Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Notes > Biology Class 9 ICSE > Revision Notes: Seeds Structure And Germination
Revision Notes: Seeds Structure And Germination | Biology Class 9 ICSE PDF Download
Seeds – Structure and Germination

Fruit and Seed Structure
- Fruit: The fruit is the enlarged, matured, or ripened ovary of a flower. It serves to protect the seed and aids in its dispersal. Examples of fruits include mangoes and pea pods.
- Seed: A seed is a mature and ripened ovule that forms after fertilization. It stores food for the embryo's nourishment during germination. The seed coat safeguards the embryo from mechanical damage. Examples of seeds include beans and peas.
- Grain: A grain is a type of fruit where the fruit wall and seed coat are fused together, forming a protective layer. Examples include maize and wheat.
Types of Seeds
- Monocotyledonous Seeds: These seeds have only one cotyledon. Examples include maize and grass.
- Dicotyledonous Seeds: These seeds have two cotyledons. Examples include peas, grams, and beans.
- Small Seeds: These seeds are very tiny and not visible to the naked eye. Examples include poppy and orchid seeds.
- Large Seeds: These seeds are bigger and easily visible. Examples include watermelon, pumpkin, and mango seeds.
- Largest Seeds: These are the biggest seeds, often double the size of large seeds. Examples include coconut and double coconut seeds.
Seed Classification Based on Endosperm
- Albuminous/Endospermic Seeds: In these seeds, the endosperm is large, thick, and fleshy, serving as the food source for the developing embryo.
- Dicot Albuminous Seeds: Examples include poppy, custard apple, muskmelon, and fenugreek.
- Monocot Albuminous Seeds: Examples include cereals, millets, palm, and onion.
- Exalbuminous/Non-Endospermic Seeds: In these seeds, the cotyledons store food and become thick and fleshy.
- Dicot Exalbuminous Seeds: Examples include gram, pea, mango, mustard, and soya bean.
- Monocot Exalbuminous Seeds: Examples include orchid, Amorphophallus, and Vallisneria.
Differences between Bean Seed and Maize Grain
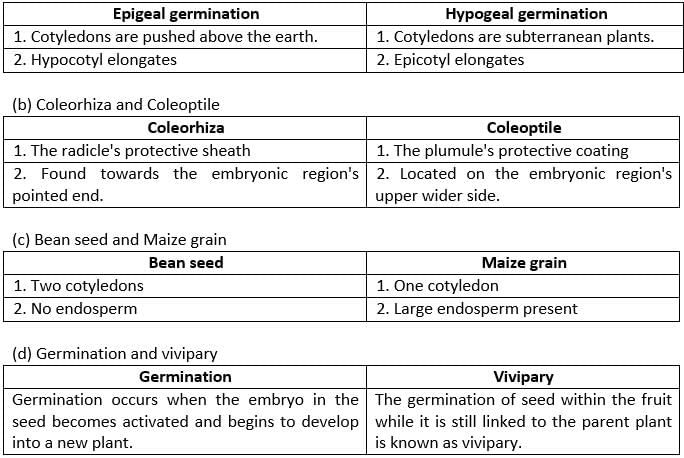
| PARTS | BEAN SEED | MAIZE GRAIN | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cotyledons | Two | One | |||||
| Endosperm | Absent | Present | |||||
| Embryo | Plumule | Leaves | Hilum | Micropyle | Seed arrangement | ||
| Radicle | Hypocotyl | Epicotyl | Separate | No separate seed | Seed wall and fruit wall are fused to form a single grain |
Germination of Seeds
Germination is the process through which the embryo breaks out of the seed by tearing the seed coat, resulting in the formation of a seedling.
Conditions Necessary for Germination
- Water: Water enters the seed and activates enzymes that mobilize and break down reserve food into simpler forms. This food is used by the embryo to start growing.
- Temperature: A moderate temperature between 25°C to 35°C is ideal for seed germination, known as the optimum temperature.
- Oxygen: Oxygen is necessary for respiration, providing energy for rapid cell division and growth.
- Light: Some seeds require a specific duration of light to germinate.
Types of Germination
| Type | Characteristics | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Hypogeal Germination | The epicotyl elongates while the cotyledons remain underground. | Pea, gram, maize, wheat |
| Epigeal Germination | The hypocotyl elongates, pushing the cotyledons above the ground. | Bean, castor, sunflower, gourd |
| Viviparous Germination | The seed germinates while still inside the fruit, attached to the mother plant. | Rhizophora, Sonneratia |
Seedling Development
- The seedling stage in plant growth is when the plant relies on the reserve food of the seed or the food produced by the cotyledons.
- A seedling comprises five parts: the radicle (embryonic root), hypocotyl, epicotyl, plumule, and cotyledons.
The document Revision Notes: Seeds Structure And Germination | Biology Class 9 ICSE is a part of the Class 9 Course Biology Class 9 ICSE.
All you need of Class 9 at this link: Class 9
|
18 videos|101 docs|19 tests
|
Related Searches
















