Assignment: Constitution - Why and How? | Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Short Q/A |

|
| Activity-Based Questions |

|
| Research-Based Question |

|
| Crossword |

|
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1: What is the primary function of a constitution?
a) To give power to a single individual
b) To allocate power and regulate relations between different branches of government
c) To give absolute power to the government
d) To control religious practices
Ans: b) The primary function of a constitution is to allocate power and regulate relations between different branches of government.
Q2: Who were the main participants in the framing of the Indian Constitution?
a) Members of the British Parliament
b) The Indian National Congress and the British Government
c) The Constituent Assembly of India
d) The rulers of princely states
Ans: c) The Indian Constitution was framed by the Constituent Assembly of India.
Q3: What principle is embodied in the Indian Constitution regarding citizenship?
a) Citizenship based on religion
b) Citizenship based on race
c) Citizenship without regard to religion, race, or caste
d) Citizenship based on land ownership
Ans: c) The Indian Constitution provides for citizenship without regard to religion, race, or caste.
Q4: What is the significance of the "Objectives Resolution" in the Indian Constitution?
a) It defines the powers of the government
b) It outlines the principles of liberty, equality, and fraternity
c) It establishes the structure of the judiciary
d) It deals with the administrative setup of India
Ans: b) The "Objectives Resolution" outlines the principles of liberty, equality, and fraternity, which were central to the Indian Constitution.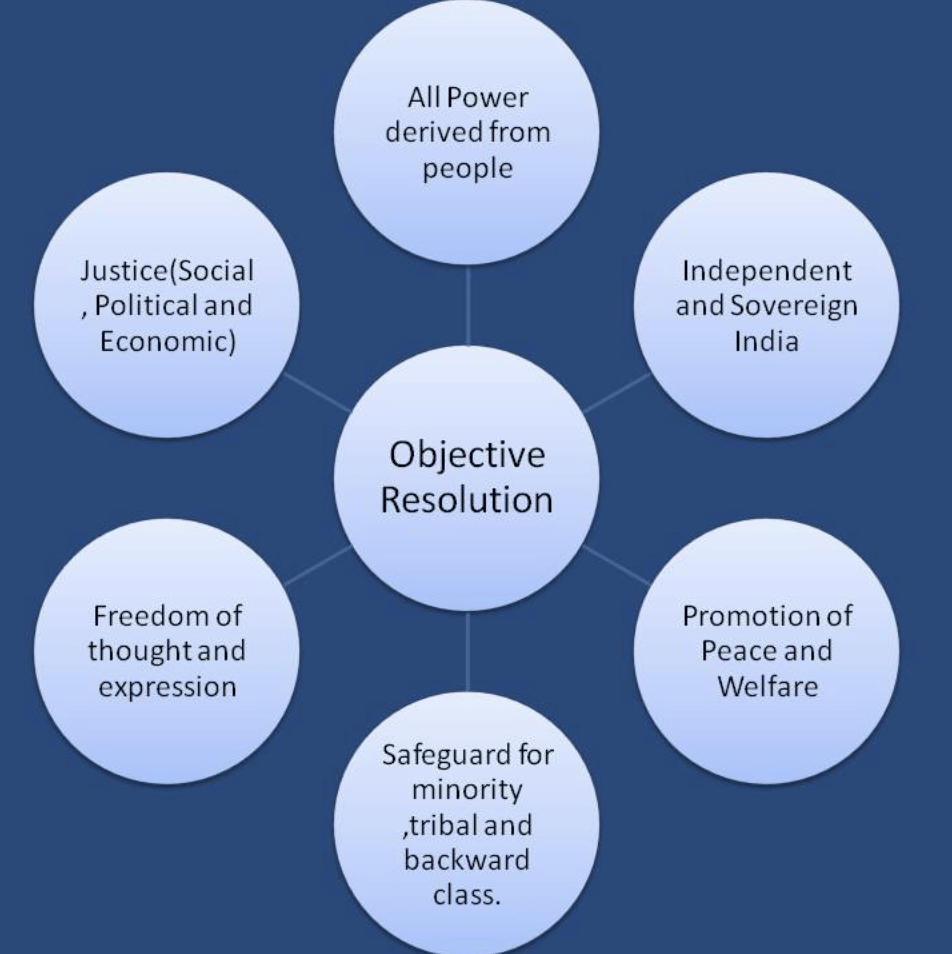
Q5: Which of these provisions were adapted from the British Constitution?
a) Directive Principles of State Policy
b) First Past the Post system
c) Fundamental Rights
d) Federal system of government
Ans: b) The "First Past the Post" electoral system was adapted from the British Constitution.
Short Q/A
Q1: What is meant by "Constitutional Morality"?
Ans: Constitutional morality refers to the adherence to the values and principles enshrined in the Constitution, ensuring that decisions taken by the government are in alignment with democratic and just practices.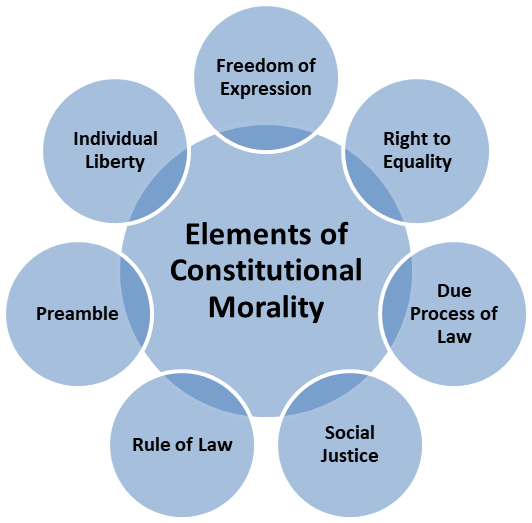
Q2: Why is the Indian Constitution considered a "living document"?
Ans: The Indian Constitution is considered a "living document" because it is adaptable to changing circumstances and can be amended to meet new challenges without compromising its core principles.
Q3: What is the role of the Directive Principles of State Policy in the Indian Constitution?
Ans: The Directive Principles of State Policy serve as guidelines for the government to formulate policies aimed at ensuring social and economic justice, reducing inequalities, and promoting welfare in the country.
Q4: Why was the Indian Constitution framed after extensive deliberation?
Ans: The Indian Constitution was framed after extensive deliberation to ensure that it addressed the diverse needs of the population, accommodated various cultural, social, and economic differences, and laid the foundation for a democratic government.
Q5: What was the "Objectives Resolution," and why was it important?
Ans: The "Objectives Resolution" was introduced by Jawaharlal Nehru in 1946. It laid down the aspirations of the Indian people and set the direction for the Constitution, emphasizing principles like justice, equality, and freedom for all citizens.
Activity-Based Questions
Q1: Have a discussion with your classmates about how decisions should be made in your classroom. Discuss how to and which decisions they can make without consulting others. Write down these decisions and display them in the classroom. Discuss the challenges and how to resolve any disagreements.
Ans: In our classroom, we can make decisions in a fair and organized way by electing representatives. These representatives can be chosen through a vote, where each student has a chance to choose who they think would be the best person to represent them. To do this, we can hold an election where each candidate tells us why they should be elected, and then everyone votes for their preferred representative.
Once we have our representatives, they can make certain decisions on their own, such as:
Deciding the order of activities or subjects for the day.
Choosing a class project or theme.
Deciding on rewards for the class, like a fun day or a special activity.
These decisions can be made by the representatives without asking everyone else. However, for more important decisions, like changing classroom rules or planning an event, the representatives should consult the whole class to ensure everyone's opinion is considered.
Challenges may arise when students disagree on decisions or feel left out. To resolve disagreements, we can:
Have open discussions where everyone shares their thoughts respectfully.
Hold a vote if the class cannot agree.
Encourage listening and understanding of others' opinions.
By following these steps, we can create a positive and fair environment in our classroom.
Q2: Discuss the Allocation of Power in groups, and discuss who should have the authority to make laws in a community. Should everyone have a say, or should representatives be elected? What kind of power-sharing model would work best for the group? Write down your conclusions.
Ans: In any group or community, the allocation of power is important for maintaining order and making decisions that benefit everyone. The question of who should have the authority to make laws is a crucial part of this process. There are two possible models to consider: everyone having a say or electing representatives to make decisions.
Should everyone have a say?
Giving everyone a say means that every member of the community has the opportunity to express their opinion on every issue, and decisions are made based on majority votes or discussions.
This model can be democratic and inclusive but might be time-consuming and difficult to manage, especially in large groups. It could also lead to disagreements if there are many conflicting opinions.
Should representatives be elected?
Electing representatives means choosing a smaller group of people to make decisions on behalf of everyone. These representatives can be selected based on their knowledge, leadership skills, or trustworthiness.
This model is efficient and allows for quicker decision-making, as representatives can focus on solving issues and making laws without needing to consult everyone on every decision.
The challenge is that representatives might not always act in the best interest of everyone, so it’s important that they are held accountable by the group.
What kind of power-sharing model would work best?
A balanced power-sharing model could be a good compromise. In this model:
Representatives are elected to handle day-to-day decisions and laws for the group.
However, everyone should still have a say on major decisions, such as changes to the laws or important group-wide issues.
Regular meetings or forums can be held where the community members can express their opinions, and the representatives can report back on their actions.
Conclusion: The best approach for allocating power in a group is a combination of both. Elected representatives should make most decisions, as they can focus on the details and manage the group effectively. However, the group should have opportunities to give feedback and participate in important decisions, ensuring that everyone’s voice is heard. This model promotes efficiency while maintaining fairness and inclusivity.
Research-Based Question
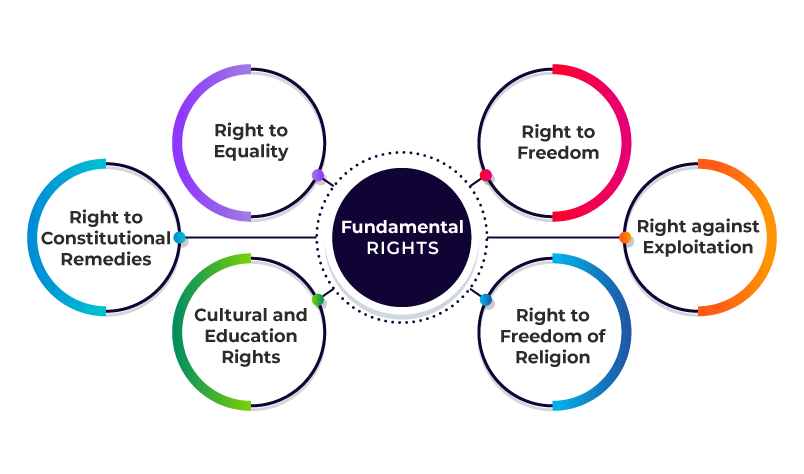
Q1: Conduct research to explore why it was deemed essential for the Indian Constitution to include both the Fundamental Rights and the Directive Principles of State Policy. Discuss their significance in ensuring justice, equality, and the welfare of citizens in India.
Ans: Importance of Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles in the Indian Constitution
1. Fundamental Rights: Fundamental Rights are found in Part III of the Indian Constitution and are very important for these reasons:
- Protection of Personal Freedom: These rights protect individual freedoms like equality, freedom of speech, and protection from discrimination.
- Legal Help: If someone's rights are violated, they can go to court to get justice.
- Justice and Fairness: These rights ensure the government does not act unfairly or arbitrarily.
- Empowering Citizens: They help people stand up against injustice and fight for their rights.
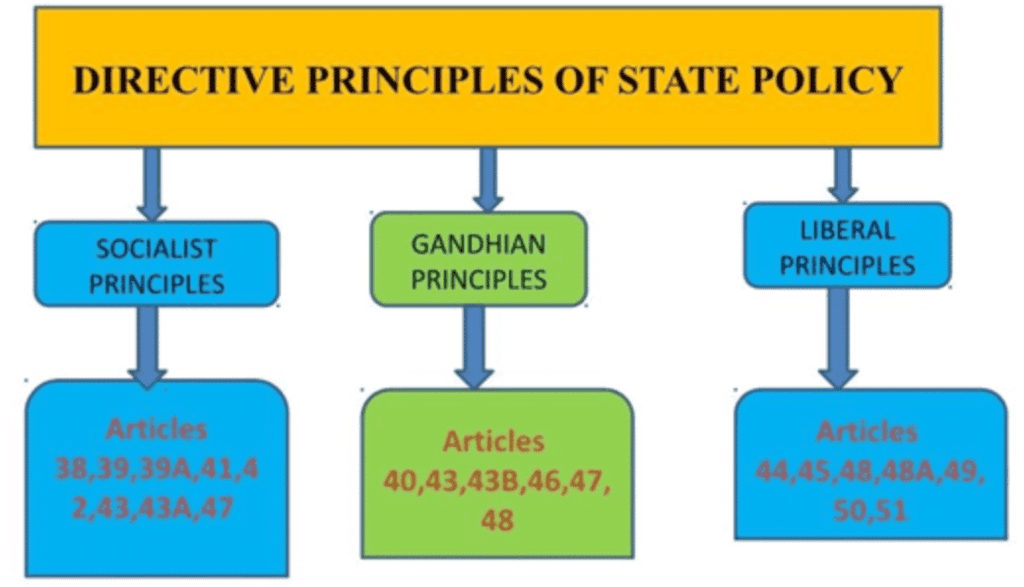
2. Directive Principles of State Policy: The Directive Principles, in Part IV of the Constitution, are important for guiding the government:
- Promoting Social Justice: These principles help ensure that all citizens live a good life, focusing on their well-being.
- Helping the Government Make Laws: They guide the government in creating laws that reduce inequality and protect people’s welfare.
- Improving Economic Welfare: They focus on uplifting the poorer sections of society and promoting fairness in the economy.
- Balancing Rights and Responsibilities: They highlight the need to balance individual rights with duties toward society.
3. : Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles work together to build a fair society:
- Complementary Role: Fundamental Rights protect freedoms, while Directive Principles guide the government in ensuring those freedoms are meaningful.
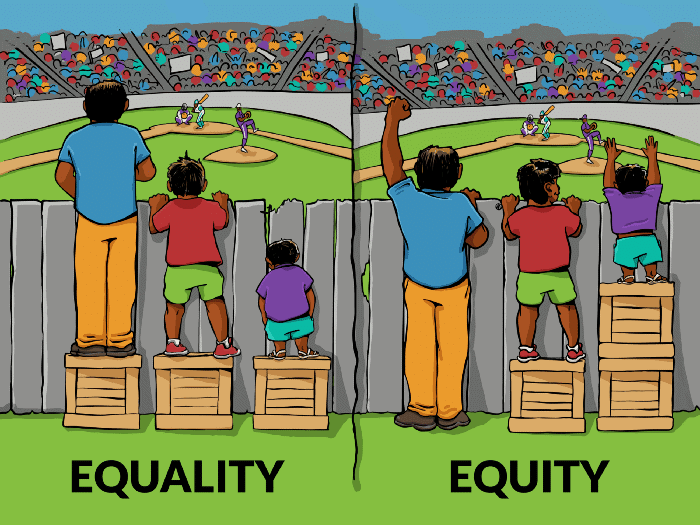
- Welfare for All: These principles make sure that justice isn’t just legal but also social and economic.
- Support for Development: Together, they create a plan to help everyone, especially the marginalized, and ensure equality.
- Social Harmony: By focusing on both rights and welfare, they help bring people together and promote unity in India’s diverse society.
Conclusion
The inclusion of both Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles in the Indian Constitution is essential for ensuring justice, equality, and the well-being of all citizens. Together, they help create a democratic society that respects individual rights while working for the common good.
Crossword
Instructions: Using the given clues, fill in the corresponding answers in the provided crossword grid.

|
43 videos|268 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Assignment: Constitution - Why and How? - Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is the purpose of a constitution? |  |
| 2. How does a constitution protect individual rights? |  |
| 3. What are the main components of a constitution? |  |
| 4. How is a constitution amended? |  |
| 5. Why is it important for a constitution to be a living document? |  |




















