Assignment: Sociology and Society | Sociology Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions |

|
| Short Q/A |

|
| Research-Based Question |

|
| Application of Theories |

|
| Comparative Analysis |

|
| Case Study Analysis |

|
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1. What is the primary focus of sociology?
A) Studying individual behavior only
B) Studying society as an interconnected whole
C) Studying only economic issues
D) Studying philosophical ideas
Ans: B) Studying society as an interconnected whole
Explanation: Sociology studies human society by examining how individuals and groups interact, how societal structures shape behavior, and the interconnections between various social institutions.
Q2. What is the main difference between sociology and common sense?
A) Sociology studies moral behavior, while common sense does not
B) Sociology is based on personal experiences, while common sense is empirical
C) Sociology uses systematic observation, while common sense is unreflective
D) Sociology focuses only on personal issues, whereas common sense deals with societal issues
Ans: C) Sociology uses systematic observation, while common sense is unreflective
Explanation: Sociology is a scientific discipline that involves systematic study and empirical evidence, while common sense is based on unreflective, personal assumptions without thorough analysis.
Q3. Which of the following is true regarding the impact of colonialism on Indian sociology?
A) Colonialism led to a homogenous Indian society
B) Colonialism had no impact on Indian sociology
C) Colonialism shaped Indian sociology through Western ideas and structures
D) Indian sociology emerged solely from indigenous ideas
Ans: C) Colonialism shaped Indian sociology through Western ideas and structures
Explanation: Indian sociology was influenced by Western ideas during the colonial period, which led to a contrast between indigenous and colonial perspectives on Indian society.
Q4. The concept of ‘sociological imagination’ was introduced by which sociologist?
A) Max Weber
B) Karl Marx
C) C. Wright Mills
D) Auguste Comte
Ans: C)
Explanation: C. Wright Mills introduced the concept of sociological imagination, which helps understand the connection between personal problems and public issues.
5. Which factor is NOT typically studied by sociologists?
A) Economic systems
B) Political institutions
C) Individual psychological traits
D) Cultural norms and values
Ans: C) Individual psychological traits
Explanation: Sociologists focus on societal structures and institutions rather than individual psychological traits, which are the domain of psychology.
Short Q/A
Q1. How does sociology differ from philosophy and common sense?
Ans: Sociology differs from philosophy and common sense by its focus on empirical evidence and systematic methods to study society. While philosophy reflects on moral and ethical ideas, sociology seeks to understand societal structures through observation and analysis. Common sense is based on personal experience and unreflected assumptions, whereas sociology uses scientific methods.
Q2. What role does culture play in determining what is considered a 'good job' in society?
Ans: Culture plays a significant role in determining what is considered a 'good job' as it shapes values, beliefs, and social norms. In some societies, jobs that offer respect and social recognition may be valued more than those offering high monetary rewards. Therefore, cultural perceptions influence how a job is viewed in terms of social esteem.
Q3. Explain the concept of ‘pluralities and inequalities’ in societies.
Ans: Pluralities refer to the existence of diverse social groups within a society, such as different caste, ethnic, or religious groups. Inequalities refer to the uneven distribution of resources, opportunities, and power among these groups. These pluralities and inequalities lead to differences in life experiences and social outcomes.
Q4. What is the relationship between sociology and economics?
Ans: Sociology and economics both study human behavior but from different perspectives. Economics focuses on the production and distribution of goods and services, while sociology looks at how economic activities are influenced by social norms, values, and practices. Sociologists study the broader social context of economic behavior, including issues like inequality and class.
Q5. Why is the study of the origin and growth of sociology important?
Ans: The study of the origin and growth of sociology is important because it helps us understand the intellectual roots of the discipline and how it evolved to address societal changes, such as industrialization and urbanization. Understanding its historical context helps us appreciate the role of sociology in analyzing contemporary issues.
Research-Based Question
Q1: Research the concept of ‘social stratification’ in contemporary Indian society. Discuss the various forms of stratification and their impact on different social groups.
Ans: Social stratification in India is the hierarchical arrangement of individuals and groups based on factors such as caste, class, gender, and ethnicity. Contemporary stratification manifests in multiple forms, including:
Caste Stratification: Despite legal measures to eradicate caste-based discrimination, caste continues to affect social mobility, access to resources, and political power. The Dalits and tribals often face systemic disadvantages.
Class Stratification: Economic disparities lead to a division between the rich and the poor. The growing divide between urban elites and rural populations has widened the class gap.
Gender Stratification: Women, especially in rural areas, face significant challenges in terms of education, employment, and social status. Gender norms restrict women's roles in many sectors of society.
The impact of social stratification on different social groups includes limited access to education, healthcare, and employment, resulting in unequal opportunities and outcomes.
Application of Theories
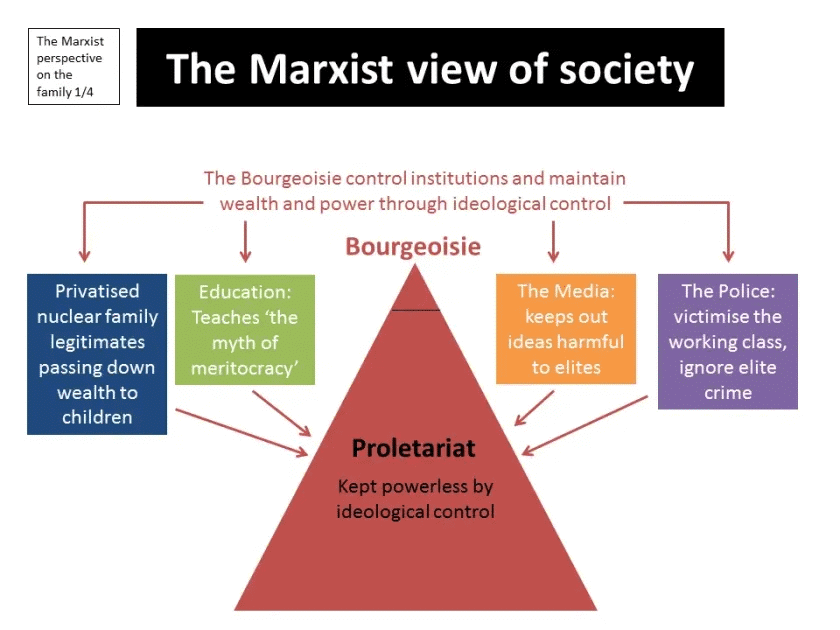
Q1: Apply Marxist theory to analyze the growing divide between the rich and poor in urban societies.
Ans: According to Marxist theory
- The growing divide between the rich and poor in urban societies is a result of capitalist exploitation. The bourgeoisie, or the capitalist class, owns the means of production and profits from the labor of the proletariat, or working class.
- This results in the concentration of wealth and power in the hands of a few, while the majority remains economically disadvantaged.
- Urbanization, as seen in many cities, exacerbates this divide by creating a dichotomy between affluent urban areas and impoverished slums, leading to increased social inequality.
Comparative Analysis
Q1: Compare the traditional family structure in rural India with the nuclear family model in urban India. Discuss the impact of urbanization on family dynamics.
Ans: Family Structure in India
1. Traditional Family Structure in Rural India
Extended Family Model: Multiple generations, such as grandparents, parents, children, often live together in rural areas.
Emotional Support: The extended family provides strong emotional connections, supporting each other in both good and bad times.
Collective Decision-Making: Family decisions are made by discussing and consulting all members, ensuring that everyone's opinion is considered.
2. Urban Family Structure in Urban India
Nuclear Family Model: This type of family consists of a couple and their children who live independently, without extended family members.
Weakened Extended Family Networks: With more people moving to cities for work, the bond with extended family, like cousins or uncles/aunts, has weakened.
Shift in Social Support Systems: Urban families tend to rely more on friends, neighbors, and acquaintances for support, rather than extended family members.
Rise in Individualism: Urban families often focus more on individual goals, with each member pursuing personal aspirations.
3. Economic Pressures and Family Dynamics
Increased Economic Pressures: Urban families face financial challenges, such as high living costs and limited job opportunities, which can strain family resources.
Impact on Work-Life Balance: The balance between work commitments and family time is harder to maintain in urban settings due to busy schedules.
Changes in Family Dynamics: Financial pressures and busy lifestyles can alter roles and relationships within the family, leading to stress and sometimes conflict.
Case Study Analysis
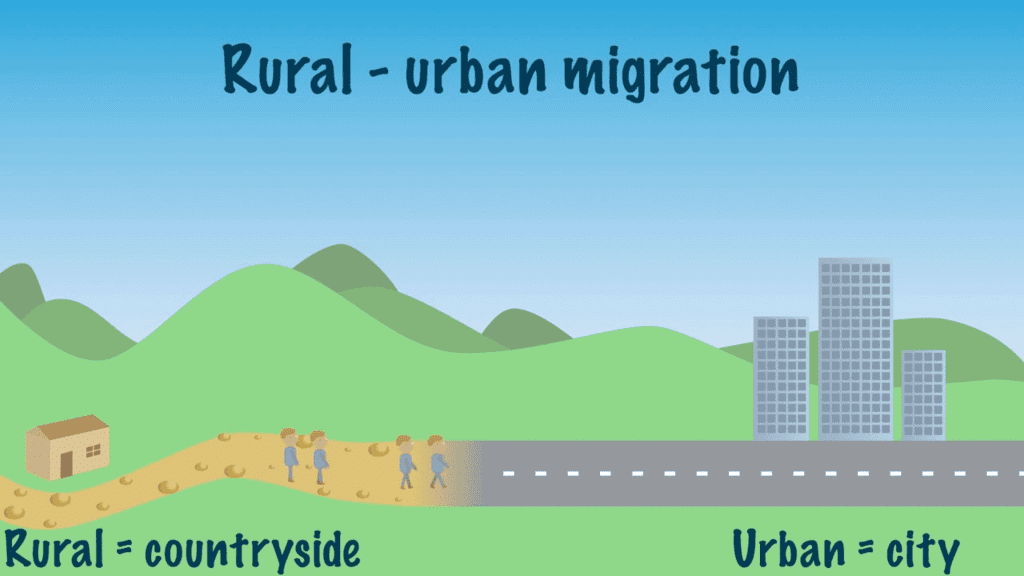
Q1: Case Study: A small rural village is witnessing rapid migration of youth to cities for better job opportunities.
Analyze this phenomenon using sociological concepts such as rural-urban migration, economic change, and social structure.
Ans:
- Rural-Urban Migration Trend:
- Migration reflects broader trends driven by economic change.
- Industrialization in urban areas creates opportunities that attract youth.
- Economic Opportunities:
- Urban centers offer better job prospects compared to agriculture-based rural economies.
- This economic pull results in significant youth migration to cities.
- Social Structure Shifts:
- Younger populations moving to cities leads to an aging demographic in rural areas.
- Rural communities experience a decline in the youth population.
- Impact on Rural Areas:
- Loss of traditional family structures and community bonds.
- Remaining populations may struggle with social cohesion.
- Urban Social Dynamics:
- Urban areas become centers of individualism and competition.
- This shift can lead to social fragmentation within cities.
|
41 videos|105 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on Assignment: Sociology and Society - Sociology Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is sociology and why is it important in understanding society? |  |
| 2. How does sociology differ from other social sciences? |  |
| 3. What are some key concepts in sociology that are essential for analysis? |  |
| 4. How can sociology contribute to solving social issues? |  |
| 5. What methods do sociologists use to conduct research? |  |