B Com Exam > B Com Notes > Business Law > The Central & State Information Commission
The Central & State Information Commission | Business Law - B Com PDF Download
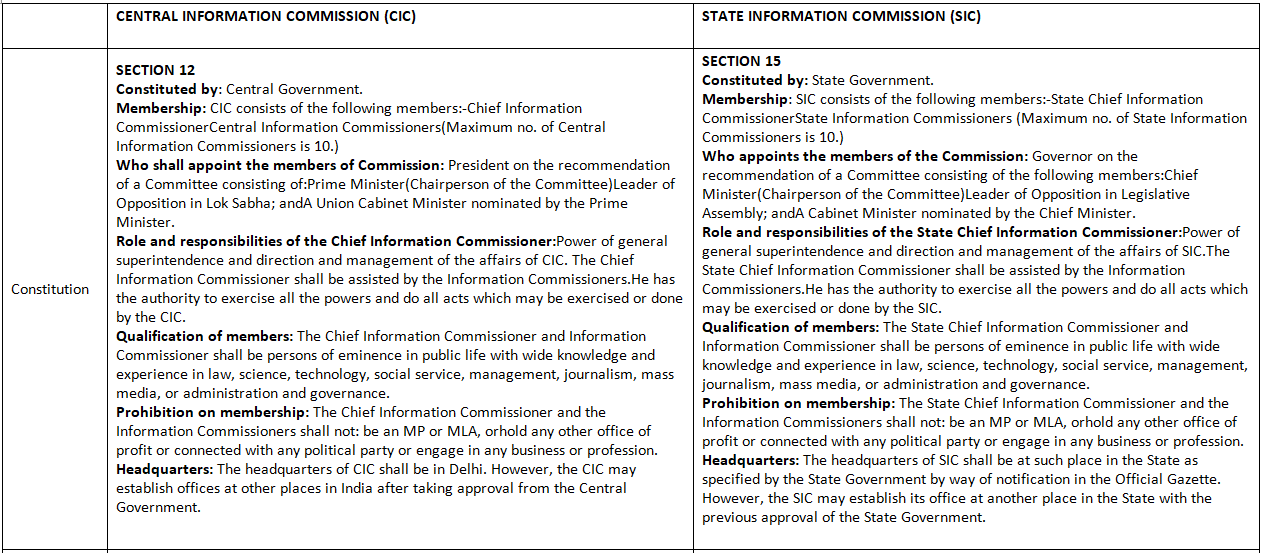
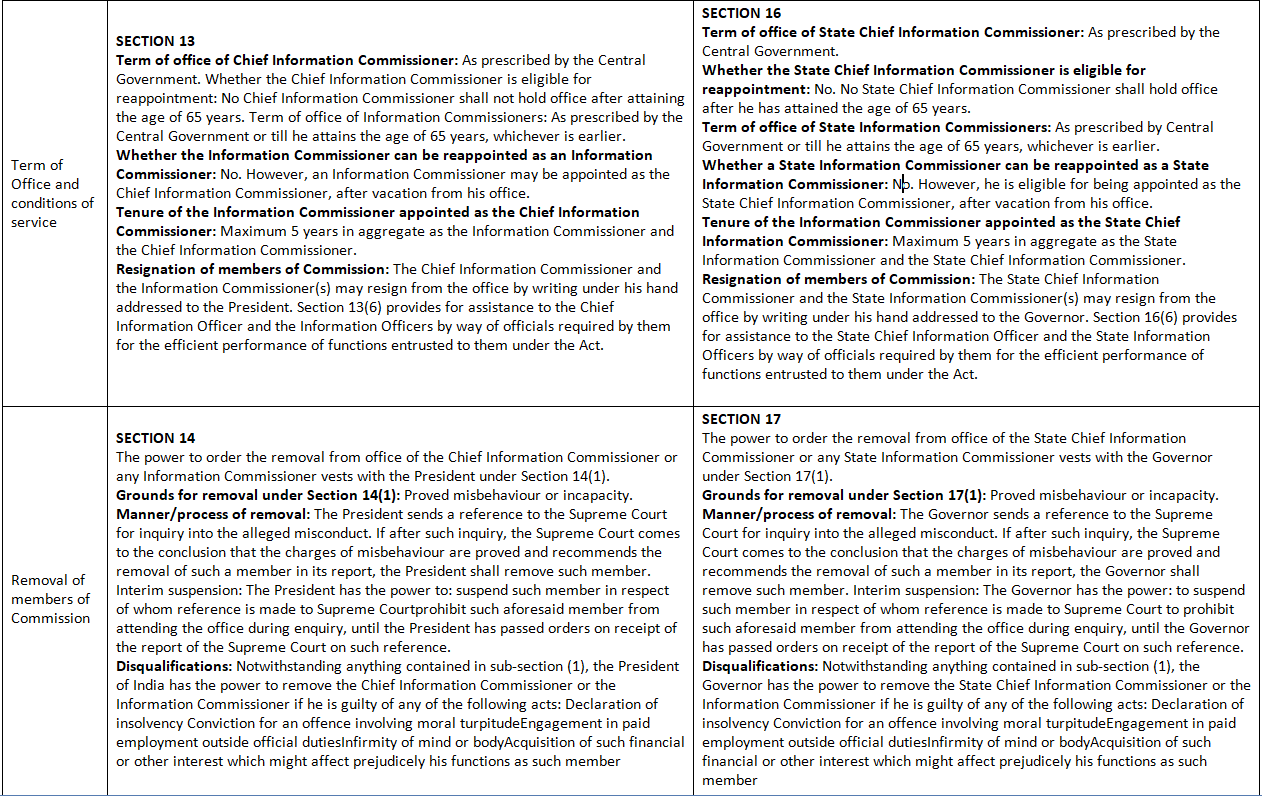
Central Information Commission and State Information Commission: Chapters III and IV

Under the RTI Act, the Information Commissions serve as the top authority and final decision-making bodies. These Commissions are established at both the central and state levels, known respectively as the Central Information Commission (CIC) and the State Information Commission (SIC).
The provisions related to the establishment, composition, and functioning of the Central Information Commission are outlined in Sections 12 to 14 of the Act. Similarly, Sections 15 to 17 cover the corresponding provisions for the State Information Commission.
The document The Central & State Information Commission | Business Law - B Com is a part of the B Com Course Business Law.
All you need of B Com at this link: B Com
|
30 videos|100 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on The Central & State Information Commission - Business Law - B Com
| 1. What is the role of the Central Information Commission in India? |  |
Ans. The Central Information Commission (CIC) is responsible for overseeing the implementation of the Right to Information Act, 2005. It acts as an appellate authority for citizens who have been denied information by public authorities. The CIC ensures transparency and accountability in governance by promoting the effective use of the RTI Act.
| 2. How can a citizen file an RTI application with the Central Information Commission? |  |
Ans. A citizen can file an RTI application by submitting a written request to the relevant public authority. The application should be addressed to the Public Information Officer (PIO) of that authority. It can be submitted in person, by post, or online, and must include details about the information being sought and the applicant's contact information.
| 3. What are the penalties for public authorities that fail to provide information under the RTI Act? |  |
Ans. Public authorities and their officials can face penalties for failing to provide information within the stipulated time frame or for providing misleading information. The penalties can include fines imposed on the PIO, disciplinary action, and even criminal charges in severe cases of willful negligence.
| 4. Can a citizen appeal if their RTI request is rejected? |  |
Ans. Yes, a citizen can appeal if their RTI request is rejected. The first appeal can be made to the senior officer of the public authority, and if that appeal is also rejected, the citizen can approach the Central Information Commission for a second appeal. This process ensures that citizens have multiple avenues to seek the information they require.
| 5. What types of information are exempt from disclosure under the RTI Act? |  |
Ans. Certain categories of information are exempt from disclosure under the RTI Act, including information that affects national security, personal privacy, and information that is prohibited from disclosure by any other law. Additionally, information that is part of an ongoing investigation or that could undermine the integrity of the judicial process may also be exempt.
Related Searches















