Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: What is the primary function of the legislature in a democratic government?
a) To control the executive
b) To implement laws
c) To make laws and hold the executive accountable
d) To appoint the president
Ans: c) The primary function of the legislature is to make laws and hold the executive accountable in a democratic government.
Q2: Which of the following is true about the Rajya Sabha?
a) It is directly elected by the people
b) It represents the people directly
c) Its members are elected indirectly by the members of the State Legislative Assemblies
d) It does not have any legislative power
Ans: c) The Rajya Sabha's members are elected indirectly by the members of the State Legislative Assemblies.
Q3: What is the role of the Lok Sabha in controlling the executive?
a) It can only suggest changes to policies
b) It can pass a no-confidence motion to dismiss the government
c) It approves the budget but has no other control
d) It is not involved in controlling the executive
Ans: b) The Lok Sabha can pass a no-confidence motion to dismiss the government, which is one of its key functions in controlling the executive.
Q4: Which of the following is NOT a function of the Parliament?
a) Law-making
b) Control of the executive
c) National defense
d) Financial control
Ans: c) National defense is not directly a function of Parliament; it is a responsibility of the executive.
Q5: How is a Money Bill different from a regular bill?
a) It can be introduced in any house
b) It can only be introduced in the Rajya Sabha
c) The Rajya Sabha cannot reject a Money Bill
d) It is not subject to approval by both Houses
Ans: c) The Rajya Sabha cannot reject a Money Bill; it can only suggest amendments.
Short Q/A
Q1: What is the importance of having a bicameral legislature?
Ans: A bicameral legislature ensures that every decision is reconsidered by two Houses, providing a double check on legislation. This system helps represent different regions, social groups, and ensures that all aspects of legislation are thoroughly debated.
Q2: Why is the Rajya Sabha called the "permanent house"?
Ans: The Rajya Sabha is called the "permanent house" because it is never fully dissolved. One-third of its members retire every two years, ensuring that the House continues to function even when the Lok Sabha is dissolved.
Q3: What is the process for passing a bill in Parliament?
Ans: A bill goes through several stages, including introduction, discussion in the House, committee reviews, voting, approval by the other House, and final assent by the President. A money bill follows a similar procedure but is not subject to rejection by the Rajya Sabha.
Q4: How does the Parliament ensure the executive remains accountable?
Ans: The Parliament ensures executive accountability through instruments like Question Hour, No-Confidence Motions, discussions, and financial control. These tools allow the Parliament to review and scrutinize the actions of the executive.
Q5: Why are Parliamentary committees important?
Ans: Parliamentary committees are important because they allow detailed scrutiny of bills, budgets, and policies. They help reduce the burden on Parliament, ensuring that decisions are well-considered and well-researched before being presented to the House.
Activity-Based Questions
Q1: Review Newspaper Reports on Parliament's Functioning
Instructions: Consider the newspaper reports related to budget proposals and the subsequent rollbacks. After reading each report, discuss how the legislature succeeded or failed in controlling the executive's actions.
Ans:
Legislature's Role: The legislature effectively controlled the executive's actions by scrutinizing the budget proposals and responding to public concerns.
Example of Control: Parliament forced the government to roll back its decision on increasing fertilizer prices, which was seen as a direct response to public pressure.
Parliament's Power: Through debates, discussions, and representing public opinion, Parliament can hold the executive accountable.
Public Influence: The public’s reaction played a significant role in Parliament’s actions, showing the power of collective opinion in influencing legislative decisions.
Successful Oversight: This event demonstrates how the legislature can use its power to ensure the executive’s policies align with the welfare of the people.
Q2: Activity: Watch the Parliament Sessions on Doordarshan
Instructions: Watch the live telecast of Parliament sessions for three continuous days or collect newspaper reports. Observe the issues discussed, the role of the speaker, and the participation of different parties.
Ans: Watching live telecasts of Parliament sessions on Doordarshan for three consecutive days provides valuable insights into the legislative process, the Speaker's role, and the dynamics of party participation.
Key Observations:
1. Issues Discussed:
Parliament addresses a wide range of topics, including national policies, economic reforms, social welfare, and international agreements.
Recent sessions have covered significant bills such as the Finance Bill 2025, the Waqf (Amendment) Bill, and the Banking Laws (Amendment) Bill, 2024.
2. Role of the Speaker:
The Speaker maintains order during debates, ensures adherence to parliamentary procedures, and provides equal opportunities for all members to express their views.
In instances of disruptions or protests, the Speaker may adjourn sessions to restore order.
3. Participation of Different Parties:
Members from various political parties actively participate in debates, presenting diverse perspectives on legislative matters.
Opposition parties often question and scrutinize government policies, leading to constructive discussions and, at times, heated exchanges.
Recent sessions have seen significant participation from parties discussing bills like the Waqf (Amendment) Bill and the Banking Laws (Amendment) Bill, 2024.
Research-Based Question
Q1: Investigate the role of parliamentary committees in the law-making process. How do these committees contribute to shaping and refining legislation? Explore the different types of parliamentary committees, their functions, and how they influence the creation, amendment, or rejection of laws. Provide examples of significant laws or amendments that have been impacted by the work of these committees.
Ans: Parliamentary committees play a crucial role in the law-making process by scrutinizing bills, proposing amendments, and ensuring legislation is well-considered. Key types of committees include:
Standing Committees: Permanent groups that examine bills and suggest amendments.
Joint Parliamentary Committees (JPCs): Formed for cross-party discussions on complex issues.
Select Committees: Address specific national issues.
Ad-Hoc Committees: Temporary groups for specific tasks.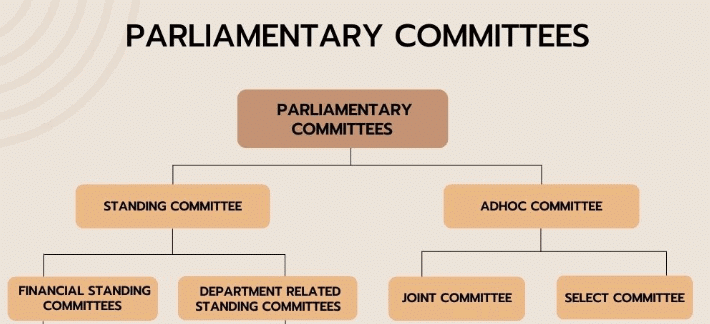
These committees review bills, hold hearings, and suggest changes based on expert opinions and public input. They help refine laws, ensuring they serve the public well. For example, the GST Act and Criminal Law (Amendment) Act, 2013 were shaped by parliamentary committees, demonstrating their influence on law creation and amendment.
Crossword
Clues:
Ans:






















