Assignment: Changing Cultural Traditions | History Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions |

|
| Short Answer Questions |

|
| Activity-Based Questions |

|
| Research-Based Question |

|
| Crossword |

|
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: Which of the following cities was NOT a major center of the Renaissance in Italy?
(a) Florence
(b) Venice
(c) Rome
(d) Paris
Ans: (d) Paris. The cities of Florence, Venice, and Rome were prominent during the Renaissance in Italy, whereas Paris, though influential in Europe, was not a key Italian Renaissance city.
Q2: Who coined the term ‘Renaissance’ to describe the cultural changes of the period?
(a) Jacob Burckhardt
(b) Francesco Petrarch
(c) Leonardo da Vinci
(d) Michelangelo
Ans: (a) Jacob Burckhardt. He was the first to use the term 'Renaissance' in the 19th century to describe the cultural rebirth during the 14th-17th centuries.
Q3: What significant technological advancement helped spread Renaissance ideas across Europe?
(a) Printing Press
(b) Telescope
(c) Compass
(d) Mechanical clock
Ans: (a) Printing Press. The printing press, especially Gutenberg’s invention in 1454, helped distribute books and ideas quickly across Europe.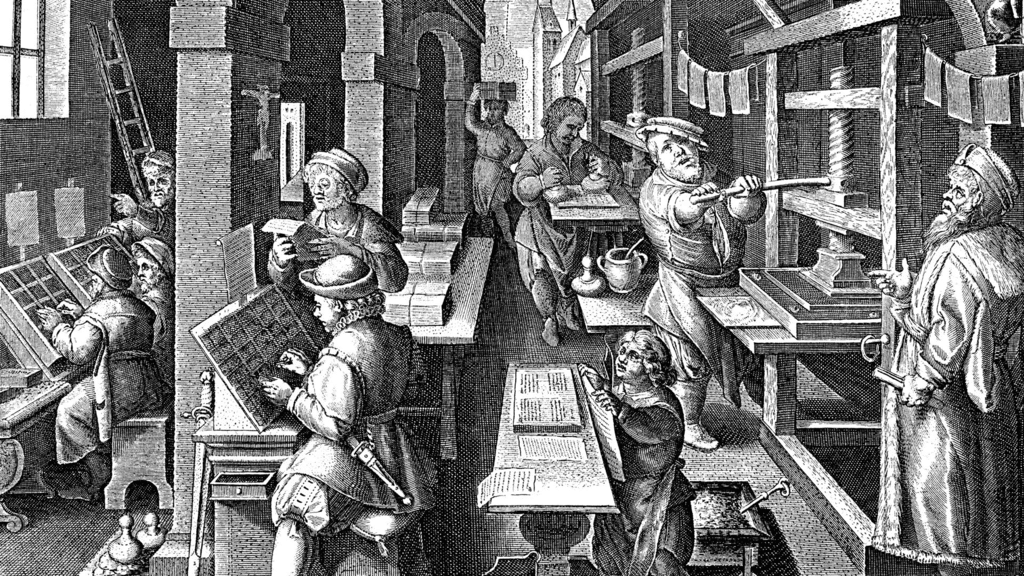
Q4: What was the major focus of Humanism during the Renaissance?
(a) Scientific discoveries
(b) Return to ancient Greek and Roman culture
(c) Religious practices
(d) Political power
Ans: (b) Return to ancient Greek and Roman culture. Humanism emphasized the revival of classical texts and the importance of individual achievements.
Q5: Who was responsible for the spread of Humanism in the early 15th century?
(a) Dante Alighieri
(b) Francesco Petrarch
(c) Thomas More
(d) Johannes Gutenberg
Ans: (b)He is often considered the father of Humanism, emphasizing the study of ancient Greek and Roman texts.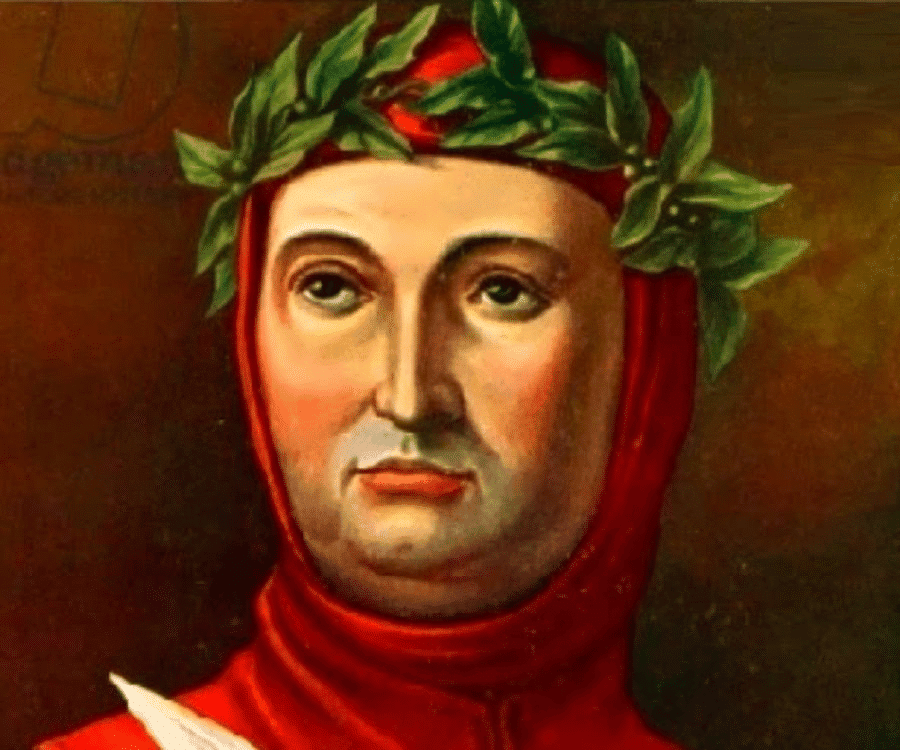
Short Answer Questions
Q1: What were some key characteristics of Italian city-states during the Renaissance?
Ans: Italian city-states, such as Florence and Venice, were independent republics or court cities, often governed by wealthy merchants and bankers. These city-states were characterized by vibrant trade, intellectual growth, and significant cultural achievements in art, architecture, and literature.
Q2: How did the fall of the Roman Empire contribute to the revival of Italian culture during the Renaissance?
Ans: The collapse of the Roman Empire left Italy fragmented and weak, but this fragmentation allowed for the rise of independent city-states. Trade with the Byzantine Empire and Islamic countries brought in wealth, enabling the revival of art, architecture, and humanist ideas in Italy.
Q3: What role did women play in Renaissance culture, especially in Italy?
Ans: Women in the Renaissance, especially from merchant families, played important roles in running businesses. Some women, like Cassandra Fedele and Isabella d’Este, were intellectuals and patrons of the arts, although their public roles were limited compared to men.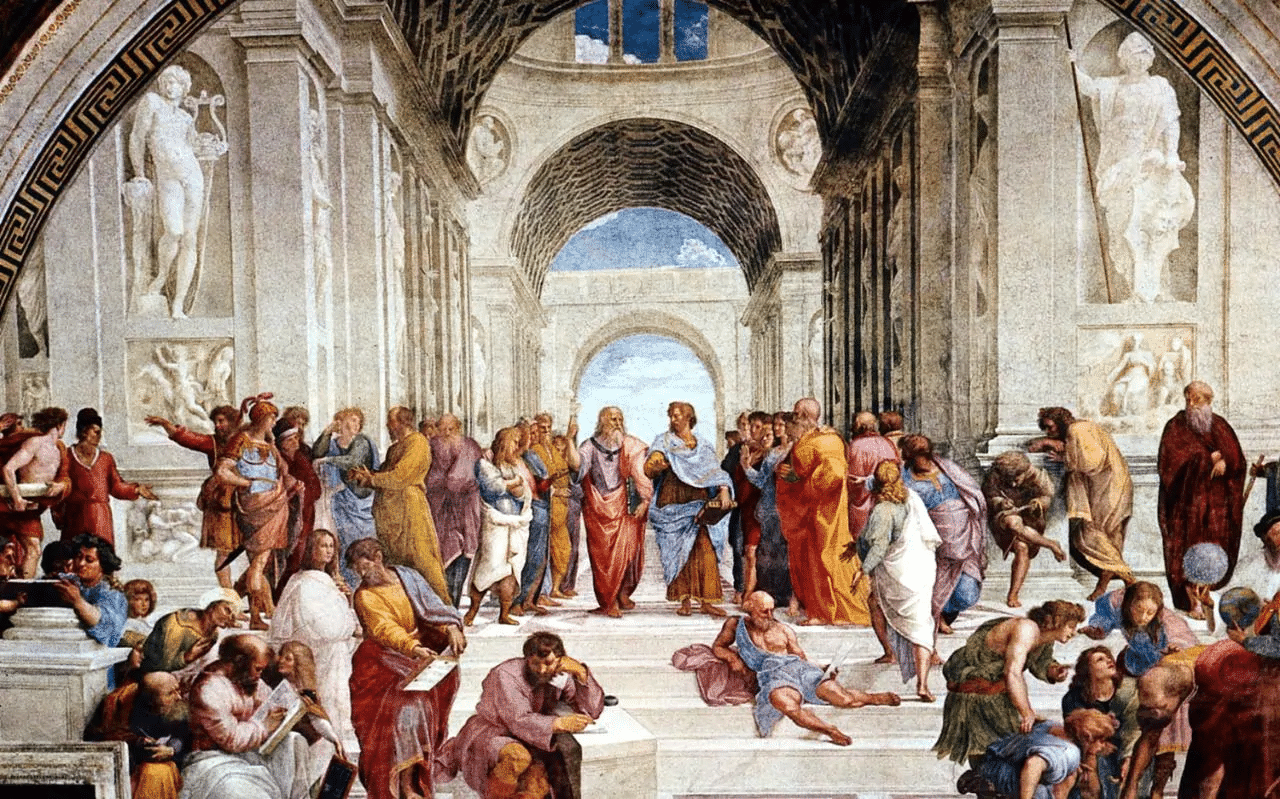
Q4: How did Renaissance artists incorporate scientific knowledge into their work?
Ans: Renaissance artists, such as Leonardo da Vinci, studied anatomy, geometry, and physics to create more realistic art. They used geometry to understand perspective and incorporated scientific principles to achieve lifelike proportions and accurate depictions.
Q5: Explain the significance of the Protestant Reformation initiated by Martin Luther.
Ans: The Protestant Reformation, started by Martin Luther in 1517, challenged the Catholic Church’s authority. Luther’s criticism of indulgences and his emphasis on faith alone led to the split of the Catholic Church, the formation of Protestant churches, and major religious and political changes in Europe.
Activity-Based Questions
Q1: Activity 1: Locate Venice on the map of Italy and describe the city’s cultural differences compared to a cathedral town.
Ans: Venice, unlike cathedral towns, was a bustling trade hub with a strong merchant class that governed the city. It had a unique culture focused on commerce and independence, contrasting with cathedral towns where the church played a central role in governance and daily life.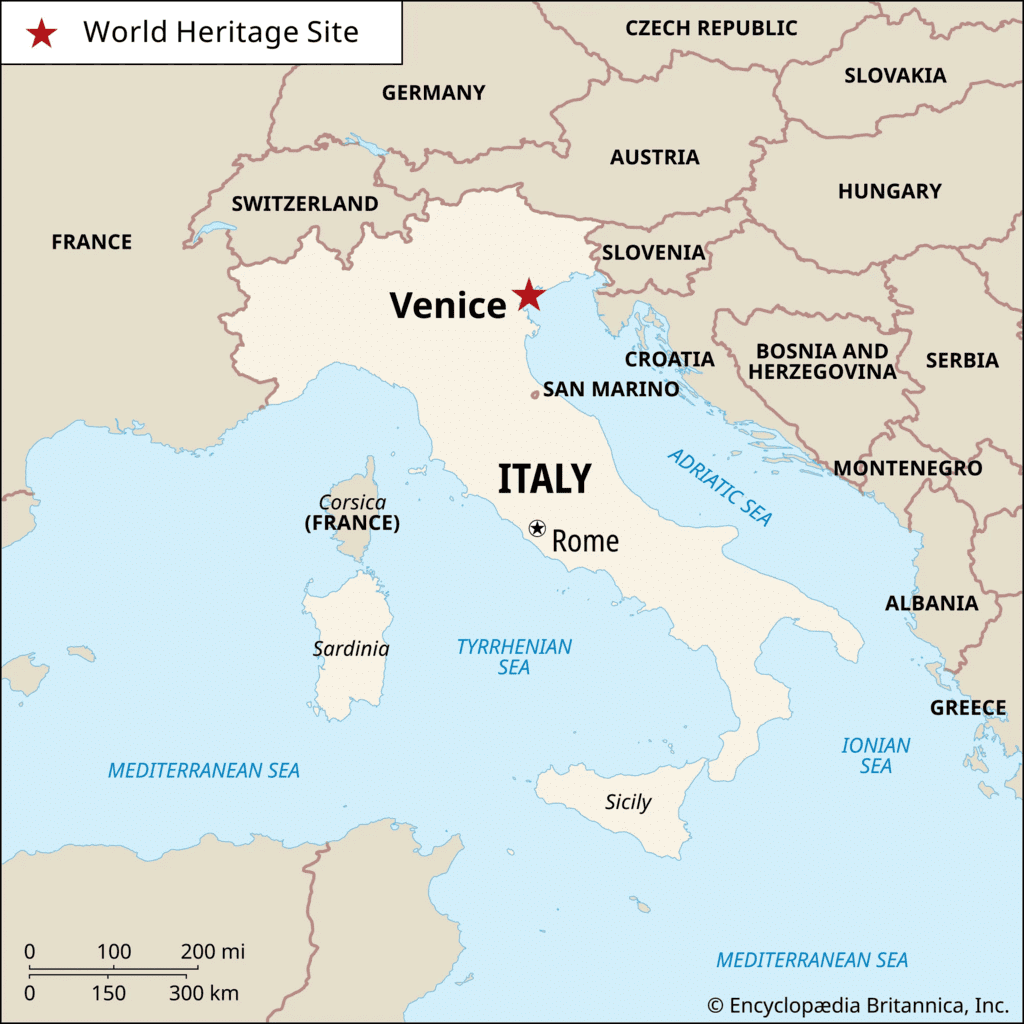
Q2: Activity 2: Describe the scientific elements in the works of sixteenth-century Italian artists.
Ans: Sixteenth-century Italian artists like Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo studied human anatomy and geometry to improve their understanding of the human body and perspective. Their works were influenced by scientific knowledge, leading to more realistic depictions in art.
Research-Based Question
Q1: Research Question: How did the development of printing during the Renaissance impact the spread of knowledge?
Ans: The invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in 1454 revolutionized the spread of knowledge. Printed books made literature and scientific ideas accessible to a wider audience, fostering literacy and intellectual exchange across Europe. This led to the rapid spread of humanist and reformist ideas, contributing to the Renaissance and the Protestant Reformation.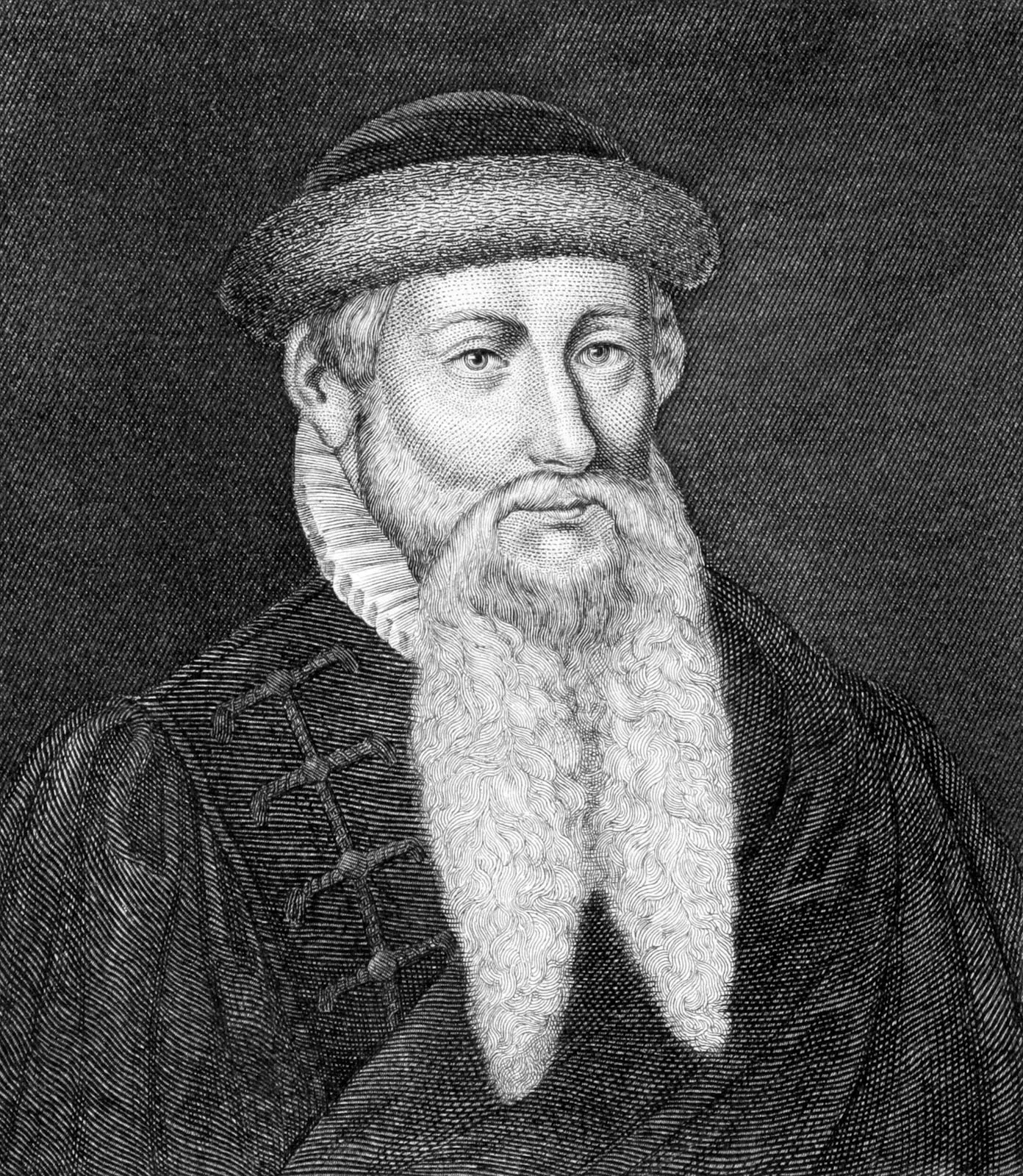
Crossword
Clues:
Down: The city-state in Italy is known for its canals. (6 letters)
Across: The Swiss historian who popularized the term 'Renaissance.' (10 letters)
Down: The famous painting by Leonardo da Vinci features a mysterious smile. (6,5 letters)
Across: The first printed book in history. (5 letters)
Down: The Italian artist who painted the Sistine Chapel ceiling. (10 letters)
Solution:
Down: Venice
Across: Burckhardt
Down: Mona Lisa
Across: Bible
Down: Michelangelo
|
27 videos|157 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on Assignment: Changing Cultural Traditions - History Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What are some examples of cultural traditions that have changed over time? |  |
| 2. How do cultural exchanges influence the transformation of traditions? |  |
| 3. What role does technology play in changing cultural traditions? |  |
| 4. How can communities preserve their cultural traditions in the face of change? |  |
| 5. What are the potential positive and negative impacts of changing cultural traditions? |  |















