Revision Notes: Respiration in Plants | Biology Class 9 ICSE PDF Download
Respiration in Plants
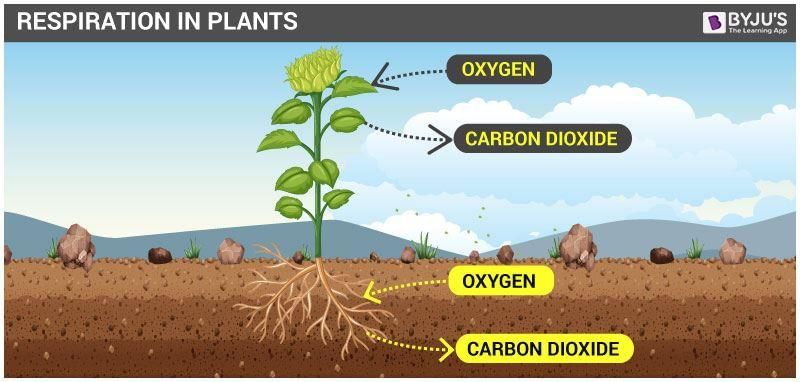
Respiration is a process in which energy is obtained from a simple sugar—glucose—for carrying out various life processes.
Respiration in plants is a catabolic process of releasing energy from a simple sugar—glucose for carrying out various life processes. C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 → 6 C O 2 + 6 H 2 O + ATP Glucose Oxygen Carbon dioxide Water Energy
Characteristics of Respiration
a. The breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide and water does not occur in a single step. It involves a series of chemical reactions—glycolysis, Krebs cycle and electron transport.
b. Each breakdown step is carried out by a specific enzyme.
c. A small amount of energy liberated in the breakdown of the glucose molecule is released as heat energy. But a major part of it is converted into chemical energy in the form of Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP).
Kinds of Respiration
Aerobic Respiration: The breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen is called aerobic respiration. Most of the animals, human beings, several bacteria and fungi are aerobic in nature.
Anaerobic Respiration: The breakdown of glucose in the absence of oxygen is called anaerobic respiration. Unicellular organisms such as yeast and some bacteria are examples of anaerobes.
Fermentation: The breakdown of pyruvic acid to ethanol and carbon dioxide in the absence of oxygen is called fermentation. Certain microorganisms or their enzymes carry out fermentation.
Differences between Respiration and Combustion
RESPIRATION
COMBUSTION
It occurs in a series of chemical steps. It occurs in a single step.
It is carried out by enzymes. It is carried out by heat.
It is a biochemical process. It is a physicochemical process.
Energy is liberated in the form of ATP and some heat. Energy is liberated in the form of heat and light.
No light energy is produced. Light energy is produced.
It is a cellular process. It is a non-cellular process.
It occurs at body temperature. It occurs at high temperature (at ignition point).
No supply of heat energy is required. Supply of heat energy is required.
The organic compound is oxidised to carbon dioxide and water. The organic compound initially chars and later burns, producing a flame.
The energy is released in a step-wise manner. The energy is released at once.
It involves the formation of several intermediates. It does not involve the formation of any intermediates.
It requires the presence of water. It does not require the presence of water.
It requires the presence of catalysts. It does not require any biological catalysts.
It is a slow process. It is a fast process.
It is a continuous process. It is not a continuous process.
Respiration in plants takes place through Stomata in leaves Lenticels in stem General surface of roots
Differences between Aerobic and Anaerobic respiration in plants
AEROBIC RESPIRATION
ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION
1. It is also called oxybiotic respiration. 1. It is also called anoxybiotic respiration.
2. It proceeds in the presence of oxygen. 2. It proceeds in the absence of oxygen.
3. It occurs in mitochondria. 3. It occurs in cytoplasm.
4. There is complete breakdown of glucose. 4. There is incomplete breakdown of glucose.
5. The end-products are carbon dioxide and water. 5. The end-products are ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide.
6. A large quantity of energy is liberated (38 ATP) from one mole of glucose. 6. A small quantity of energy is liberated (2 ATP) from one mole of glucose.
7. It normally occurs throughout life. 7. It occurs temporarily for short periods.
Characteristics of Respiration in plants
- Oxygen is used up during respiration.
- Carbon dioxide is produced during respiration in germinating seeds.
- Carbon dioxide is produced during respiration in green plants.
- Heat is evolved during respiration in plants.
Differences between Respiration and Photosynthesis
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
It occurs in chloroplast.
It occurs in cytoplasm/mitochondria.
It occurs only in the presence of chlorophyll.
It occurs in all living cells.
It occurs only in the presence of light.
It occurs continuously at all times.
It utilises carbon dioxide and water.
It utilises oxygen and glucose.
Oxygen is released as an end-product.
Carbon dioxide is released as an end-product.
Light energy is converted into chemical energy and stored.
Chemical energy is partly converted into heat and partly into useful energy for various activities.
It results in gain of weight.
Differences between Respiration in Plants and Animals
Respiration in Plants
- External Ventilation: Plants do not exhibit external ventilation or breathing movements during respiration.
- Gaseous Transport: There is no need for gaseous transport in plants. Respiratory gases, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, simply diffuse in and out of the cells.
- Source of Oxygen: Plants can use oxygen released during photosynthesis as an additional source for respiration.
- End-Product of Anaerobic Respiration: In anaerobic conditions, plants produce ethanol as the end-product.
- Heat Production: Respiration in plants produces a small amount of heat.
- Rate of Respiration: The rate of respiration in plants is generally slow.
Respiration in Animals
- External Ventilation: Animals exhibit external ventilation or breathing movements during respiration.
- Gaseous Transport: The transport of respiratory gases is facilitated by tissue fluid and blood in animals.
- Source of Oxygen: Air is the primary source of oxygen for respiration in animals.
- End-Product of Anaerobic Respiration: In anaerobic conditions, animals produce lactic acid as the end-product.
- Heat Production: A larger quantity of heat is released during respiration in animals.
- Rate of Respiration: The rate of respiration in animals is comparatively faster.
|
18 videos|101 docs|19 tests
|
















