Assignment: Structure and Physiography | Geography Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Short Answer Questions (Q/(a) |

|
| Activity-Based Questions |

|
| Research-Based Question |

|
| Word Search |

|
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1. Which one of the following is NOT a major component of the Peninsular Block?
(a) Aravali Hills
(b) Satpura Range
(c) Himalayas
(d) Nallamala Hills
Ans:
(c) The Himalayas are not part of the Peninsular Block; they are located in the northern part of India.
Q2. Which of the following rivers flows through the Peninsular Plateau and drains into the Bay of Bengal?
(a) Narmada
(b) Godavari
(c) Luni
(d) Mahi
Ans:
(b) The Godavari River flows through the Peninsular Plateau and drains into the Bay of Bengal.
Q3. What is the primary characteristic of the Peninsular Plateau?
(a) It is a young and flexible landmass.
(b) It is a highly stable and ancient landmass.
(c) It is entirely submerged.
(d) It is characterized by large rivers and deltas.
Ans:
(b) The Peninsular Plateau is one of the oldest and most stable landmasses in India.
Q4. Which of the following is a major feature of the northern plains of India?
(a) Desert-like features
(b) Alluvial deposits
(c) Rocky terrain
(d) High mountain ranges
Ans:
(b) The northern plains of India are characterized by alluvial deposits brought by the rivers Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra.
Q5. The Barren Island, known for its active volcano, is located in which group of islands?
(a) Lakshadweep
(b) Andaman and Nicobar Islands
(c) Seychelles
(d) Maldives
Ans:
(b) The Barren Island, which is the only active volcano in India, is located in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Short Answer Questions (Q/(a)
Q1. Define physiography in simple terms.
Ans: Physiography refers to the study of the physical features of the Earth's surface, including landforms such as mountains, plateaus, plains, and rivers, and how these features are formed by natural processes.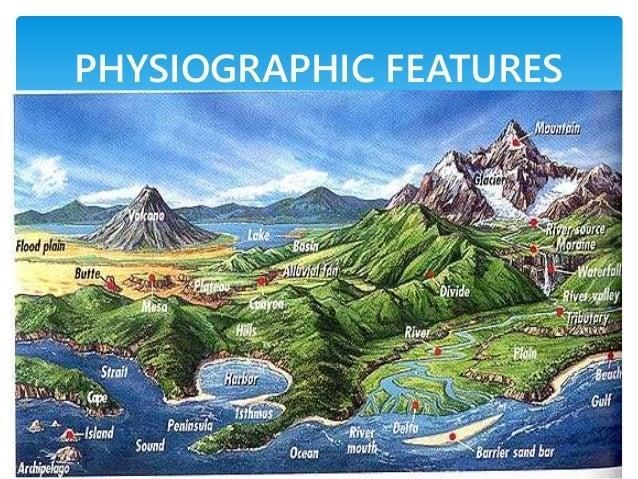
Q2. How does the Himalayas divide the Indian subcontinent?
Ans: The Himalayas act as a physical barrier between the Indian subcontinent and the countries of Central and East Asia. They also serve as a climatic divide, preventing cold winds from entering the Indian subcontinent and creating distinct weather patterns.
Q3. What are the major rivers that form deltas in the eastern coastal plains?
Ans: The major rivers forming deltas in the eastern coastal plains are the Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, and Kaveri. These rivers flow into the Bay of Bengal and create large fertile deltas.
Q4. Mention two key differences between the Western and Eastern Ghats.
Ans:
The Western Ghats are continuous and higher in elevation compared to the Eastern Ghats, which are discontinuous and lower.
The Western Ghats receive more rainfall and are richer in biodiversity, while the Eastern Ghats are more eroded by river action.
Q5. Explain the formation of the Indian Desert.
Ans: The Indian Desert, also known as the Great Indian Desert, is located in the northwest of India. It is characterized by low rainfall (below 150 mm per year) and has a dry, arid climate. The desert was once part of the sea during the Mesozoic era, and today it features shifting dunes, barchans, and an arid landscape with sparse vegetation.
Activity-Based Questions
Q1. Identify the major landforms in your region. How do these landforms influence the local economy?
Ans: Major Landforms in the Region:
Rivers: Rivers are vital water bodies that flow through the region, providing essential water for both irrigation and domestic use.
Plateaus: Plateaus are elevated flat or gently sloping landforms, often rich in mineral deposits.
Hills: Hills are elevated areas of land that are generally smaller than mountains and may have scenic views.

Economic Influence:
Rivers: Rivers provide water for agriculture through irrigation, especially in regions that experience dry spells. They also support fishing industries and act as natural transportation routes for trade and commerce.
Plateaus: Plateaus are often rich in natural resources such as minerals (coal, iron, and precious metals), which fuel mining activities. These mining operations support local economies through job creation and resource extraction.
Hills: Hills are often used for tourism due to their scenic beauty, contributing to the local economy through tourism-related businesses such as hotels, restaurants, and recreational activities. Additionally, hillside agriculture (like tea plantations) can also thrive in hilly regions, contributing to local food production and exports.
In conclusion, these landforms support the local economy by fostering agricultural productivity, mining, and tourism, each playing a crucial role in the region's overall economic development.
Research-Based Question
Q1. Research the geomorphological features of the Indo-Ganga-Brahmaputra Plain and their significance for agriculture.
Ans: The Indo-Ganga-Brahmaputra Plain is a vast alluvial region formed by the continuous deposition of sediments by the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra rivers. This plain is characterized by flat, low-lying terrain, rich soil, and extensive floodplains.
Key Geomorphological Features:
- Alluvial Deposits: The constant deposition of silt and clay by the rivers has created highly fertile soil, making the region ideal for agriculture.
- Floodplains: The plain is made up of extensive floodplains that are periodically replenished with fresh sediment, maintaining the fertility of the soil.
- River Channels and Deltas: The rivers' winding channels and deltas provide natural irrigation systems, which support agricultural productivity.
Significance for Agriculture:
Fertile Soil: The fertile alluvial soil supports the cultivation of a wide range of crops, such as wheat, rice, sugarcane, jute, and maize. This soil is rich in nutrients, making it highly productive for agriculture.
Water Availability: The extensive river system ensures a consistent water supply for irrigation, making it possible to cultivate crops throughout the year. This is particularly beneficial for crops like rice, which require abundant water.
Multiple Cropping Seasons: Due to the fertile soil and water availability, the region allows for multiple cropping seasons, enhancing agricultural output.
Conclusion:
The geomorphological features of the Indo-Ganga-Brahmaputra Plain, especially its alluvial deposits and river systems, make it one of the most agriculturally productive regions in India. These features enable the cultivation of a variety of crops, making agriculture a cornerstone of the region's economy.
Word Search
Clues:
Across
A river forming a delta in the Bay of Bengal (6 letters) Krishna
A major mountain range separating India from China (8 letters) Himalayas
The island group in the Bay of Bengal with an active volcano (7 letters) Andaman
Down
2. The coastal plain in India that is a submerged feature (8 letters) Western
4. The highest peak in the Western Ghats (6 letters) Anaimudi
|
70 videos|289 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Assignment: Structure and Physiography - Geography Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is the importance of structure and physiography in understanding human culture? |  |
| 2. How does physiography affect the economy of a region? |  |
| 3. Can you explain the relationship between structure and physiography in urban planning? |  |
| 4. What are some examples of how physiography has influenced historical events? |  |
| 5. How do modern technologies interact with traditional structures and physiography? |  |















