Revision Notes: Skin | Biology Class 9 ICSE PDF Download
Skin – ‘The Jack Of All Trades’
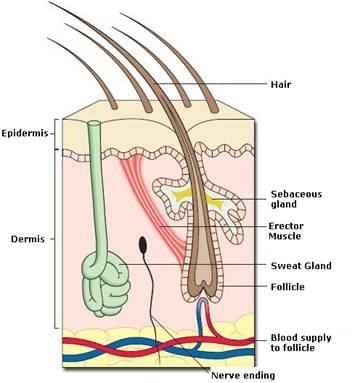
The skin is the largest organ of the body.
Functions of the Skin
a. Protection
b. Sensation
c. Temperature regulation
d. Synthesis of vitamin D
e. Excretion
COMPONENT OF SKIN
DESCRIPTION
Epidermis
Outermost layer of the skin, made up of epithelial cells. Contains melanocytes which are responsible for imparting colour to the skin.
Dermis
Middle layer of the skin. Made up of collagen and elastic fibres which provide strength and elasticity to the skin.
Hypodermis
Lowermost layer of the skin which contains adipose tissue. Insulates the skin, acts as a shock absorber and anchors the skin to the underlying bones and muscles. Common route for administration of injections.
Hair
Filamentous structure which grows from the hair follicles found in the dermis. Consists of three parts—hair shaft, hair root and hair bulb. Provides protection, regulates body temperature and acts as a sense organ.
Nails
Hardened structures which grow as dead cells from the nail root. Consist of three parts—nail plate, nail bed and matrix. Protect the sensitive tips of the digits
Sebaceous glands
Small sac-like glands situated in the dermis associated with the hair follicle. Secretes sebum which makes hair and outer surface of the skin oily and waterproof, to prevent the loss of water due to evaporation.
Sweat
Small tubular structures on the skin which are made up of two parts—secretory part and excretory part Separates sweat from blood.
Mammary glands
Modified sweat glands. The activity of mammary glands is related to reproductive hormones—prolactin, oestrogen and progesterone, which are prominently secreted during pregnancy.
Temperature Regulation
Sources of heat production:
- Chemical reactions in body cells, especially glucose oxidation in the liver.
- Vigorous muscle activity.
- Ingestion of hot foods and beverages.
Sources of heat loss:
- Skin: About 85% of body heat is lost through the skin by convection, conduction, radiation, and evaporation of sweat.
- Lungs: Heat is lost during expiration and through water vaporization from the lungs.
- Urine and faeces: Elimination occurs at body temperature.
- Foods: Heat is lost when consuming cold food, water, or beverages.
Role of hypothalamus in temperature regulation:
- The hypothalamus acts as the body's thermostat, regulating heat production and loss to maintain a stable internal temperature.
Temperature regulation in cold weather:
- Blood vessels constrict (vasoconstriction), reducing blood supply to the skin.
- Decreased heat loss through convection, conduction, radiation, and reduced sweat secretion.
- Increased heat production through metabolic rate and muscular activity (shivering).
Temperature regulation in hot weather:
- Blood vessels dilate (vasodilation), increasing blood supply to the skin.
- Enhanced heat loss through convection, conduction, radiation, and increased sweat secretion.
- Risk of heatstroke or sunstroke if sweat production cannot keep up with evaporation.
- Preventive measures include drinking plenty of water and consuming more salt during hot weather.
|
18 videos|101 docs|19 tests
|
















