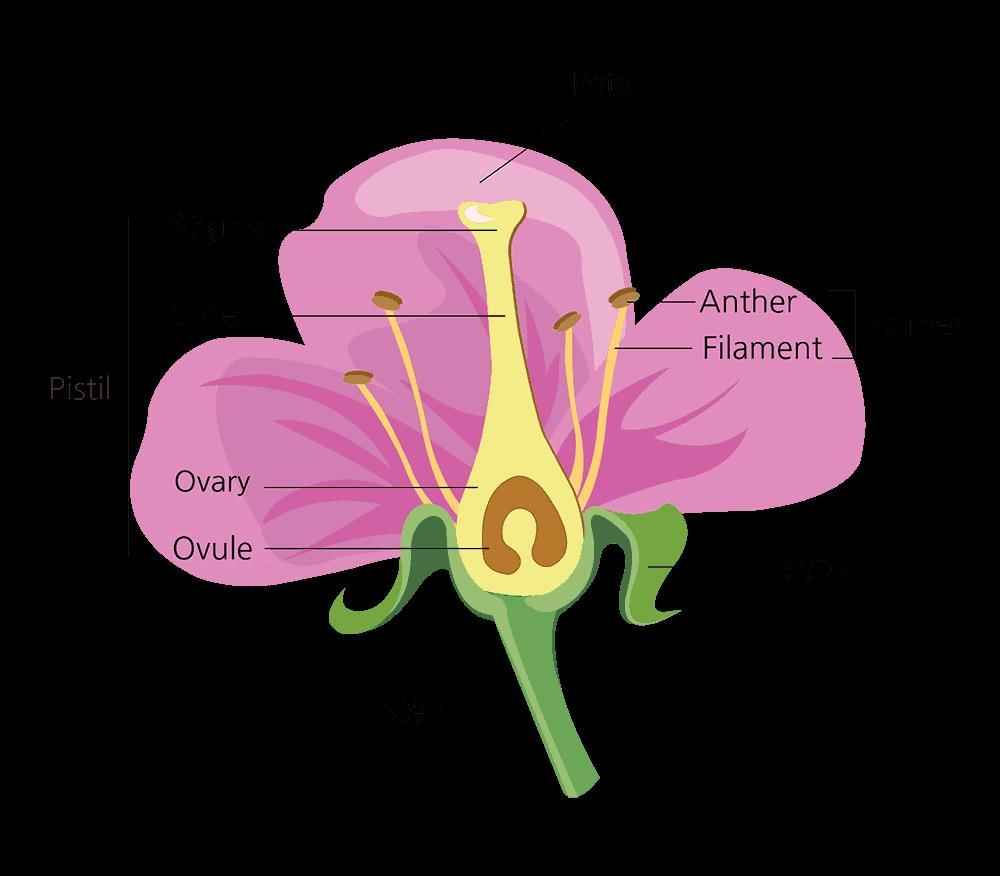
Calyx:
- The calyx is the outermost whorl of a flower, composed of green, leaf-like structures called sepals.
- Sepals protect the inner whorls of the flower during the bud stage. Green sepals can perform photosynthesis, contributing to the plant's food production, while non-green sepals may attract pollinators.
- If sepals are joined together, the calyx is gamosepalous, as seen in hibiscus. If sepals are free, the calyx is polysepalous, found in roses and mustard.
- In hibiscus, bracts form a whorl called epicalyx below the calyx.
Corolla:
- The corolla is the second whorl of a flower, consisting of petals.
- If petals are fused into a tube-like structure, they are gamopetalous, as seen in nerium and ipomea. If petals are free from each other, they are polypetalous, found in roses and mustard.
- Petals are usually arranged in a single whorl, but some plants have double whorls, like poppy. In some cases, petals are spirally arranged, as in water lily.
- The number of petals may equal the number of sepals in some flowers, like buttercup, or differ, as in roses.
- The corolla's main functions are pollination and protection.
Androecium:
- The androecium is the third whorl and represents the male reproductive part of the flower, consisting of stamens.
- When stamens are free, the condition is called polyandrous, as in petunia. When stamens are fused, the condition is adelphous, as in hibiscus.
- Monadelphous refers to filaments of anthers fused into one group, diadelphous to filaments fused into two groups, and polyadelphous to filaments fused into more than two groups, as seen in bombax.
Gynoecium or Pistil
Gynoecium or Pistil is the female reproductive part of the plant. The pistil is made of units called carpels. The pistil consists of either a single carpel or many carpels.
Types of Gynoecium
- Apocarpous: If the carpels of a flower are free, then the gynoecium is said to be apocarpous. Example: Buttercup flower etc.
- Syncarpous: If the carpels of a flower are fused, then the gynoecium is said to be syncarpous. Example: Orchid etc.
Ovary Types
- Bicarpellary Ovary: Has two carpels.
- Tricarpellary Ovary: Has three carpels.
Ovary Position
- Superior Ovary: Attached to the receptacle above the attachment of other floral parts such as the thalamus and the calyx. Example: Onion etc.
- Inferior Ovary: Lies below the attachment of other floral parts such as the thalamus and the calyx. Example: Rose etc.
Placentation Types
- Marginal Placentation: The ovary is monocarpellary and single chambered. The placenta, along with the ovules, develops along the margins of the carpel. Example: Pea etc.
- Axile Placentation: The ovary is two chambered or many chambered, with the margins of the carpels fusing together to form a central axis. The placenta, along with the ovules, develops from this axis. Examples: China rose, lemon, orange etc.
- Parietal Placentation: The ovules are attached to the walls of a unilocular ovary, borne on the inner surface of the ovary wall. Examples: Mustard, Argemone etc.
Inflorescence
An inflorescence is a cluster or a group of flowers arranged on the plant stem.
The document Revision Notes: Flower | Biology Class 9 ICSE is a part of the Class 9 Course Biology Class 9 ICSE.
All you need of Class 9 at this link: Class 9
|
18 videos|101 docs|19 tests
|
Related Searches
















